Chemistry:Malonyl chloride
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propanedioyl dichloride[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H2Cl2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 140.95 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Boiling point | 58 °C (136 °F; 331 K) 28 mm Hg |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H314 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P370+378, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
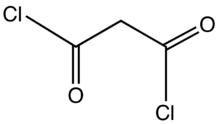
Malonyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula CH2(COCl)2. It is the acyl chloride derivative of malonic acid. It is a colorless liquid although samples are often deeply colored owing to impurities. The compound degrades at room temperature after a few days. It used as a reagent in organic synthesis.[2]
Synthesis and reactions
Malonyl chloride can be synthesized from malonic acid in thionyl chloride.[3] As a bifunctional compound, it is used in the preparation of a number of cyclic compounds by diacylation. Heating in the presence of non-nucleophilic base gives the ketene derivative O=C=C(H)COCl.
References
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 797. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Thomas Ziegler (2001). "Malonyl Chloride". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rm016. ISBN 0471936235.
- ↑ Chittaranjan Raha (1953). "Di-tert-Butyl Malonate". Organic Syntheses 33: 20. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.034.0026. http://orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=CV4P0261.
 |