Company:Merya language
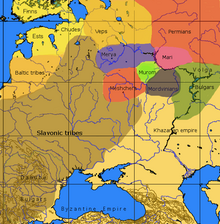
Merya or Meryanic is an extinct Finno-Ugric language, which was spoken by the Meryans.[1][2] Merya began to be assimilated by East Slavs when their territory became incorporated into Kievan Rus' in the 10th century.[3][4] However some Merya speakers might have even lived in the 18th century.[5] There is also a theory that the word for "Moscow" originates from the Merya language.[6][7] The Meryan language stretched to the western parts of Vologda Oblast and Moscow[8]
| Meryan | |
|---|---|
Native speakers | 0 |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
 | |
Classification
There is no general agreement on the relationship of Merya with its neighboring Uralic languages. It is sometimes left as unclassified within the western end of the family.[9]
- A traditional account places Merya as a member of the Volga-Finnic group, comprising also the Mordvinic and Mari languages.[3][10] However, Volga Finnic is today considered obsolete.
- Eugene Helimski supposed that the Merya language was part of a "northwest" group of Finno-Ugric, including also Balto-Finnic and Sami. Helimski argued that even though there are Mari parallels, they do not justify a close relationship with Mari and could be due to adjacency of the language areas.[2]
- Gábor Bereczki supposed that the Merya language was a part of the Balto-Finnic group.[11]
- One hypothesis classifies the Merya as a western branch of the Mari people rather than as a separate tribe. Their ethnonyms are basically identical, Merya being a Russian transcription of the Mari self-designation, Мäрӹ (Märӛ).[12]
- T. Semenov and M. Fasmer believed Merya to be a close relative of Mari.[13] Max Vasmer saw that many Merya toponyms have Mari parallels.[14]
- Aleksandr Sharonov claimed that Merya is an Erzyan dialect, however this doesn't have much support.[15]
Rahkonen (2013)[8] argues that the likewise unattested and unclassified-within-Uralic Muromian language was a close relative of Merya, perhaps even a dialect of Meryan.
A probable characteristic of the Merya language, which some researchers have noted is the plural -k, while most Uralic languages use -t for the plural.[16]
Reconstruction
There have been attempts to re-construct Merya based on toponyms, onomastics and words in Russian dialects by O. B. Tkachenko, Arja Ahlqvist and A. K. Matveev among others. The first reconstructions were done in 1985 by O. B. Tkachenko. The latest book about Merya reconstructions was published in 2019.[17][18][16] A Merya-Russian dictionary based on the reconstructions has also been made.[19] As an example: in Russian toponyms around where Merya was spoken, an ending -яхр (-jaxr) is regularly seen in names relating to lakes. This also resembles, but does not exactly match, the words for 'lake' in western Uralic languages, such as Finnish järvi, Northern Sami jávri, Erzya ерьке (jerʹke), Meadow Mari ер (jer) (from a common proto-form *jäwrä). From these it can be inferred that -яхр likely continues the Meryan word for 'lake', which may have had a shape such as jäkrä, jähr(e)[20] or [jäγrä] Error: {{Transliteration}}: transliteration text not Latin script (pos 3: γ) (help).
According to Rahkonen, in Merya areas there is a word veks, which is probably cognate with the Komi word вис (vis) 'middle river', and similar also to an element vieksi which appears in Finnish toponyms. From Merya toponyms it can also be seen that words such as volo 'down' (Finnish: ala), vondo 'give' (Finnish: antaa) existed in the Merya language. However some others have constructed the word 'give' as ando in Merya.[19]
From this it can be concluded that Finnish a- corresponds to vo- or o- in the Merya language. Another thing that can be observed is the Finnish sound "a" corresponding to a Merya "o", for example a hydronym kol(o) can be seen, which can be compared to Finnish kala 'fish'. In the Muroma-Merya territory a word il(e) can be observed, which can be compared to Finnic *ülä ‘upper’.[8][18] Other words reconstructed directly from toponyms are šun 'clay', vyj 'head', vur 'cow', kuvar 'bridge'.[21] Some words have also been constructed from proper names, such as the words kolyzo 'fisher' and tujba 'hope'.[21] The reconstructed native name for Merya is merjan jelma (мерян елма)[19]
| Word | Meaning | Source of the word |
|---|---|---|
| jähre | lake | Toponym, Tkachenko |
| ila | live | Tkachenko |
| jole | be | Tkachenko |
| jon' | is | Tkachenko |
| palo | village | Tkachenko |
| tul | fire | Tkachenko |
| uhtoma | connection | Toponym |
| at'a | father | Tkachenko |
| tup | back | Matveev |
| pelyš | fear | Tkachenko |
| tohte | want | Tkachenko |
| kuu/kuv | moon | Matveev |
| ner | nose | Tkachenko |
| juk/jug | river | Tkachenko |
| voj | butter | Tkachenko |
| pu | tree | Toponym |
| kil'm | frozen | Matveev |
| n'orga | young | Matveev |
| kolema | death | Tkachenko |
| kol | fish | Toponym, Tkachenko |
| jokšo | swan | Matveev |
| ando | give | Tkachenko |
| tudo | know | Tkachenko |
| il(e) | upper | Toponym |
Phonology
