Earth:La Huérguina Formation
| La Huérguina Formation Stratigraphic range: Late Barremian 129.4–126.3 Ma | |
|---|---|
 Lithographic limestones of the Las Hoyas locality | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Underlies | Contreras Formation or Unconformity with the Utrillas Group |
| Overlies | Tragacete Formation |
| Thickness | 60–100 m (200–330 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Limestone, marl |
| Other | Conglomerate |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] 40°05′23″N 1°53′52″W / 40.0897°N 1.8978°W |
| Region | Cuenca, Castile-La Mancha |
| Country | |
| Extent | South Iberian Basin |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Huérguina |
| Lua error in Module:Location_map/multi at line 27: Unable to find the specified location map definition: "Module:Location map/data/Spain Castile-La Mancha" does not exist. | |
The La Huérguina Formation (also known as the Calizas de La Huérguina Formation, La Huérguina Limestone Formation or as the Una Formation) is a geological formation in Spain whose strata date back to the Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous.[1] Las Hoyas is a Konservat-Lagerstätte within the formation, located near the city of Cuenca, Spain. The site is mostly known for its exquisitely preserved dinosaurs, especially enantiornithines.[2] The lithology of the formation mostly consists of lacustrine limestone deposited in a freshwater wetland environment.
Las Hoyas
Taphonomy
As a Konservat-Lagerstätten, the preservation is exceptional. This may be a result of three factors: Microbial mats, Obruption and Stagnation.
Microbial mats may be responsible for the preservation of soft tissue in many fossils from Las Hoyas, like Pelecanimimus' crest. The iron carbonate depositions, a result from bacterial metabolism which covered the dinosaur's crest enhanced the preservation of those soft tissues. Evidence of these mats comes from the studies on microfacies and the fossils themselves.
Obruption is notable in the formation, due to the presence of highly articulated specimens. From actuotaphonomy studies on several different organisms it can be estimated that the burial of most entities was quick. Concornis may have been buried in less than 15 days, after a period of sub-areal exposition.
Paleoenvironment
Las Hoyas was an inland lacustrine environment which presents an important aquatic and terrestrial flora (with many specimens of Charophytes, Montsechia, Weischelia or Frenelopsis) and diverse fauna, with specimens of at least five or six Phyla: arthropods, molluscs, Chordata and many vermiform soft bodied animals which might be Nemertines or annelids.
Among vertebrates the most abundant and diverse group are fish. The presence of mostly articulated skeletons, exceptional preservation of tissue and lack of any other signs of transportation may indicate that these are demic and autochthonous entities (meaning that they lived and died in the same place where they fossilized).
Crocodylomorphs are the most abundant amniotes from Las Hoyas.
Dinosaurs from Las Hoyas (avian and non avian) are unique in many ways. The first ornithomimosaur dinosaur described in Europe, Pelecanimimus polyodon, shows some characters previously unknown in these dinosaurs which enhanced the knowledge on the evolution of the group, such as a high number of teeth. Concavenator corcovatus presents two unique features: very tall neural spines on the vertebrae near the hip, which look like a hump, and a structure on its forearm, which if homologous to quill knobs would push back the origin of feathers earlier in theropod evolution.
Las Hoyas birds are enantiornithes, the most diverse Cretaceous bird clade, which became extinct at the end of the period. Iberomesornis romerali shows both derived ("avian") and primitive ("dinosaurian") characters. Within the derived characters we can underline the presence of a pygostile, although it is still very large compared to that of modern neornithines and the presence of a quilled sternum. Eoalulavis hoyasi shows the first report of an alula or "bastard wing", which means it had a flight manoeuvrability analogous to that of modern birds.
Research
The Las Hoyas site has been studied for more than two decades by researchers from the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, the Universidad Complutense de Madrid and the National University of Distance Education, in collaboration with the Museo de las Ciencias de Castilla-La Mancha, which is responsible for the fossil record from the area.
