Long and short scales
The long and short scales are two of several naming systems for integer powers of ten which use some of the same terms for different magnitudes.[1][2]
Some languages, particularly in East Asia and South Asia, have large number naming systems that are different from both the long and short scales, such as the Indian numbering system and the Chinese, Japanese, or Korean numerals.[1][2]
Much of the remainder of the world adopted either the short scale or the long scale for everyday counting powers of ten. Countries with the usage of the long scale include most countries in continental Europe and most that are French-speaking, German-speaking and Spanish-speaking.[3] Usage of the short scale is found in Brazil and in most English-speaking and Arabic-speaking countries.
For whole numbers smaller than 1,000,000,000 (109), such as one thousand or one million, the two scales are identical. For larger numbers, starting with 109, the two systems differ. For identical names, the long scale proceeds by powers of one million, whereas the short scale proceeds by powers of one thousand. For example, on the short scale, "one billion" means one thousand million (1,000,000,000), whereas in the long scale, it means one million million (1,000,000,000,000). The long scale system employs additional terms for interleaved values, typically replacing the word ending -ion by -iard.
To avoid confusion resulting from the coexistence of the two terms, the International System of Units (SI) recommends using the metric prefix to indicate orders of magnitude, associated with physical quantities.
Scales
In both short and long scale naming, names are given each multiplication step for increments of the base-10 exponent of three, i.e. for each integer n in the sequence of multipliers 103n. Both systems use the same names for certain multipliers, including those for all numbers smaller than 10. Both systems use the same names for certain multipliers, including those for all numbers smaller than 109. The differences arise from the assignment of identical names to specific values of n, for numbers starting with 109, for which n=3. In the short scale system, the identical names are for n=3, 4, 5, ..., while the long scale places them at n=4, 6, 8, etc.
Short scale
In the short scale, a billion means a thousand millions (1,000,000,000 which is 109), a trillion means one thousand (short scale) billions (1012), and so on. Thus, a short scale n-illion equals 103n+3.[4]
Long scale
In the long scale, a billion means one million millions (1012) and a trillion means one million (long scale) billions (1018), and so on. Therefore, a long scale n-illion equals 106n.[1][2] In some languages, the long scale uses additional names for the intermediate multipliers, replacing the ending -ion with -iard; for example, the next multiplier after million is milliard (109); after a (long scale) billion it is billiard (1015). Hence, a (long scale) n-iard equals 106n+3.
Comparison
The relationship between the numeric values and the corresponding names in the two scales can be described as:
| Value in positional notation | Value in scientific notation |
Metric prefix | Short scale | Long scale | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prefix | Symbol | Name | Logic | Name | Alternative name | Logic | ||
| 1 | 100 | one | one | |||||
| 10 | 101 | deca | da | ten | ten | |||
| 100 | 102 | hecto | h | hundred | hundred | |||
| 1,000 | 103 | kilo | k | thousand | thousand | |||
| 1,000,000 | 106 | mega | M | million | 1,000 × 1,0001 | million | 1,000,0001 | |
| 1,000,000,000 | 109 | giga | G | billion | 1,000 × 1,0002 | thousand million | milliard | 1,000 × 1,000,0001 |
| 1,000,000,000,000 | 1012 | tera | T | trillion | 1,000 × 1,0003 | billion | 1,000,0002 | |
| 1,000,000,000,000,000 | 1015 | peta | P | quadrillion | 1,000 × 1,0004 | thousand billion | billiard | 1,000 × 1,000,0002 |
| 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 | 1018 | exa | E | quintillion | 1,000 × 1,0005 | trillion | 1,000,0003 | |
| 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 | 1021 | zetta | Z | sextillion | 1,000 × 1,0006 | thousand trillion | trilliard | 1,000 × 1,000,0003 |
| 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 | 1024 | yotta | Y | septillion | 1,000 × 1,0007 | quadrillion | 1,000,0004 | |
| 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 | 1027 | ronna | R | octillion | 1,000 × 1,0008 | thousand quadrillion | quadrilliard | 1,000 × 1,000,0004 |
| 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 | 1030 | quetta | Q | nonillion | 1,000 × 1,0009 | quintillion | 1,000,0005 | |
The relationship between the names and the corresponding numeric values in the two scales can be described as:
| Name | Short scale | Long scale | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value in scientific notation |
Metric prefix | Logic | Value in scientific notation |
Metric prefix | Logic | |||
| Prefix | Symbol | Prefix | Symbol | |||||
| million | 106 | mega | M | 1,000 × 1,0001 | 106 | mega | M | 1,000,0001 |
| billion | 109 | giga | G | 1,000 × 1,0002 | 1012 | tera | T | 1,000,0002 |
| trillion | 1012 | tera | T | 1,000 × 1,0003 | 1018 | exa | E | 1,000,0003 |
| quadrillion | 1015 | peta | P | 1,000 × 1,0004 | 1024 | yotta | Y | 1,000,0004 |
| quintillion | 1018 | exa | E | 1,000 × 1,0005 | 1030 | quetta | Q | 1,000,0005 |
| etc. | For the next order of magnitude, multiply by 1,000 | For the next order of magnitude, multiply by 1,000,000 | ||||||
The root mil in million does not refer to the numeral, 1. The word, million, derives from the Old French, milion, from the earlier Old Italian, milione, an intensification of the Latin word, mille, a thousand. That is, a million is a big thousand, much as a great gross is a dozen gross or 12 × 144 = 1728.[5]
The word milliard, or its translation, is found in many European languages and is used in those languages for 109. However, it is not found in American English, which uses billion, and not used in British English, which preferred to use thousand million before the current usage of billion. The financial term yard, which derives from milliard, is used on financial markets, as, unlike the term billion, it is internationally unambiguous and phonetically distinct from million. Likewise, many long scale countries use the word billiard (or similar) for one thousand long scale billions (i.e., 1015), and the word trilliard (or similar) for one thousand long scale trillions (i.e., 1021), etc.[6][7][8][9][10]
History
Although this situation has been developing since the 1200s, the first recorded use of the terms short scale (French: échelle courte) and long scale (French: échelle longue) was by the French mathematician Geneviève Guitel in 1975.[1][2]
The short scale was never widespread before its universal adoption in the United States. It has been taught in American schools since the early 1800s.[5] It has since become common in other English-speaking nations and several other countries. For most of the 19th and 20th centuries, the United Kingdom largely used the long scale,[4][11] whereas the United States used the short scale,[11] so that the two systems were often referred to as British and American in the English language. After several decades of increasing informal British usage of the short scale, in 1974 the government of the UK adopted it,[12] and it is used for all official purposes.[13][14][15][16][17][18] The British usage and American usage are now identical.
