Chemistry:Norsalsolinol
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
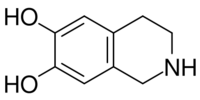
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline-6,7-diol | |
| Other names
6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 165.189 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Neurotoxin |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Norsalsolinol is a chemical compound that is produced naturally in the body through metabolism of dopamine.[1] It has been shown to be a selective dopaminergic neurotoxin,[2][3][4] and has been suggested as a possible cause of neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson's disease and the brain damage associated with alcoholism,[5][6] although evidence for a causal relationship is unclear.[7][8][9]
(R)-Salsolinol which has been shown to be a product of ethanol metabolism, stereospecifically induces behavioral sensitization and leads to excessive alcohol intake in rats[10]
See also
References
- ↑ "Cytotoxicity of dopamine-derived 6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines". Advances in Neurology 60: 224–30. 1993. PMID 8093579.
- ↑ "Norsalsolinol uptake into secretory vesicles via vesicular monoamine transporter and its secretion by membrane depolarization or purinoceptor stimulation in PC12 cells". The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science 63 (5): 493–7. May 2001. doi:10.1292/jvms.63.493. PMID 11411492.
- ↑ "Uptake of the dopaminergic neurotoxin, norsalsolinol, into PC12 cells via dopamine transporter". Archives of Toxicology 75 (4): 209–13. June 2001. doi:10.1007/s002040000202. PMID 11482518.
- ↑ "The mechanisms of oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis induced by norsalsolinol, an endogenous tetrahydroisoquinoline derivative associated with Parkinson's disease". Journal of Neurochemistry 108 (2): 397–407. January 2009. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05774.x. PMID 19012744.
- ↑ "Dopamine-derived tetrahydroisoquinolines and Parkinson's disease". Advances in Neurology 60: 218–23. 1993. PMID 8420138.
- ↑ "Salsolinol and norsalsolinol in human urine samples". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 58 (2): 545–50. October 1997. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(97)00251-7. PMID 9300617.
- ↑ "Simultaneous gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric determination of dopamine, norsalsolinol and salsolinol enantiomers in brain samples of a large human collective". Cellular and Molecular Biology (Noisy-le-Grand, France) 49 (5): 837–49. July 2003. PMID 14528920.
- ↑ "Increased systemic levels of norsalsolinol derivatives are induced by levodopa treatment and do not represent biological markers of Parkinson's disease". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 75 (4): 634–6. April 2004. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2003.010769. PMID 15026514.
- ↑ "Systematic regional study of dopamine, norsalsolinol, and (R/S)-salsolinol levels in human brain areas of alcoholics". Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 29 (1): 46–52. January 2005. doi:10.1097/01.ALC.0000150011.81102.C2. PMID 15654290.
- ↑ "(R)-Salsolinol, a product of ethanol metabolism, stereospecifically induces behavioral sensitization and leads to excessive alcohol intake. | PubFacts.com". https://www.pubfacts.com/detail/26032572/R-Salsolinol-a-product-of-ethanol-metabolism-stereospecifically-induces-behavioral-sensitization-and.
 |