Fossil content
Crustaceans
| Crustaceans | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Austropotamobius | A. llopisi | Las Hoyas | Numerous specimens[3] | A crayfish | ||
| Delclosia | D. martinelli | An atyid shrimp | ||||
| Lahuerguinagrapta[4] | L. multicostata | A clam shrimp belonging to the family Afrograptidae | ||||
| Skyestheria[4] | Indeterminate | A clam shrimp belonging to the family Polygraptidae | ||||
| Pseudestherites[4] | A clam shrimp belonging to the family Antronestheriidae | |||||
| Spinogriphus [5] | S. ibericus | A member of Peracarida belonging to Spelaeogriphacea | ||||
Chondrichthyes
| Chondrichthyes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Lonchidion[6] | Indeterminate | Las Hoyas | A full body impression of a juvenile | Hybodont | ||
Osteichthyes
| Osteichthyes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Caturus | Caturus sp. | Las Hoyas | Amiiformes | |||
| Gordichthys | G. conquensis | Las Hoyas | Gonorynchiform | |||
| Hispanamia[7] | H. newbreyi | Las Hoyas | Amiid, originally described as Amiopsis | |||
| cf. "Holophagus"[8] | Indeterminate | Las Hoyas | Coelacanth | |||
| Hoyasotes | H. tanyrhis | Las Hoyas | Member of Lepidotidae, originally described as Lepidotes[9] | |||
| Lepidohyas | L. microrhis | Las Hoyas | ||||
| Notagogus | N. aff. N. ferreri | Las Hoyas | Macrosemiid | |||
| Pleuropholis | P. sp. | Las Hoyas | ||||
| Propterus | P. sp. | Las Hoyas | Macrosemiid | |||
| Rubiesichthys | R. gregalis | Las Hoyas | Gonorynchiform | |||
| Stenamara | S. mia | Las Hoyas | Pycnodont | |||
| Turbomesodon | T. praeclarus | Las Hoyas | ||||
| Vidalamia | V. cf. catalunica | Las Hoyas | Amiid | |||
Amphibians
| Amphibians | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Albanerpeton | Indeterminate | Uña | Frontals | Albanerpetontid | ||
| Celtedens | C. ibericus | Las Hoyas | ||||
| C. megacephalus | Uña | |||||
| Gracilibatrachus | G. avallei | Las Hoyas | Pipimorph frog | |||
| Hylaeobatrachus | Indeterminate | Las Hoyas | Salamander | |||
| Iberobatrachus | I. angelae | Las Hoyas | Frog | |||
| Valdotriton | V. gracilis | Las Hoyas | Salamander | |||
| Wealdenbatrachus | W. jucarensis | Uña | Frog | |||
Turtles
| Turtles | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Hoyasemys | H. jimenezi | Las Hoyas | A eucryptodire[10] | |||
| Pleurosternidae | Indeterminate | Uña | ||||
| Pelomedusidae | Indeterminate | Uña | ||||
Squamates
| Squamates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Becklesius | Indeterminate, B. cataphractus | Uña | Paramacellodid lizard | |||
| Cuencasaurus | C. estesi | Uña | ||||
| Hoyalacerta | H. sanzi | Las Hoyas | ||||
| Jucaraseps | J. grandipes | Las Hoyas | Scleroglossa | |||
| Meyasaurus | M. diazromerali | Las Hoyas | teiioid lizard | |||
| M. unaensis | Uña | |||||
| Paramacellodus | P. sinuosus | Uña | Paramacellodid lizard | |||
| Scandensia | S. ciervensis | Las Hoyas | ||||
Mammals
| Mammals | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
| Crusafontia | C. cuencana | Uña | Dryolestid | ||||
| Eobaatar | E. hispanicus | Uña | Eobaatarid multituberculate | ||||
| Galveodon | G. nannothus | Uña | Paulchoffatiid multituberculate | ||||
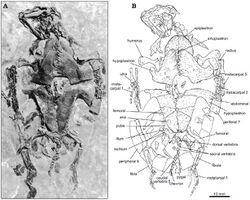
| Spinolestes[11] | S. xenarthrosus | Las Hoyas | Exceptionally complete specimen, preserving soft tissues such as pelage, ears and internal organs. | Gobiconodont Eutriconodont | |||
Crocodyliformes
| Crocodyliformes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Bernissartia | Indeterminate | Uña | ||||
| Cassissuchus | C. sanziuami | Las Hoyas | Gobiosuchid | |||
| Montsecosuchus | Indeterminate | Las Hoyas | ||||
| Sabresuchus | S.ibericus | Uña | ||||
| Unasuchus | U. reginae | Uña | ||||
| Bernissartiidae | Indeterminate | Las Hoyas | ||||
Ornithodirans