The existence of the different scales means that care must be taken when comparing large numbers between languages or countries, or when interpreting old documents in countries where the dominant scale has changed over time. For example, British English, French, and Italian historical documents can refer to either the short or long scale, depending on the date of the document, since each of the three countries has used both systems at various times in its history. Today, the United Kingdom officially uses the short scale, but France and Italy use the long scale.
The pre-1974 former British English word billion, post-1961 current French word billion, post-1994 current Italian word bilione, Spanish billón, German Billion, Dutch biljoen, Danish billion, Swedish biljon, Finnish biljoona, Slovenian bilijon, Polish bilion, and European Portuguese word bilião (with a different spelling to the Brazilian Portuguese variant, but in Brazil referring to short scale) all refer to 1012, being long-scale terms. Therefore, each of these words translates to the American English or post-1974 British English word: trillion (1012 in the short scale), and not billion (109 in the short scale).
On the other hand, the pre-1961 former French word billion, pre-1994 former Italian word bilione, Brazilian Portuguese word bilhão, and Welsh word biliwn all refer to 109, being short scale terms. Each of these words translates to the American English or post-1974 British English word billion (109 in the short scale).
The term billion originally meant 1012 when introduced.[5]
- In long scale countries, milliard was defined to its current value of 109, leaving billion at its original 1012 value and so on for the larger numbers.[5] Some of these countries, but not all, introduced new words billiard, trilliard, etc. as intermediate terms.[6][7][8][9][10]
- In some short scale countries, milliard was defined to 109 and billion dropped altogether, with trillion redefined down to 1012 and so on for the larger numbers.[5]
- In many short scale countries, milliard was dropped altogether and billion was redefined down to 109, adjusting downwards the value of trillion and all the larger numbers.
- Timeline
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 13th century | The word million was not used in any language before the 13th century. The monk and polymath Maximus Planudes (c. 1260–1305) was among the first recorded users of the word to document Mediterranean trade between Constantinople and Italian states.[5] Over the next two centuries, the term became widely accepted and was adopted by other Italian states, France and other European countries. |
| Late 14th century |  Piers Plowman, a 17th-century copy of the original 14th-century allegorical narrative poem by William Langland
Translation:
|
| 1475 | French mathematician Jehan Adam, writing in Middle French, recorded the words bymillion and trimillion as meaning 1012 and 1018 respectively in a manuscript Traicté en arismetique pour la practique par gectouers, now held in the Bibliothèque Sainte-Geneviève in Paris.[19][20][21]
Translation:
|
| 1484 |  Le Triparty en la Science des Nombres par Maistre Nicolas Chuquet Parisien an extract from Chuquet's original 1484 manuscript
Translation:
The extract from Chuquet's manuscript, the transcription and translation provided here all contain an original mistake: one too many zeros in the 804300 portion of the fully written out example: 745324'8043000 '700023'654321 ... |
| 1516 |  Guilielmus Budaeus or Guillaume Budé (1467–1540)
Translation:
|
| 1549 | The influential French mathematician Jacques Pelletier du Mans used the name milliard (or milliart) to mean 1012, attributing the term to the earlier usage by Guillaume Budé[25] |
| 17th century | |
| 1676 | The first published use of milliard as 109 occurred in the Netherlands.[5][26]
Translation:
|
| 1729 | The short-scale meaning of the term billion had already been brought to the British American colonies. The first American appearance of the short scale value of billion as 109 was published in the Greenwood Book of 1729, written anonymously by Prof. Isaac Greenwood of Harvard College.[5] |
| Late 18th century | As early as 1762 (and through at least the early 20th century), the dictionary of the Académie française defined billion as a term of arithmetic meaning a thousand millions.[27][28][29][30] |
