Chemistry:Oxalic anhydride
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Oxiranedione | |
| Other names
oxalic anhydride
ethanedioic anhydride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 72.019 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
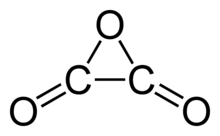
Oxalic anhydride or ethanedioic anhydride, also called oxiranedione, is a hypothetical organic compound, one of several isomers having the formula C2O3 that have been studied computationally. It can be viewed as the anhydride of oxalic acid or the two-fold ketone of ethylene oxide. It is an oxide of carbon (an oxocarbon).
The simple compound apparently has yet to be observed (as of 2009). In 1998, however, Paolo Strazzolini and others have claimed the synthesis of dioxane tetraketone (C4O6), which can be viewed as the cyclic dimer of oxalic anhydride.[1]
It has been conjectured to be a fleeting intermediate in the thermal decomposition of certain oxalates[2] and certain chemoluminescent reactions of oxalyl chloride.[3]
See also
- 1,2-dioxetanedione
- α-acetolactone
References
- ↑ Paolo Strazzolini; Alberto Gambi; Angelo G. Giumanini; Hrvoj Vancik (1998). "The reaction between ethanedioyl (oxalyl) dihalides and Ag2C2O4: a route to Staudinger's elusive ethanedioic (oxalic) acid anhydride". J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 (16): 2553–2558. doi:10.1039/a803430c.
- ↑ Ahmed A. El-Sherif; Bakir J. A. Jeragh (2007). "Mixed ligand complexes of Cu(II)-2-(2-pyridyl)-benzimidazole and aliphatic or aromatic dicarboxylic acids: Synthesis, characterization and biological activity". Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 68 (1): 877–882. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2006.12.073. PMID 17320475. Bibcode: 2007AcSpA..68..877E.
- ↑ Template:Cite tech report
External links
 |