| Ornithodirans | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Concavenator | C. corcovatus | Las Hoyas | "Nearly complete and articulated skeleton." | Carcharodontosaurid dinosaur[12] | ||
| Concornis[13] | C. lacustris[13] | Las Hoyas | "Postcranial skeleton."[14] | enantiornithean bird | ||
| Eoalulavis[13] | E. hoyasi[13] | Las Hoyas | "Thoracic region and forelimbs."[14] | enantiornithean bird | ||
| Euronychodon | Indeterminate | Las Hoyas | [15] | |||
| Europejara | E. olcadesorum | Las Hoyas | Tapejarid pterosaur | |||
| Iberomesornis | I. romerali | Las Hoyas | "Postcranial skeleton." | enantiornithean bird[13][16] | ||
| Mantellisaurus | M. atherfieldensis | Las Hoyas | "incomplete but fully-articulated right hindlimb" | Iguanodontian dinosaur[17] | ||
| Pelecanimimus | P. polyodon | Las Hoyas | "Skull and partial skeleton" | Ornithomimosaurian dinosaur[13][18] | ||
| Paronychodon | Indeterminate | Las Hoyas | [19] | |||
| Ricardoestesia | Indeterminate | Las Hoyas | [20] | |||
Correlation
See also
- List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations
- Paja Formation, contemporaneous Lagerstätte of Colombia
- Yixian Formation, contemporaneous Lagerstätte of China
References
- ↑ Martínez et al., 2017
- ↑ Weishampel et al., 2004, pp.556-563
- ↑ Barrios-de Pedro, Sandra; Chin, Karen; Buscalioni, Ángela D. (June 2020). "The late Barremian ecosystem of Las Hoyas sustained by fishes and shrimps as inferred from coprofabrics" (in en). Cretaceous Research 110: 104409. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104409. Bibcode: 2020CrRes.11004409B. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0195667119304628.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Gallego, Oscar F.; Monferran, Mateo D.; Zacarías, Iracema A.; Jiménez, Victoria C.; Buscalioni, Angela D.; Liao, Huanyu (June 2020). "Clam shrimp fauna (Diplostraca-Spinicaudata and Estheriellina) from the Lower Cretaceous of Las Hoyas, Cuenca (Spain)" (in en). Cretaceous Research 110: 104389. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104389. Bibcode: 2020CrRes.11004389G. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0195667119302721.
- ↑ Jaume, Damià; Pinardo‐Moya, Eva; Boxshall, Geoff A. (January 2013). "A presumed spelaeogriphacean crustacean from an upper Barremian wetland (Las Hoyas; Lower Cretaceous; Central Spain)" (in en). Palaeontology 56 (1): 15–28. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2012.01144.x. ISSN 0031-0239. Bibcode: 2013Palgy..56...15J. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1475-4983.2012.01144.x.
- ↑ Marugán-Lobón, Jesús; Martín-Abad, Hugo; Buscalioni, Ángela D. (2023-04-03). "The Las Hoyas Lagerstätte: a palaeontological view of an Early Cretaceous wetland". Journal of the Geological Society 180 (3). doi:10.1144/jgs2022-079. ISSN 0016-7649.
- ↑ MartÍn-Abad, Hugo; Poyato-Ariza, Francisco JosÉ (2017-06-05). "A new genus and species for the amiiform fishes previously assigned to Amiopsis from the Early Cretaceous of Las Hoyas, Cuenca, Spain". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 181 (3): 604–637. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlx010. ISSN 0024-4082.
- ↑ Martín-Abad, Hugo; Martínez, Marian Fregenal- (2021-12-02). "The ecology of the Lower Cretaceous coelacanths from Las Hoyas Konservat- Lagerstätte (Cuenca, Spain): A new insight after the integration of palaeontological and sedimentological data" (in en). Spanish Journal of Palaeontology 36 (2): 191–204. doi:10.7203/sjp.36.2.21966. ISSN 2660-9568. https://ojs.uv.es/index.php/sjpalaeontology/article/view/21966.
- ↑ Paiva, Hanna Carolina Lins de; Gallo, Valéria (2018-12-01). "Quasimodichthys gen. nov. (Neopterygii: Semionotiformes): A morphological and ontogenetic study" (in en). Journal of South American Earth Sciences 88: 132–143. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2018.08.010. ISSN 0895-9811. Bibcode: 2018JSAES..88..132P. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895981118301950.