| Early 19th century | France widely converted to the short scale, and was followed by the U.S., which began teaching it in schools. Many French encyclopedias of the 19th century either omitted the long scale system or called it "désormais obsolète", a now obsolete system. Nevertheless, by the mid 20th century France would officially convert back to the long scale. |
| 1926 |  A Dictionary of Modern English Usage by H. W. Fowler
Although American English usage did not change, within the next 50 years French usage changed from short scale to long and British English usage changed from long scale to short. |
| 1948 | The 9th General Conference on Weights and Measures received requests to establish an International System of Units. One such request was accompanied by a draft French Government discussion paper, which included a suggestion of universal use of the long scale, inviting the short-scale countries to return or convert.[31] This paper was widely distributed as the basis for further discussion. The matter of the International System of Units was eventually resolved at the 11th General Conference in 1960. The question of long scale versus short scale was not resolved and does not appear in the list of any conference resolutions.[31][32] |
| 1960 | The 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures adopted the International System of Units (SI), with its own set of numeric prefixes.[33] SI is therefore independent of the number scale being used. SI also notes the language-dependence of some larger-number names and advises against using ambiguous terms such as billion, trillion, etc.[34] The National Institute of Standards and Technology within the US also considers that it is best that they be avoided entirely.[35] |
| 1961 | The French Government confirmed their official usage of the long scale in the Journal officiel (the official French Government gazette).[36] |
| 1974 |  British prime minister Harold Wilson (1916–1995)
The BBC and other UK mass media quickly followed the government's lead within the UK. During the last quarter of the 20th century, most other English-speaking countries (Ireland, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Zimbabwe, etc.) either also followed this lead or independently switched to the short scale use. However, in most of these countries, some limited long scale use persists and the official status of the short scale use is not clear. |
| 1975 | French mathematician Geneviève Guitel introduced the terms long scale (French: échelle longue) and short scale (French: échelle courte) to refer to the two numbering systems.[1][2] |
| 1994 | The Italian Government confirmed their official usage of the long scale.[10] |
As large numbers in natural sciences are usually represented by metric prefixes, scientific notation or otherwise, the most commonplace occurrence of large numbers represented by long or short scale terms is in finance. The following table includes some historic examples related to hyper-inflation and other financial incidents.
- Timeline
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 1923 | Using German banknotes as wallpaper following the 1923 hyperinflation German hyperinflation in the 1920s Weimar Republic caused 'Eintausend Mark' (1000 Mark = 103 Mark) German banknotes to be over-stamped as 'Eine Milliarde Mark' (109 Mark). This introduced large-number names to the German populace. The Mark or Papiermark was replaced at the end of 1923 by the Rentenmark at an exchange rate of 1 Rentenmark = 1 billion (long scale) Papiermark = 1012 Papiermark = 1 trillion (short scale) Papiermark |
| 1946 |
Hyperinflation in Hungary in 1946 led to the introduction of the 1020 pengő banknote. 100 million b-pengő (long scale) = 100 trillion (long scale) pengő = 1020 pengő = 100 quintillion (short scale) pengő. On 1 August 1946, the forint was introduced at a rate of 1 forint = 400 quadrilliard (long scale) pengő = 4 × 1029 pengő = 400 octillion (short scale) pengő. |
| 1993 |  5 × 1011 Yugoslav dinar banknotes from 1993 Hyperinflation in Yugoslavia led to the introduction of 5 × 1011 dinar banknotes. 500 thousand million (long scale) dinars = 5 × 1011 dinar banknotes = 500 billion (short scale) dinars. The later introduction of the new dinar came at an exchange rate of 1 new dinar = 1 × 1027 dinars = ~1.3 × 1027 pre 1990 dinars. |