Meryan phonology has been studied only in general terms, relying on Russian dialects in the Kostroma and Yaroslavl regions. Helimski suggests[2] that Merya likely developed massive reduction of word-final syllables. The Merya language only allowed one consonant at the beginning of words, and likely places stress on the first syllable of the word. It likely did not feature vowel harmony. The vowels /ö/, /ä/ and /y/ likely existed in the Merya language.[16]
Grammar
This grammar section is the reconstructed grammar of Merya, based on linguistic evidence, while not being attested facts about the Merya language:[17][21][22]
| Case | Case ending |
| nominative | - |
| Genetive | -n/-an |
| Partitive | -ta/da |
| Inessive | -sna/ssa/ššo |
| Illative | -s |
| ellative | sta |
| adessive | -lna/lla |
| allative | -l'/le |
| ablative | -lta |
| translative | -kš |
| vokative | -aj |
| abessive | -to/do |
| dative | -lan/len |
| accusative | -m/-am/-ym |
| comitative | -ge |
| prolative | -te |
| subessive | -nna |
| delative | -lta/-lda |
| plural | -k/-ak |
| Person | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| 1sg | -em | -en |
| 2sg | -et | -ent |
| 3sg | -eš | -enže |
| 1pl | -amo | -ano |
| 2pl | -ato | -anto |
| 3pl | -ašto | -ažno |
| Person | Ending |
|---|---|
| 1sg | -am |
| 2sg | -at |
| 3sg | -a/-as |
| 1pl | em/ama |
| 2pl | et/ata |
| 3pl | es |
| Person | Ending |
|---|---|
| 1sg | ym |
| 2sg | yt |
| 3sg | yš/ys |
| 1pl | yma/im/ym |
| 2pl | yta/yt/it |
| 3pl | iš/is |
See also
- Volga Finns
- Mari language
References
- ↑ "Уральские языки". http://bse.sci-lib.com/article114382.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Helimski, Eugene (2006). "The «Northwestern» group of Finno-Ugric languages and its heritage in the place names and substratum vocabulary of the Russian North". in Nuorluoto, Juhani. The Slavicization of the Russian North (Slavica Helsingiensia 27). Helsinki: Department of Slavonic and Baltic Languages and Literatures. pp. 109–127. ISBN 978-952-10-2852-6. http://www.helsinki.fi/venaja/nwrussia/eng/Conference/pdf/Helimski.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Janse, Mark; Sijmen Tol; Vincent Hendriks (2000). Language Death and Language Maintenance. John Benjaminsf Publishing Company. p. A108. ISBN 978-90-272-4752-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=JdzVePSApMgC&pg=PA108.
- ↑ Smolitskaya, G.P. (2002) (in ru). Toponimicheskyi slovar' Tsentral'noy Rossii. pp. 211–2017.
- ↑ Pauli, Rahkonen (2013). "Itämerensuomalaisten kielten kaakkoinen kontaktialue nimistöntutkimuksen valossa". Virittäjä (2). https://journal.fi/virittaja/article/view/8316.
- ↑ Tarkiainen, Kari (2010). Ruotsin itämaa. Helsinki: Svenska litteratursällskapet i Finland. p. 19. ISBN 978-951-583-212-2.
- ↑ "Early East Slavic Tribes in Russia" (in en). http://study.com/academy/lesson/early-east-slavic-tribes-in-russia.html.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Rahkonen, Pauli (2013). The South-Eastern Contact Area of Finnic Languages in the Light of Onomastics (PhD thesis). University of Helsinki. hdl:10138/38908.
- ↑ "Merya". MultiTree. 2009-06-22. http://multitree.org/codes/0tw.
- ↑ Wieczynski, Joseph (1976). The Modern Encyclopedia of Russian and Soviet History. Academic International Press. ISBN 978-0-87569-064-3. https://books.google.com/books?q=%22Merian+and+Muromian%2C+belong+to+the+so-called+Volga+branch+of+the+Finno-Ugric+languages%22&btnG=Search+Books.
- ↑ Bereczki, Gábor (1996). "Le méria, une language balto-finnoise disparue". in Fernandez, M.M. Jocelyne; Raag, Raimo. Contacts de languages et de cultures dans l'aire baltique / Contacts of Languages and Cultures in the Baltic Area. Uppsala Multiethnic Papers. pp. 69–76.
- ↑ Petrov A., KUGARNYA, Marij kalykyn ertymgornyzho, #12 (850), 2006, March, the 24th.
- ↑ "Меря - Меряния - Залесская Русь - Мерянский язык". http://www.merjamaa.ru/index/merjanskij_jazyk/0-10.
- ↑ Матвеев, А. К. (1997). "К проблеме расселения летописной мери". Известия Уральского Государственного Университета. 1997. № 7. https://elar.urfu.ru/handle/10995/23523.
- ↑ "Народ Эрзя и Русь: в фокусе русского неславянина. Александр Шаронов | Эрзянь ки. Культурно-образовательный портал". http://erzan.ru/news/narod-erzja-i-rus-v-fokuse-russkogo-neslavjanina-aleksandr-sharonov.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 ”Allikas: Ткаченко О. Б., Мерянский язык, Kiova 1985.”
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Andrey, Malyšev (2019). Merjanskij jazyk.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Rahkonen, Pauli (2013). "Suomen etymologisesti läpinäkymätöntä vesistönimistöä [Etymologically opaque hydronyms of Finland"]. Virittäjä (1). https://journal.fi/virittaja/article/view/7843.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Malyshev, A. M. (2013). "Merjan jelma: меряно-русский и русско-мерянский словарь; Мерянский ономастикон". https://books.google.com/books?id=82ytnQEACAAJ.
- ↑ О.Б., Ткаченко (2007). исследованиа по мерянскому языку. kostroma.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 Andrey, Malyšev (2013). Merjan jelma Мерянский язык. Moscow.
- ↑ "Info". costroma.k156.ru. http://costroma.k156.ru/tk/066-125.pdf. Retrieved 2021-03-03.
External links
 |
