Chemistry:Perfluorooctanesulfonamide
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
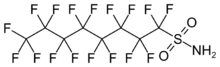
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-Heptadecafluorooctane-1-sulfonamide | |
| Other names
Perfluoroctylsulfonamide, Perfluorooctane sulfonamide, Heptadecafluorooctanesulphonamide, Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid amide, Deethylsulfluramid, FC-99
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | FOSA, DESFA, PFOSA |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H2F17NO2S | |
| Molar mass | 499.14 g/mol |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS), Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS), Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), Perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Perfluorooctanesulfonamide (PFOSA) is a synthetic organofluorine compound. It is a fluorocarbon derivative and a perfluorinated compound, having an eight-carbon chain and a terminal sulfonamide functional group. PFOSA, a persistent organic pollutant, was an ingredient in 3M's former Scotchgard formulation[1][2] from 1956 until 2003, and the compound was used to repel grease and water in food packaging[3] along with other consumer applications.[4] It breaks down to form perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS).[5] The perfluorooctanesulfonyl fluoride-based chemistry that was used to make sulfonamides like PFOSA was phased out by 3M in the United States (US) during 2000–2002 but it has grown in China by other producers.
PFOSA can be synthesized from perfluorooctanesulfonyl halides by reaction with liquid ammonia[5] or by a two step reaction via an azide followed by reduction with Zn and HCl.[6] PFOSA is also a metabolic by-product of N-alkylated perfluorooctanesulfonamides.[5] For example, N-ethyl perfluorooctanesulfonamidoethanol (N-EtFOSE), which was primarily used on paper,[7] and N-methyl perfluorooctanesulfonamidoethanol (N-MeFOSE), which was primarily used on carpets and textiles, both metabolize via acetates to PFOSA.[8]
In addition, PFOSA is thought to be the biologically active form of the insecticide Sulfluramid (N-ethyl perfluorooctanesulfonamide)[9][10] as it is an extremely potent uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation[10][11] with an IC50 of about 1 micromolar[5] (≈500 nanograms per milliliter or parts per billion). PFOSA was the most toxic perfluorinated compound in a study with PC12 cells.[12][13] Concentrations ranged from 10 to 250 micromolar in the study (or 5000 to 125,000 parts per billion).
Wildlife biomonitoring studies have found the highest level of PFOSA in the liver of common dolphin (Mediterranean Sea, Italy) with a concentration of 878 parts per billion; the liver of mink from Illinois, US, contained 590 parts per billion.[14] In fish, the highest levels detected were in the liver of Norway Pike (91 parts per billion) and homogenates of slimy sculpin (150 parts per billion) from Lake Ontario.[14] Differences in biotransformation across species could explain some of its presence.[14] In humans, PFOSA has been detected in sub- to low-parts per billion levels;[14] for example, in 1999–2000 US serum samples, the 95th percentile (or value where only 5% of the population was higher) was 1.4 parts per billion[15] while in 2003–2004 the 95th percentile fell to 0.2 parts per billion.[16] However, whole-blood concentrations are about five times higher than those in blood plasma or serum.[17]
See also
References
- ↑ Stephen K. Ritter (January 2006). "Crystal Ball On The Environment: Detective work and expertise are used to evaluate environmental contaminants of emerging concern". Chemical & Engineering News 84 (5): 37–40. doi:10.1021/cen-v084n049.p037. http://pubs.acs.org/cen/science/84/8405sci1.html.
- ↑ "Evaluation of perfluorooctane surfactants in a wastewater treatment system and in a commercial surface protection product". Environ. Sci. Technol. 39 (15): 5524–30. August 2005. doi:10.1021/es050213u. PMID 16124283. Bibcode: 2005EnST...39.5524B. Supporting Information (PDF).
- ↑ "Perfluorinated compounds – Exposure assessment for the general population in western countries". Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 212 (3): 239–70. May 2009. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2008.04.007. PMID 18565792.
- ↑ "Serum concentrations of perfluorooctanesulfonate and other fluorochemicals in an elderly population from Seattle, Washington". Chemosphere 54 (11): 1599–611. March 2004. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.09.025. PMID 14675839. Bibcode: 2004Chmsp..54.1599O.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Lehmler, HJ (March 2005). "Synthesis of environmentally relevant fluorinated surfactants—a review". Chemosphere 58 (11): 1471–96. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.078. PMID 15694468. Bibcode: 2005Chmsp..58.1471L.
- ↑ "Synthesis and Structure of Environmentally Relevant Perfluorinated Sulfonamides". J. Fluor. Chem. 128 (6): 595–607. June 2007. doi:10.1016/j.jfluchem.2007.01.013. PMID 18516235.
- ↑ Renner R (March 2004). "Perfluorinated sources outside and inside". Environ. Sci. Technol. 38 (5): 80A. doi:10.1021/es040387w. PMID 15046317. Bibcode: 2004EnST...38...80R.
- ↑ "Perfluorooctanesulfonate and other fluorochemicals in the serum of American Red Cross adult blood donors". Environ. Health Perspect. 111 (16): 1892–901. December 2003. doi:10.1289/ehp.6316. PMID 14644663.
- ↑ "Distribution and tissue elimination in rats during and after prolonged dietary exposure to a highly fluorinated sulfonamide pesticide". J. Agric. Food Chem. 40 (12): 2505–9. December 1992. doi:10.1021/jf00024a033.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Structural determinants of fluorochemical-induced mitochondrial dysfunction". Toxicol. Sci. 66 (2): 244–52. April 2002. doi:10.1093/toxsci/66.2.244. PMID 11896291.
- ↑ "Perfluorooctane sulfonamide: a structurally novel uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1016 (3): 344–8. April 1990. doi:10.1016/0005-2728(90)90167-3. PMID 2331477.
- ↑ Fields S (June 2008). "Brain Effects Stick Around: PFCs and Neural Cell Development". Environ. Health Perspect. 116 (6): A258. doi:10.1289/ehp.116-a258b.
- ↑ "Developmental Neurotoxicity of Perfluorinated Chemicals Modeled in Vitro". Environ. Health Perspect. 116 (6): 716–22. June 2008. doi:10.1289/ehp.11253. PMID 18560525.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 "Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalkyl substances: A review". Environ. Sci. Technol. 40 (11): 3463–73. June 2006. doi:10.1021/es052580b. PMID 16786681. Bibcode: 2006EnST...40.3463H. Supporting Information (PDF).
- ↑ "Serum concentrations of 11 polyfluoroalkyl compounds in the U.S. population: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES)". Environ. Sci. Technol. 41 (7): 2237–42. April 2007. doi:10.1021/es062686m. PMID 17438769. https://figshare.com/articles/Serum_Concentrations_of_11_Polyfluoroalkyl_Compounds_in_the_U_S_Population_Data_from_the_National_Health_and_Nutrition_Examination_Survey_NHANES_1999_2000/3015763.
- ↑ "Polyfluoroalkyl Chemicals in the U.S. Population: Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003–2004 and Comparisons with NHANES 1999–2000". Environ. Health Perspect. 115 (11): 1596–602. November 2007. doi:10.1289/ehp.10598. PMID 18007991. Supplemental Material (PDF).
- ↑ "Exposure of Perfluorinated Chemicals through Lactation: Levels of Matched Human Milk and Serum and a Temporal Trend, 1996–2004, in Sweden". Environ. Health Perspect. 115 (2): 226–30. February 2007. doi:10.1289/ehp.9491. PMID 17384769.
External links
 |