| 2009 |  1014 Zimbabwean dollars banknote from 2009 Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe led to banknotes of 1014 Zimbabwean dollars, marked "One Hundred Trillion Dollars" (short scale), being issued in 2009, shortly ahead of the currency being abandoned[37][38][39] after a final redenomination to the 'fourth dollar'. From 2013 to 2019 when the RTGS Dollar entered use, no new currency was announced, and so foreign currencies were used instead. 100 trillion (short scale) Zimbabwean dollars = 1014 Zimbabwean dollars = 100 billion (long scale) Zimbabwean dollars = 1027 pre-2006 Zimbabwean dollars = 1 quadrilliard (long scale) pre-2006 Zimbabwean dollars. |
| 2022 | (As of November 2022), the combined total public debt of the United States stood at United States dollar 31.299 trillion.[40]
31 trillion (short scale) US Dollars = 3.1 × 1013 US Dollars = 31 billion (long scale) US Dollars |
Current usage
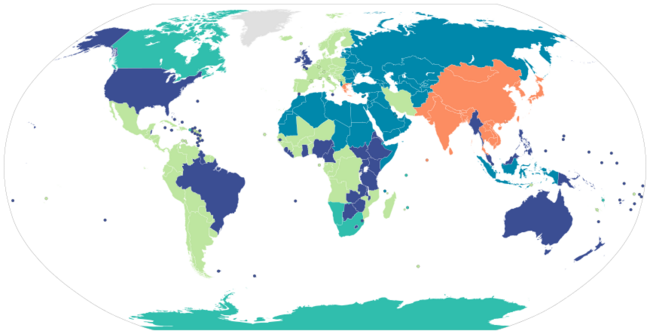
Short scale users
English-speaking
Most English-language countries and regions use the short scale with 109 being billion. For example:[shortscale note 1]
 Australia[shortscale note 2][41]
Australia[shortscale note 2][41] Canada (English-speaking) see Using both below
Canada (English-speaking) see Using both below Ireland (English-speaking, Irish: billiún, trilliún)
Ireland (English-speaking, Irish: billiún, trilliún) United Kingdom[shortscale note 3][12][13][42][15][16]
United Kingdom[shortscale note 3][12][13][42][15][16] United States[shortscale note 4][43][44]
United States[shortscale note 4][43][44]
Arabic-speaking
Most Arabic-language countries and regions use the short scale with 109 being مليار milyar, except for a few countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE which use the word بليون billion for 109. For example:[shortscale note 5][45][46]
 Algeria
Algeria Egypt
Egypt Iraq
Iraq Morocco
Morocco Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
Other short scale
Other countries also use a word similar to trillion to mean 1012, etc. Whilst a few of these countries like English use a word similar to billion to mean 109, most like Arabic have kept a traditionally long scale word similar to milliard for 109. Some examples of short scale use, and the words used for 109 and 1012, are
 Brazil (Brazilian Portuguese: bilhão, trilhão)
Brazil (Brazilian Portuguese: bilhão, trilhão) Indonesia (miliar, triliun)[shortscale note 6][47]
Indonesia (miliar, triliun)[shortscale note 6][47] Israel (Hebrew: מיליארד milyard, טריליון trilyon)
Israel (Hebrew: מיליארד milyard, טריליון trilyon) Russia (миллиард milliard, триллион trillion)
Russia (миллиард milliard, триллион trillion) Turkey (milyar, trilyon)
Turkey (milyar, trilyon)
Long scale users
The long scale is used by most Continental European countries and by most other countries whose languages derive from Continental Europe (with the notable exceptions of Albania, Greece, Romania,[48] and Brazil). These countries use a word similar to billion to mean 1012. Some use a word similar to milliard to mean 109, while others use a word or phrase equivalent to thousand millions.
Dutch-speaking
Most Dutch-language countries and regions use the long scale with 109 = miljard.[49][50]
French-speaking
Most French-language countries and regions use the long scale with 109 = milliard, for example:[longscale note 1][51][52]
 Canada (Canadian French) see Using both below
Canada (Canadian French) see Using both below France
France
German-speaking
German-language countries and regions use the long scale with 109 = Milliarde.
Portuguese-speaking
With the notable exception of Brazil, a short scale country, most Portuguese-language countries and regions use the long scale with 109 = mil milhões or milhar de milhões.
Spanish-speaking
Most Spanish-language countries and regions use the long scale, for example:[longscale note 2][54][55]
 Argentina
Argentina Mexico (mil millones or millardo)
Mexico (mil millones or millardo) Spain (millardo or typ. mil millones)
Spain (millardo or typ. mil millones)
Other long scale
Some examples of long scale use, and the words used for 109 and 1012, are
 Italy (miliardo, bilione) [longscale note 3][10][57]
Italy (miliardo, bilione) [longscale note 3][10][57] Poland (miliard, bilion)
Poland (miliard, bilion) Switzerland (French: milliard, billion; German: Milliarde, Billion; Italian: miliardo, bilione; Romansh: milliarda, billiun[58])
Switzerland (French: milliard, billion; German: Milliarde, Billion; Italian: miliardo, bilione; Romansh: milliarda, billiun[58])
Using both
Some countries use either the short or long scales, depending on the internal language being used or the context.
