Chemistry:Teflic acid
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pentafluoroorthotelluric acid
| |||
| Other names
Teflic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| HOTeF 5 | |||
| Molar mass | 239.60 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless solid | ||
| Melting point | 39.1 °C (102.4 °F; 312.2 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 59.7 °C (139.5 °F; 332.8 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | corrosive, toxic | ||
| GHS pictograms | 
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H314 | |||
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
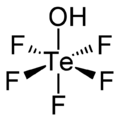
Teflic acid is a chemical compound with the formula HOTeF
5. This strong acid is related to orthotelluric acid, Te(OH)
6. Teflic acid has a slightly distorted octahedral molecular geometry.
Preparation
Teflic acid was accidentally discovered by Engelbrecht and Sladky. Their synthesis did not yield the anticipated telluryl fluoride TeO
2F
2, but a mixture of volatile telluric compounds, containing HOTeF
5:[1]
- BaTeO
4 + 10 FSO
2OH → HOTeF
5 (25%)
Teflic acid can also be prepared from fluorosulfonic acid and barium tellurate:[2]
- 5 FSO
2OH + Ba2+[TeO
2(OH)
4]2− → HOTeF
5 + 4 H
2SO
4 + BaSO
4
It is also the first hydrolysis product of tellurium hexafluoride:
- TeF
6 + H
2O → HOTeF
5 + HF
Teflates
The conjugate base of teflic acid is called the teflate anion, F
5TeO−
(not to be confused with triflate). Many teflates are known, one example being B(OTeF
5)
3, that can be pyrolysed to give acid anhydride O(TeF
5)
2.[2]
- 2 B(OTeF
5)
3 → 2 B(OTeF
5)
2F + O(TeF
5)
2
The teflate anion is known to resist oxidation. This property has allowed the preparation several highly unusual species such as the hexateflates M(OTeF
5)−
6 (in which M = As, Sb, Bi). Xenon forms the cation Xe(OTeF
5)+
.[3]
References
- ↑ Engelbrecht, A.; Sladky, F. "Pentafluoro-orthotellursaure, HOTeF
5" Angewandte Chemie 1964. 76(9), 379-380, doi:10.1002/ange.19640760912. - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN:0-12-352651-5.
- ↑ Mercier, H. P.A.; Sanders, J. C. P.; Schrobilgen, G. J. "The Hexakis(pentafluorooxotellurato)pnictate(V) Anions, M(OTeF
5)−
6 (M = As, Sb, Bi): A Series of Very Weakly Coordinating Anions" Journal of the American Chemical Society, volume 116, 2921, (1994). doi:10.1021/ja00086a025.
Further reading
- R.B. King; Inorganic Chemistry of Main Group Elements, VCH Publishers, New York,1994.
 |