Chemistry:Sacubitril
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | AHU-377 |
| License data | |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
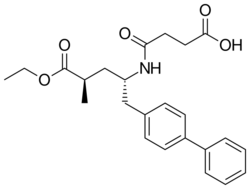
| Formula | C24H29NO5 |
| Molar mass | 411.498 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Sacubitril (/səˈkjuːbɪtrɪl/; INN) is an antihypertensive drug used in combination with valsartan. The combination drug sacubitril/valsartan, known during trials as LCZ696 and marketed under the brand name Entresto, is a treatment for heart failure.[1] It was approved under the FDA's priority review process for use in heart failure on July 7, 2015.
Side effects
Sacubitril increases levels of bradykinin, which is responsible for the edema seen sometimes in patients with the medication. This is why the medication is not recommended for patients with a history of pulmonary edema with the usage of ACE inhibitors.[citation needed]
Mechanism of action
Sacubitril is a prodrug that is activated to sacubitrilat (LBQ657) by de-ethylation via esterases.[2] Sacubitrilat inhibits the enzyme neprilysin,[3] which is responsible for the degradation of atrial and brain natriuretic peptide, two blood pressure–lowering peptides that work mainly by reducing blood volume.[4] In addition, neprilysin degrades a variety of peptides including bradykinin,[5] an inflammatory mediator.

Synthesis

The large scale synthesis of Sacubritil begins with 4-bromo-1,1'-biphenyl, which is converted to its corresponding Grignard reagent; this is reacted directly with (S)-epichlorohydrin regioselectively at less-substituted site of the epoxide.[6][7]
A Mitsunobu reaction with succinimide is performed, followed by acidic hydrolysis of the succinimide protecting group, hydrolysis of the alkyl chloride using sodium hydroxide and protection of the free amine with a tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) group. The primary alcohol is oxidized using bleach with TEMPO as the catalyst. This aldehyde undergoes a Wittig reaction to for the α.β-unsaturated ester, which is converted to the lithium carboxylate by hydrolysis using lithium hydroxide in aqueous ethanol. Asymmetric hydrogenation using a ruthenium catalyst and a chiral bisphosphine ligand sets the second stereocenter. The carboxylate is esterified by reaction with thionyl chloride to form the acyl chloride, which is reacted with ethanol. The acidic conditions under which the acyl chloride is generated result in removal of the Boc group, which allows for direct reaction of the amine with succinic anhydride in the presence of pyridine as a base.
See also
References
- ↑ "Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure". The New England Journal of Medicine 371 (11): 993–1004. September 2014. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1409077. PMID 25176015.
- ↑ "HFpEF in the Future: New Diagnostic Techniques and Treatments in the Pipeline". Boston. p. 48. http://spo.escardio.org/eSlides/view.aspx?eevtid=46&fp=13.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of LCZ696, a novel dual-acting angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNi)". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 50 (4): 401–414. April 2010. doi:10.1177/0091270009343932. PMID 19934029.
- ↑ (in de) Neue Arzneimittel 2010/2011.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: Membrane metallo-endopeptidase". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/4311.
- ↑ "Synthetic Approaches to the New Drugs Approved During 2015". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 60 (15): 6480–6515. August 2017. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00010. PMID 28421763.
- ↑ , Guoliang; Wenfa Ye & Hui Zheng et al."New process" patent WO2014032627A1, issued 2014-03-06
 |