| Country or territory | Short scale usage | Long scale usage |
|---|---|---|
| Canadian English (109 = billion, 1012 = trillion) | Canadian French (109 = milliard, 1012 = billion[60] or mille milliards). | |
|
English (109 = billion, 1012 = trillion) | French (109 = milliard, 1012 = billion) |
|
South African English (109 = billion, 1012 = trillion) | Afrikaans (109 = miljard, 1012 = biljoen) |
| Economic and technical (109 = billón, 1012 = trillón) | Latin American export publications (109 = millardo or mil millones, 1012 = billón) |
Using neither
The following countries use naming systems for large numbers that are not etymologically related to the short and long scales:
| Country | Number system | Naming of large numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Indian numbering system | Traditional system for everyday use, but short or long scale may also be in use [other scale note 1] | |
| Dzongkha numerals | Traditional system | |
| Khmer numerals | Traditional system | |
|
East Asian numbering system: | Traditional myriad system for the larger numbers; special words and symbols up to 1068 |
| Calque of the short scale | Names of the short scale have not been loaned but calqued into Greek, based on the native Greek word for million, εκατομμύριο ekatommyrio ("hundred-myriad", i.e. 100 × 10,000):
| |
| Lao numerals | Traditional system | |
| Mongolian numerals | Traditional myriad system for the larger numbers; special words up to 1067 | |
| Traditional systems | ||
| Thai numerals | Traditional system based on millions | |
| Vietnamese numerals | Traditional system(s) based on thousands |
By continent
The long and short scales are both present on most continents, with usage dependent on the language used. Examples include:
| Continent | Short scale usage | Long scale usage |
|---|---|---|
| Africa | Arabic (Egypt, Libya), South African English | French (Benin, Guinea), Portuguese (Mozambique) |
| North America | American English, Canadian English | Canadian French, Mexican Spanish, U.S. Spanish |
| South America | Brazilian Portuguese, English (Guyana) | American Spanish, Dutch (Suriname), French (French Guiana) |
| Antarctica | Australian English, British English, New Zealand English, Russian | American Spanish (Argentina, Chile), French (France), Norwegian (Norway) |
| Asia | Hebrew (Israel), Indonesian, Philippine English | Persian (Iran), Portuguese (East Timor, Macau) |
| Europe | British English, Russian, Turkish | Dutch, French, German, Italian, Portuguese, Spanish |
| Oceania | Australian English, New Zealand English | French (French Polynesia, New Caledonia) |
Notes on current usage
Short scale
- ↑ English language countries: Apart from the United States, the long scale was used for centuries in many English language countries before being superseded in recent times by short scale usage. Because of this history, some long scale use persists[18] and the official status of the short scale in anglophone countries other than the UK and US is sometimes obscure.[5]
- ↑ Australian usage: In Australia, education, media outlets, and literature all use the short scale in line with other English-speaking countries. The current recommendation by the Australian Government Department of Finance and Deregulation (formerly known as AusInfo), and the legal definition, is the short scale.[41] As recently as 1999, the same department did not consider short scale to be standard, but only used it occasionally. Some documents use the term thousand million for 109 in cases where two amounts are being compared using a common unit of one 'million'.
- ↑ British usage: Billion has meant 109 in most sectors of official published writing for many years now. The UK government, the BBC, and most other broadcast or published mass media, have used the short scale in all contexts since the mid-1970s.[12][13][42][15] Before the widespread use of billion for 109, UK usage generally referred to thousand million rather than milliard.[16] The long scale term milliard, for 109, is obsolete in British English, though its derivative, yard, is still used as slang in the London money, foreign exchange, and bond markets.
- ↑ American usage: In the United States, the short scale has been taught in school since the early 19th century. It is therefore used exclusively.[43][44]
- ↑ Arabic language countries: Most Arabic-language countries use: 106, مليون million; 109, مليار milyar; 1012, ترليون trilyon; etc.[45][46]
- ↑ Indonesian usage: Large numbers are common in Indonesia, in part because its currency (rupiah) is generally expressed in large numbers (the lowest common circulating denomination is Rp100 with Rp1000 is considered as base unit). The term juta, equivalent to million (106), is generally common in daily life. Indonesia officially employs the term miliar (derived from the long scale Dutch word miljard) for the number 109, with no exception. For 1012 and greater, Indonesia follows the short scale, thus 1012 is named triliun. The term seribu miliar (a thousand milliards) or more rarely sejuta juta (a million millions) or sejuta berkali-kali (a millions after a million or a millions over a million) are also used for 1012 less often. Terms greater than triliun are not very familiar to Indonesians.[47]
Long scale
- ↑ French usage: France, with Italy, was one of two European countries which converted from the long scale to the short scale during the 19th century, but returned to the original long scale during the 20th century. In 1961, the French Government confirmed their long scale status.[36][51][52] However the 9th edition of the dictionary of the Académie française describes billion as an outdated synonym of milliard, and says that the new meaning of 1012 was decreed in 1961, but never caught on.[53]
- ↑ Spanish language countries: Spanish-speaking countries sometimes use millardo (milliard)[54] for 109, but mil millones (thousand millions) is used more frequently. The word billón is sometimes used in the short scale sense in those countries more influenced by the United States, where "billion" means "one thousand millions". The usage of billón to mean "one thousand millions", controversial from the start, was denounced by the Royal Spanish Academy as recently as 2010,[55] but was finally accepted in a later version of the official dictionary as standard usage among educated Spanish speakers in the United States (including Puerto Rico).[56]
- ↑ Italian usage: Italy, with France, was one of the two European countries which partially converted from the long scale to the short scale during the 19th century, but returned to the original long scale in the 20th century. In 1994, the Italian Government confirmed its long scale status.[10] In Italian, the word bilione officially means 1012, trilione means 1018, etc.. Colloquially, bilione[57] can mean both 109 and 1012; trilione can mean both 1012 and (rarer) 1018 and so on. Therefore, in order to avoid ambiguity, they are seldom used. Forms such as miliardo (milliard) for 109, mille miliardi (a thousand milliards) for 1012, un milione di miliardi (a million milliards) for 1015, un miliardo di miliardi (a milliard of milliards) for 1018, mille miliardi di miliardi (a thousand milliard of milliards) for 1021 are more common.[10]
Both long and short scale
- ↑ Canadian usage: Both scales are in use currently in Canada. English-speaking regions use the short scale exclusively, while French-speaking regions use the long scale, though the Canadian government standards website recommends that in French billion and trillion be avoided, recommending milliard for 109, and mille milliards (a thousand milliards) for 1012.[59]
- ↑ South African usage: South Africa uses both the long scale (in Afrikaans and sometimes English) and the short scale (in English). Unlike the 1974 UK switch, the switch from long scale to short scale took time. (As of 2011) most English language publications use the short scale. Some Afrikaans publications briefly attempted usage of the "American System" but that has led to comment in the papers[61] and has been disparaged by the "Taalkommissie" (The Afrikaans Language Commission of the South African Academy of Science and Art)[62] and has thus, to most appearances, been abandoned.
