Chemistry:Holothurin
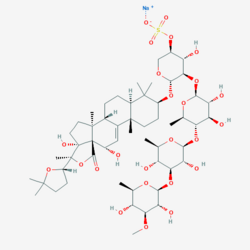
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium;[(3R,4R,5R,6S)-5-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-5-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-4-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,5-dihydroxy-4-methoxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-3,4-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6-(1S,2S,5R,6S,9S,10S,13S,16S,18R)-6-[(2S)-5,5-dimethyloxolan-2-yl]-5,10-dihydroxy-2,6,13,17,17-pentamethyl-8-oxo-7-oxapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.05,9.013,18]icos-11-en-16-yl]oxy]-4-hydroxyoxan-3-yl sulfate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C54H85NaO25S | |
| Molar mass | 1189.3 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
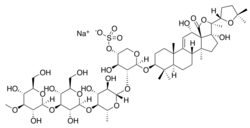
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium;[(3R,4R,5R,6S)-5-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-5-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-4-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4-methoxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-3,4-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6-(1S,2S,5R,6S,9R,10S,13S,16S,18R)-6-(5,5-dimethyloxolan-2-yl)-5,10-dihydroxy-2,6,13,17,17-pentamethyl-8-oxo-7-oxapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.05,9.013,18]icos-11-en-16-yl]oxy]-4-hydroxyoxan-3-yl sulfate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C54H85NaO27S | |
| Molar mass | 1221.3 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
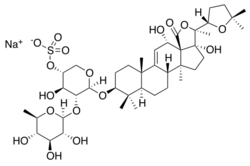
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium;[(3R,4R,5R,6S)-6-(5R,6R,10S,13S,16S)-6-[(2S)-5,5-dimethyloxolan-2-yl]-5,10-dihydroxy-2,6,13,17,17-pentamethyl-8-oxo-7-oxapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.05,9.013,18]icos-11-en-16-yl]oxy]-4-hydroxy-5-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-3-yl sulfate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C41H63NaO17S | |
| Molar mass | 883 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The holothurins are a group of toxins originally isolated from the sea cucumber Actinopyga agassizii.[4] They are contained within clusters of sticky threads called Cuvierian tubules which are expelled from the sea cucumber as a mode of self-defence.[5] The holothurins belong to the class of compounds known as saponins and are anionic surfactants which can cause red blood cells to rupture.[6][7] The holothurins can be toxic to humans if ingested in high amounts.
Pharmacology
Effects on nerves
Holothurin is shown to have a blocking effect on nerves in desheathed bullfrog sciatic nerve and rat phrenic nerve preparations, and its potency can be compared to that of cocaine, procaine, and physostigmine. Unlike the other mentioned blocking agents, the disrupting effect of holothurin appears to be quite irreversible upon washing.[8]
In another experiment on frog sciatic nerve, holothurin A is shown to be capable of destroying electrical excitability of a node of Ranvier along with basophilic macromolecular material found in and near the cytoplasm of the node. In another experiment on rat phrenic nerve, the nerve-disrupting effect of holothurin A is found to be preventable when specific concentrations of physostigmine are present.[9]
Other effects
Holothurin A and holothurin A1, along with other sea cucumber saponins, are found to reduce weight gain in mice. They improve glucose tolerance, reduce levels of lipids in blood and liver, and inhibit the absorption of lipids in the intestine. They also inhibit the activity of pancreatic lipase, decrease the growth of white adipocytes, a factor which contributes to obesity, and stimulate the production of LXR-β nuclear receptor and ABCA1 protein. These findings suggest a possibility of the holothurins and other sea cucumber saponins being used in the development of anti-obesity drug.[10]
The holothurins are shown to have anti-melanogenic and anti-wrinkling effects on human skin by inhibiting melanin production in Melan-A cells and promoting collagen production in human dermal fibroblasts via the ERK pathway.[11]
References
- ↑ "Holothurin" (in en). National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Holothurin.
- ↑ "Holothurin A" (in en). National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Holothurin-A.
- ↑ "Holothurin B" (in en). National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Holothurin-B.
- ↑ Chanley, J. D.; Ledeen, R.; Wax, J.; Nigrelli, R. F.; Sobotka, Harry (1959). "Holothurin. I. Isolation, properties, and sugar components of holothurin A". Journal of the American Chemical Society 81 (19): 5180–5183. doi:10.1021/ja01528a040.
- ↑ Ruppert, Edward E.; Fox, Richard, S.; Barnes, Robert D. (2004). Invertebrate Zoology, 7th edition. Cengage Learning. pp. 915. ISBN 81-315-0104-3.
- ↑ Kitagawa, I (1979). "Structure of holothurin A a biologically active triterpene-oligoglycoside from the sea cucumber holothuria leucospilota brandt". Tetrahedron Letters 20 (16): 1419–1422. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)86166-9.
- ↑ "Holothurin". National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68006697.
- ↑ Friess, S.L.; Standaert, F.G.; Whitcomb, E.R.; Nigrelli, R.F.; Chanley, J.D.; Sobotka, H. (August 1959). "Some pharmacologic properties of holothurin, an active neurotoxin from the sea cucumber.". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 126: 323–9. PMID 13825214.
- ↑ Thron, C.Dennis; Durant, R.C.; Friess, S.L. (March 1964). "Neuromuscular and cytotoxic effects of holothurin A and related saponins at low concentration levels. III". Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 6 (2): 182–196. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(64)90104-8. PMID 14129991.
- ↑ Guo, Lu; Gao, Ziyang; Zhang, Liuqiang; Guo, Fujiang; Chen, Yan; Li, Yiming; Huang, Cheng (6 October 2015). "Saponin-enriched sea cucumber extracts exhibit an antiobesity effect through inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity and upregulation of LXR-β signaling". Pharmaceutical Biology 54 (8): 1312–1325. doi:10.3109/13880209.2015.1075047. PMID 26440226.
- ↑ Kwon, Tae-Rin; Oh, Chang Taek; Bak, Dong-Ho; Kim, Jong Hwan; Seok, Joon; Lee, Jong Hoon; Lim, Su Hwan; Yoo, Kwang Ho et al. (November 2018). "Effects on skin of Stichopus japonicus viscera extracts detected with saponin including Holothurin A: Down-regulation of melanin synthesis and up-regulation of neocollagenesis mediated by ERK signaling pathway". Journal of Ethnopharmacology 226: 73–81. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2018.08.007. PMID 30102992.
Further reading
- Halstead, Bruce W. (1965) (in en). Poisonous and Venomous Marine Animals of the World: Invertebrates. U.S. Government Printing Office. https://books.google.com/books?id=iqEgMQAACAAJ.
 |
