Chemistry:Triacetone amine
From HandWiki
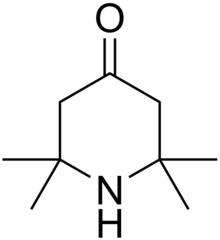
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidinone
| |
| Other names
Triacetone amine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H17NO | |
| Molar mass | 155.23 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless low-melting solid |
| Density | ? g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 43 °C (109 °F; 316 K) |
| Boiling point | 205 °C (401 °F; 478 K) |
| Moderate | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Most organic solvents |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable |
| R-phrases (outdated) | 22-36/37/38 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | 26-36/37 |
| Flash point | 73 °C; 164 °F; 346 K |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Piperidine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Triacetone amine is the heterocycle that arises via the condensation of acetone and ammonia, with phorone being a likely intermediate.
- 3 CH3C(O)CH3 + NH3 → OC(CH2C(CH3)2)2NH + 2 H2O
It is primarily used as a stabilizer for plastics, typically via its conversion to number of hindered amine light stabilizers, but also finds use as a chemical feedstock. It is used to prepare the hindered amine 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine, CH2[CH2C(CH3)2]2NH,[1] as well as the radical oxidizer 4-Hydroxy-TEMPO.[2]
References
- ↑ Sorgi, K. L. "2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. doi:10.1002/047084289.
- ↑ Ciriminna, Rosaria; Pagliaro, Mario (15 January 2010). "Industrial Oxidations with Organocatalyst TEMPO and Its Derivatives". Organic Process Research & Development 14 (1): 245–251. doi:10.1021/op900059x.