Neither long nor short scale
- ↑ Indian, Pakistani and Bangladeshi usage: Outside of financial media, the use of billion by Bangladeshi, Indian and Pakistani English speakers highly depends on their educational background. Some may continue to use the traditional British long scale. In everyday life, Bangladeshis, Indians and Pakistanis largely use their own common number system, commonly referred to as the Indian numbering system – for instance, Bangladeshi, Pakistani, and Indian English commonly use the words lakh to denote 100 thousand, crore to denote ten million (i.e. 100 lakhs) and arab to denote thousand million.[63]
Alternative approaches
- In written communications, the simplest solution for moderately large numbers is to write the full amount, for example 1,000,000,000,000 rather than 1 trillion (short scale) or 1 billion (long scale).
- Combinations of the unambiguous word million, for example: 109 = "one thousand million"; 1012 = "one million million".[65]
- Scientific notation (also known as standard form or exponential notation, for example 1×109, 1×1010, 1×1011, 1×1012, etc.), or its engineering notation variant (for example 1×109, 10×109, 100×109, 1×1012, etc.), or the computing variant E notation (for example
1e9,1e10,1e11,1e12, etc.). This is the most common practice among scientists and mathematicians, and is both unambiguous and convenient. - SI prefixes in combination with SI units, for example, giga for 109 and tera for 1012 can give gigawatt (=109 W) and terawatt (=1012 W). The International System of Units (SI) is independent of whichever scale is being used.[33] Use with non-SI units (e.g. "giga-dollars", "megabucks") is possible. k€ and M€ is frequently encountered.
See also
- Googol (number)
- Googolplex (number)
- Names of large numbers
- Names of small numbers
- Orders of magnitude (numbers)
- Hindu units of time which displays some similar issues
- Indian numbering system
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Guitel, Geneviève (1975) (in fr). Histoire comparée des numérations écrites. Paris: Flammarion. pp. 51–52. ISBN 978-2-08-211104-1.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Guitel, Geneviève (1975). ""Les grands nombres en numération parlée (État actuel de la question)", i.e. "The large numbers in oral numeration (Present state of the question)"" (in fr). Histoire comparée des numérations écrites. Paris: Flammarion. pp. 566–574. ISBN 978-2-08-211104-1.
- ↑ "Authoritative Real Academia Española (RAE) dictionary: billón". http://lema.rae.es/drae/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 British-English usage of 'Billion vs Thousand million vs Milliard'. Google Inc. https://books.google.com/ngrams/graph?content=billion%2Cthousand+million%2Cmilliard&year_start=1808&year_end=1967&corpus=18&smoothing=3&share=. Retrieved 26 April 2014.
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 Smith, David Eugene (1953). History of Mathematics. II. Courier Dover Publications. pp. 81. ISBN 978-0-486-20430-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=uTytJGnTf1kC&pg=PA81.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Wortschatz-Lexikon: Milliarde" (in de). Universität Leipzig: Wortschatz-Lexikon. http://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/cgi-bin/wort_www.exe?site=1&Wort=Milliarde.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Wortschatz-Lexikon: Billion" (in de). Universität Leipzig: Wortschatz-Lexikon. http://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/cgi-bin/wort_www.exe?site=1&Wort=Billion.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Wortschatz-Lexikon: Billiarde" (in de). Universität Leipzig: Wortschatz-Lexikon. http://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/cgi-bin/wort_www.exe?site=1&Wort=Billiarde.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Wortschatz-Lexikon: Trilliarde" (in de). Universität Leipzig: Wortschatz-Lexikon. http://wortschatz.uni-leipzig.de/cgi-bin/wort_www.exe?site=1&Wort=Trilliarde.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 "Direttiva CEE / CEEA / CE 1994 n. 55, p.12" (in it). Italian Government. 21 November 1994. http://www.frareg.com/news/legislazione/ambiente/direttiva_1994_55_CE.pdf.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Fowler, H. W. (1926). A Dictionary of Modern English Usage. Great Britain: Oxford University Press. pp. 52–53. ISBN 978-0-19-860506-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=hrtIDakUpA4C&q=billion&pg=PT169.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 ""BILLION" (DEFINITION) — HC Deb 20 December 1974 vol 883 cc711W–712W". Hansard Written Answers. Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). 20 December 1972. https://api.parliament.uk/historic-hansard/written-answers/1974/dec/20/billion-definition#S5CV0883P0_19741220_CWA_439.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 O'Donnell, Frank (30 July 2004). "Britain's £1 trillion debt mountain – How many zeros is that?". The Scotsman. http://news.scotsman.com/latestnews/Britains-1-trillion-debt-mountain.2550147.jp.
