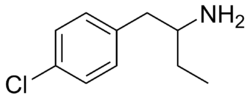
Chemistry:4-Chlorophenylisobutylamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14ClN |
| Molar mass | 183.68 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
4-Chlorophenylisobutylamine (4-CAB, AEPCA), also known as 4-chloro-α-ethylphenethylamine, is an entactogen and stimulant drug of the phenethylamine class.[1] It is an analogue of para-chloroamphetamine (PCA) where the alpha position methyl has been replaced with an ethyl group.[1]
In comparison to PCA, 4-CAB is approximately 2- and 5-fold less potent at inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin (IC50 = 330 nM) and dopamine (IC50 = 2,343 nM), respectively, and is about 3-fold less potent in substituting for MDMA in animals in drug discrimination assays.[1] Though its dopaminergic activity is significantly attenuated compared to PCA, unlike the case of MBDB, it is not abolished[clarification needed], and is actually similar to that of MDMA.[1]
Relative to PCA, 4-CAB is also substantially less effective as a serotonergic neurotoxin.[1] A single 10 mg/kg administration of PCA to rats produces an approximate 80% decrease in serotonin markers as observed 1 week later.[1] In contrast, 11 mg/kg and 22 mg/kg doses of 4-CAB result in only 20% and 50% decreases, respectively.[1] This is once again similar to MDMA which causes a 40-60% reduction with a single 20 mg/kg dose.[2]
See also
- Phenylisobutylamine
- 4-Methylphenylisobutylamine
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "Behavioral, biochemical and neurotoxicological actions of the alpha-ethyl homologue of p-chloroamphetamine". European Journal of Pharmacology 191 (1): 1–10. November 1990. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(90)94090-K. PMID 1982656.
- ↑ "Alpha-lipoic acid prevents 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine (MDMA)-induced neurotoxicity". NeuroReport 10 (17): 3675–80. November 1999. doi:10.1097/00001756-199911260-00039. PMID 10619665.
| Phenylalkyl- amines (other than cathinones) |
|
|---|---|
| Cyclized phenyl- alkylamines | |
| Cathinones | |
| Tryptamines | |
| Chemical classes | |
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
 | 0.00      (0 votes) (0 votes) |
