Chemistry:Myriocin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
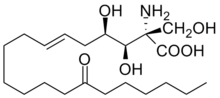
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4R,6E)-2-Amino-3,4-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-14-oxoicos-6-enoic acid | |
| Other names
Antibiotic ISP-1; Thermozymocidin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 5113331 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2811 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H39NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 401.54 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Myriocin, also known as antibiotic ISP-1 and thermozymocidin, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid derived from certain thermophilic fungi.
Myriocin is a very potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase, the first step in sphingosine biosynthesis.[1] Due to this property, it is used in biochemical research as a tool for depleting cells of sphingolipids.
Myriocin was shown to inhibit the proliferation of an IL-2-dependent mouse cytotoxic T cell line.[citation needed]
Myriocin possesses immunosuppressant activity. It is reported to be 10- to 100-fold more potent than ciclosporin.[citation needed]
The multiple sclerosis drug fingolimod was derived from myriocin by using structure–activity relationship studies to determine the parts of the molecule important to its activity.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ "Serine palmitoyltransferase is the primary target of a sphingosine-like immunosuppressant, ISP-1/myriocin". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 211 (2): 396–403. 1995. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.1827. PMID 7794249.
 |