- ↑ "Who wants to be a trillionaire?" (in en-GB). BBC News. 7 May 2007. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/programmes/more_or_less/6625545.stm.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Comrie, Bernard (24 March 1996). "billion:summary". Linguist List (Mailing list). Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 "Oxford Dictionaries: How many is a billion?". Oxford University Press. https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/explore/how-many-is-a-billion/.
- ↑ "Oxford Dictionaries: Billion". Oxford University Press. http://oxforddictionaries.com/definition/billion.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Nielsen, Ron (2006). The Little Green Handbook. Macmillan Publishers. p. 290. ISBN 978-0-312-42581-4. https://archive.org/details/littlegreenhandb00ronn/page/290.
- ↑ Adam, Jehan (1475) (in frm). Traicté en arismetique pour la practique par gectouers... (MS 3143). Paris: Bibliothèque Sainte-Geneviève.
- ↑ "HOMMES DE SCIENCE, LIVRES DE SAVANTS A LA BIBLIOTHÈQUE SAINTE-GENEVIÈVE, Livres de savants II" (in fr). Traicté en arismetique pour la practique par gectouers…. Bibliothèque Sainte-Geneviève. 2005. http://www-bsg.univ-paris1.fr/ExposVirtuelles/exposvirtuellesreserves/sciences/savants2.htm.
- ↑ Thorndike, Lynn (1926). "The Arithmetic of Jehan Adam, 1475 A.D". The American Mathematical Monthly (Mathematical Association of America) 1926 (January): 24–28. doi:10.2307/2298533.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Chuquet, Nicolas (1880). "Le Triparty en la Science des Nombres par Maistre Nicolas Chuquet Parisien" (in frm). Bulletino di Bibliographia e di Storia delle Scienze Matematische e Fisische (Bologna: Aristide Marre) XIII (1880): 593–594. ISSN 1123-5209. http://www.miakinen.net/vrac/nombres#lettres_zillions. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ↑ Chuquet, Nicolas (1880). "Le Triparty en la Science des Nombres par Maistre Nicolas Chuquet Parisien" (in frm). miakinen.net. http://www.miakinen.net/vrac/nombres#lettres_zillions.
- ↑ Flegg, Graham (23–30 December 1976). "Tracing the origins of One, Two, Three.". New Scientist (Reed Business Information) 72 (1032): 747. ISSN 0262-4079. https://books.google.com/books?id=obHSBCxiJ1YC&pg=PA747. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Budaeus, Guilielmus (1516) (in la). De Asse et partibus eius Libri quinque. pp. folio 93.
- ↑ Houck (1676). Arithmetic. Netherlands. p. 2.
- ↑ Dictionnaire de l'académie françoise (4th ed.). Paris, France: Institut de France. 1762. p. 177. https://books.google.com/books?id=0oM-AAAAcAAJ&q=Dictionnaire+de+l'Académie+Française&pg=PA1.
- ↑ Dictionnaire de l'Académie française (6th ed.). Paris, France. 1835. p. 189. http://portail.atilf.fr/cgi-bin/dico1look.pl?strippedhw=billion&dicoid=ACAD1835&headword=&dicoid=ACAD1835.
- ↑ Dictionnaire de l'Académie française (7th ed.). Paris, France: Institut de France. 1877. p. 182. https://books.google.com/books?id=P2whAQAAMAAJ&q=Dictionnaire+de+l'Académie+Française&pg=PR23.
- ↑ Dictionnaire de l'Académie française (8th ed.). Paris, France: Institut de France. 1932–1935. p. 144. http://portail.atilf.fr/cgi-bin/dico1look.pl?strippedhw=billion&headword=&docyear=ALL&dicoid=ACAD1932&articletype=1.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 "Resolution 6 of the 9th meeting of the CGPM (1948)". BIPM. http://www.bipm.org/en/CGPM/db/9/6/.
- ↑ "Resolution 6 of the 10th meeting of the CGPM (1954)". BIPM. http://www.bipm.org/en/CGPM/db/10/6/.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 "Resolution 12 of the 11th meeting of the CGPM (1960)". BIPM. http://www.bipm.org/jsp/en/ViewCGPMResolution.jsp?CGPM=11&RES=12.
- ↑ The International System of Units (SI) (8 ed.). BIPM. May 2006. pp. 134 / 5.3.7 Stating values of dimensionless quantities, or quantities of dimension one. ISBN 92-822-2213-6. http://www.bipm.org/utils/common/pdf/si_brochure_8_en.pdf. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ↑ Thompson, Ambler; Taylor, Barry N. (30 March 2008). "Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI), NIST SP – 811". NIST (US: National Institute of Standards and Technology): 21. https://www.nist.gov/manuscript-publication-search.cfm?pub_id=200349. Retrieved 13 September 2014.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "Décret 61-501" (in fr). Journal Officiel (French Government): 4587 note 3a, and erratum on page 7572. 11 August 1961. http://www.ensmp.net/pdf/1961/decr-61-0501.pdf. Retrieved 31 January 2008.
- ↑ "BBC News: Zimbabweans play the zero game". BBC. 23 July 2008. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/7516874.stm.
- ↑ "BBC News: Zimbabwe rolls out Z$100tr note". BBC. 16 January 2009. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/7832601.stm.
- ↑ "BBC News: Zimbabwe abandons its currency". BBC. 29 January 2009. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/7859033.stm.
