Chemistry:Neohesperidin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
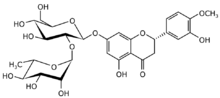
(2S)-3′,5-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxy-7-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranosyloxy]flavan-4-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S)-7-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-Dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-{[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}oxan-2-yl]oxy}-5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Hesperetin 7-O-neohesperidoside
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H34O15 | |
| Molar mass | 610.565 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Neohesperidin is a flavanone glycoside found in citrus fruits.[1] It is the 7-O-neohesperidose derivative of hesperetin, which in turn is the 4'-methoxy derivative of eriodictyol. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone has an intense sweet taste, and is listed as a Generally Recognized as Safe flavour enhancer by the Flavour and Extract Manufacturers' Association.[2]
References
- ↑ Rouseff, Russell L.; Martin, Shirley F.; Youtsey, Charles O. (1987). "Quantitative survey of narirutin, naringin, hesperidin, and neohesperidin in citrus". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 35 (6): 1027–1030. doi:10.1021/jf00078a040. ISSN 0021-8561.
- ↑ Cohen, S.M.; Eisenbrand, G; Fukushima, S; Gooderham, N.J.; Guengerich, F.P.; Hecht, S.S.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Harman, C et al. (July 2018). "GRAS 28 Flavoring Substances". https://www.femaflavor.org/sites/default/files/2018-07/gras28-cohen_et_al_2018.pdf.
External links
 |