- ↑ Pérez García et al., 2012
- ↑ Martin et al., 2015
- ↑ Ortega et al., 2010
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 "15.9 Provincia de Quenca, Spain; 4. Calizas de La Huergina Formation," in Weishampel et al., 2004, pp.561-562
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Table 11.1," in Weishampel et al. ,2004, p.212
- ↑ Listed as "cf. Euronychodon sp." in "15.9 Provincia de Quenca, Spain; 4. Calizas de La Huergina Formation," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.561
- ↑ "Table 11.1," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.213
- ↑ Serrano et al., 2013
- ↑ "Table 6.1," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.138
- ↑ Listed as "cf. Paranychodon sp." in "15.9 Provincia de Quenca, Spain; 4. Calizas de La Huergina Formation," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.561
- ↑ Listed as "cf. Ricardoestesia sp." in "15.9 Provincia de Quenca, Spain; 4. Calizas de La Huergina Formation," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.561
Bibliography
- Martínez, Marian Fregenal; Nieves Meléndez; M. Belén Muñoz García; Javier Elez, and Raúl de la Horra. 2017. The stratigraphic record of the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous rifting in the Alto Tajo-Serranía de Cuenca region (Iberian Ranges, Spain): genetic and structural evidences for a revision and a new lithostratigraphic proposal. Revista de la Sociedad Geológica de España 30. 113–142. Accessed 2019-10-12.
- Serrano, Mercedes Llandres; Romain Vullo; Jesús Marugán-Lobón; Francisco Ortega, and Ángela D. Buscalioni. 2013. An articulated hindlimb of a basal iguanodont (Dinosauria, Ornithopoda) from the Early Cretaceous Las Hoyas Lagerstätte (Spain). Geological Magazine 150. 572–576. Accessed 2019-10-12. doi:10.1017/S0016756813000095 ISSN 0016-7568
- Pérez García, Adán; Marcelo S. de la Fuente, and Francisco Ortega. 2012. A New Freshwater Basal Eucryptodiran Turtle from the Early Cretaceous of Spain. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 57. 285–298. Accessed 2019-10-12. doi:10.4202/app.2011.0031 ISSN 0567-7920
- Thomas Martin, Jesús Marugán-Lobón, Romain Vullo, Hugo Martín-Abad, Zhe-Xi Luo & Angela D. Buscalioni (2015). A Cretaceous eutriconodont and integument evolution in early mammals. Nature 526, 380–384. doi:10.1038/nature14905
- Ortega, F., Escaso, F. & Sanz, J. L. (2010): A bizarre, humped Carcharodontosauria (Theropoda) from the Lower Cretaceous of Spain Nature 467: 203-206. HTML abstract
- Weishampel, David B.; Peter Dodson, and Halszka Osmólska (eds.). 2004. The Dinosauria, 2nd edition, 1–880. Berkeley: University of California Press. Accessed 2019-02-21. ISBN:0-520-24209-2
- Sanz, José L.; Chiappe, Luis M.; Pérez Moreno, Bernardino P.; Buscalioni, Ángela D.; Moratalla, José J.; Ortega, Francisco & Poyato Ariza, Francisco J. (1996): An Early Cretaceous bird from Spain and its implications for the evolution of avian flight. Nature 382(6590): 442-445. doi:10.1038/382442a0 (HTML abstract)
- Pérez Moreno, B. P., Sanz, J. L., Buscalioni, A. D., Moratalla, J. J., Ortega, F., and Raskin-Gutman, D. (1994). "A unique multitoothed ornithomimosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of Spain." Nature, 30: 363-367.
- Sanz, J. L. & Bonaparte, José F. (1992): A New Order of Birds (Class Aves) from the Lower Cretaceous of Spain. In: Jonathan J. Becker (ed.): Papers in Avian Paleontology Honoring Pierce Brodkorb. Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County Contributions in Science 36: 38-49.
- Sanz, J. L. & Buscalioni, A.D. (1992): A new bird from the Early Cretaceous of Las Hoyas, Spain, and the early radiation of birds. Palaeontology 35(4): 829-845. PDF fulltext
External links
 |