- ↑ "US National Debt Clock". https://usdebtclock.org/.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 "RBA: Definition of billion". Reserve Bank of Australia. http://www.rba.gov.au/glossary/index.html?search=billion.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 "BBC News: Who wants to be a trillionaire?". BBC. 7 May 2007. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/programmes/more_or_less/6625545.stm.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 "billion". billion. Cambridge University Press. http://dictionaries.cambridge.org/define.asp?key=billion*1+0&dict=A. Retrieved 21 August 2011.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 "trillion". Cambridge Dictionaries Online. Cambridge University Press. http://dictionaries.cambridge.org/define.asp?key=trillion*1+0&dict=A.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 "Al Jazem English-Arabic online dictionary: Billion". Al Jazem English-Arabic online dictionary. Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.aljazem.com/en/billion.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 "Al Jazem English-Arabic online dictionary:Trillion". Al Jazem English-Arabic online dictionary. Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.aljazem.com/en/trillion.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 Robson S. O. (Stuart O.), Singgih Wibisono, Yacinta Kurniasih. Javanese English dictionary Tuttle Publishing: 2002, ISBN:0-7946-0000-X, 821 pages
- ↑ Avram, Mioara; Sala, Marius (2000), May We Introduce the Romanian Language to You?, Editura Fundatiei Culturale Române, p. 151, ISBN 9789735772246, "the numeral miliard "billion""
- ↑ "De Geïntegreerde Taal-Bank: miljard" (in nl). Instituut voor Nederlandse Lexicologie. http://www.wnt.inl.nl/iWDB/search?actie=article&wdb=WFT&id=63043&lemmodern=miljard.
- ↑ "De Geïntegreerde Taal-Bank: biljoen" (in nl). Instituut voor Nederlandse Lexicologie. http://gtb.inl.nl/iWDB/search?actie=article&wdb=WFT&id=8253&lemmodern=biljoen.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 "French Larousse: milliard" (in fr). Éditions Larousse. http://www.larousse.com/en/dictionaries/french/milliard.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 "French Larousse: billion" (in fr). Éditions Larousse. http://www.larousse.com/en/dictionaries/french/billion.
- ↑ "billion" (in fr). billion (9th ed.). Académie française. 1992. http://atilf.atilf.fr/dendien/scripts/generic/cherche.exe?15;s=802200930;;. Retrieved 17 January 2016. "BILLION (les deux l se prononcent sans mouillure) n. m. XVe siècle, byllion, « un million de millions »; XVIe siècle, « mille millions ». Altération arbitraire de l'initiale de million, d'après la particule latine bi-, « deux fois ».
Rare. Mille millions. Syn. vieilli de Milliard. Selon un décret de 1961, le mot Billion a reçu une nouvelle valeur, à savoir un million de millions (1012), qui n'est pas entrée dans l'usage.". - ↑ 54.0 54.1 "Diccionario Panhispánico de Dudas: millardo" (in es). Real Academia Española. http://buscon.rae.es/dpdI/SrvltConsulta?lema=millardo.
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 "Diccionario Panhispánico de Dudas: billon" (in es). Real Academia Española. http://buscon.rae.es/dpdI/SrvltConsulta?lema=billon.
- ↑ "Diccionario de la lengua española" (in es). Real Academia Española. http://dle.rae.es/?id=5WQzD1r.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 "Italian-English Larousse: bilione". Éditions Larousse. http://www.larousse.com/en/dictionaries/italian-english/bilione/5726.
- ↑ "Switzerland: Words and Phrases". TRAMsoft Gmbh. 29 August 2009. http://www.about.ch/culture/languages/words_n_phrases.html#numbers.
- ↑ "Canadian government standards website". Canadian Government. 2010. http://btb.termiumplus.gc.ca/tpv2alpha/alpha-eng.html?lang=eng&i=&index=frt&__index=frt&srchtxt=billion&comencsrch.x=12&comencsrch.y=10.
- ↑ "billion". Granddictionnaire.com. 13 May 2013. http://www.granddictionnaire.com/ficheOqlf.aspx?Id_Fiche=8872290.
- ↑ "Taalkommissie se reaksie op biljoen, triljoen" (in af). Naspers: Media24. http://152.111.1.88/argief/berigte/beeld/2008/02/20/B1/14/01milbiltril.html.
- ↑ "'Groen boek': mooiste, beste, gebruikersvriendelikste" (in af). Naspers:Media24. http://152.111.1.87/argief/berigte/dieburger/2009/07/13/SK/9/BBfpistorAWS.html.
- ↑ Gupta, S.V. (2010). Units of measurement: past, present and future: international system of units. Springer. pp. 12 (Section 1.2.8 Numeration). ISBN 978-3642007385. https://books.google.com/books?id=pHiKycrLmEQC&q=crore%20lakh%20arab&pg=PA12. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
- ↑ Foundalis, Harry. "Greek Numbers and Numerals (Ancient and Modern)". http://www.foundalis.com/lan/grknum.htm.
- ↑ "BBC: GCSE Bitesize – The origins of the universe". BBC. http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/edexcel/space/theoriginsoftheuniverserev1.shtml.
External links
 |




