Medicine:Metaphyseal chondrodysplasia Schmid type
From HandWiki
| Schmid metaphyseal chondrodysplasia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MCDS[1] |
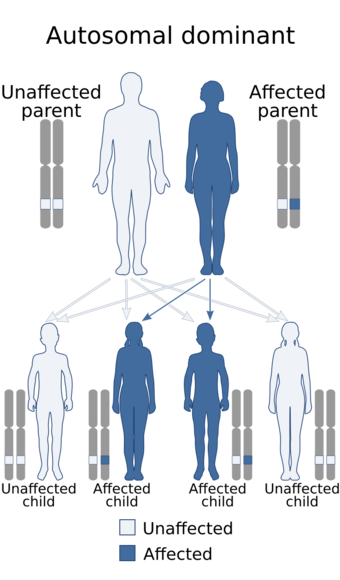 | |
| This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. | |
| Specialty | Orthopedic |
Metaphyseal chondrodysplasia Schmid type is a type of chondrodysplasia associated with a deficiency of collagen, type X, alpha 1.[2][3][4]
Unlike other "rickets syndromes", affected individuals have normal serum calcium, phosphorus, and urinary amino acid levels. Long bones are short and curved, with widened growth plates and metaphyses.[5]
It is named for the German researcher F. Schmid, who characterized it in 1949.[6]
References
- ↑ "Metaphyseal chondrodysplasia Schmid type | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/7029/index. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ↑ "Schmid type of metaphyseal chondrodysplasia and COL10A1 mutations--findings in 10 patients". Am. J. Med. Genet. A 137A (3): 241–8. September 2005. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.30855. PMID 16088909.
- ↑ "COL10A1 nonsense and frame-shift mutations have a gain-of-function effect on the growth plate in human and mouse metaphyseal chondrodysplasia type Schmid". Hum. Mol. Genet. 16 (10): 1201–15. May 2007. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm067. PMID 17403716.
- ↑ "Competency for nonsense-mediated reduction in collagen X mRNA is specified by the 3' UTR and corresponds to the position of mutations in Schmid metaphyseal chondrodysplasia". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82 (3): 786–93. March 2008. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.01.006. PMID 18304492.
- ↑ Benson, Michael. "Children's Orthopaedics and Fractures". Springer. p. 93.
- ↑ Schmid, F. Beitrag zur Dysostosis enchondralis metaphysarea. Mschr. Kinderheilk. 97: 393-397, 1949.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

