Chemistry:Methyl p-toluate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
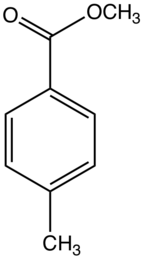
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl 4-methylbenzoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 150.177 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.058 |
| Melting point | 32–35 °C (90–95 °F; 305–308 K) |
| Boiling point | 222.4 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H315, H317, H318, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P272, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 95.5 °C (203.9 °F; 368.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Methyl p-toluate is the organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4CO2CH3. It is a waxy white solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. It is the methyl ester of p-toluic acid. Methyl p-toluate per se is not particularly important but is an intermediate in some routes to dimethyl terephthalate, a commodity chemical.[1]
References
- ↑ Tomas, Rogerio A. F.; Bordado, Joao C. M.; Gomes, Joao F. P. (2013). "p-Xylene Oxidation to Terephthalic Acid: A Literature Review Oriented toward Process Optimization and Development". Chemical Reviews 113 (10): 7421–69. doi:10.1021/cr300298j. PMID 23767849.
 |

