Physics:Monocline
From HandWiki
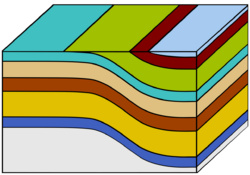
A monocline (or, rarely, a monoform) is a step-like fold in rock strata consisting of a zone of steeper dip within an otherwise horizontal or gently dipping sequence.
Formation

Monoclines may be formed in several different ways (see diagram)
- By differential compaction over an underlying structure, particularly a large fault at the edge of a basin due to the greater compactibility of the basin fill, the amplitude of the fold will die out gradually upwards.[1]
- By mild reactivation of an earlier extensional fault during a phase of inversion causing folding in the overlying sequence.[2]
- As a form of fault propagation fold during upward propagation of an extensional fault in basement into an overlying cover sequence.[3]
- As a form of fault propagation fold during upward propagation of a reverse fault in basement into an overlying cover sequence.[4]
Examples
- Waterpocket Fold in Capitol Reef National Park, Utah[5]
- Comb Ridge in southern Utah[6]
- Grandview-Phantom Monocline in Grand Canyon, Arizona[7]
- Grand Hogback in Colorado[8]
- Lebombo Mountains in Southern Africa[9]
- Lapstone Monocline in the Blue Mountains (Australia)[10]
- Beaumaris Monocline in Victoria (Australia)[11]
- Purbeck Monocline on the Isle of Purbeck, Dorset, England[12]
- Fore-Sudetic Monocline, Poland[13]
- Sindh Monocline, Pakistan [14]
- Torres Flexure, southern Brazil [15]
See also
References
- ↑ Skuce, A.G. (1996). "Forward modelling of compaction above normal faults: an example from the Sirte Basin, Libya". in Buchanan, P.G.. Modern Developments in Structural Interpretation, Validation and Modelling. Special Publications. 99. London: Geological Society. pp. 135–146. ISBN 978-1-897799-43-7. http://s-s-consulting.com/pdf_articles/geol%20soc%201996.pdf.
- ↑ Chadwick, R.A. (1993). "Aspects of basin inversion in southern Britain". Journal of the Geological Society 150 (2): 311–322. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.150.2.0311. Bibcode: 1993JGSoc.150..311C. http://jgs.lyellcollection.org/cgi/content/abstract/150/2/311?ijkey=075ea7d0d92cd14125f610d8bc8feed0be8fb091&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha.
- ↑ Willsey, S.P.; Umhoefer, P.J.; Hilley, G.E. (2002). "Early evolution of an extensional monocline by a propagating normal fault: 3D analysis from combined field study and numerical modeling". Journal of Structural Geology 24 (4): 651–669. doi:10.1016/S0191-8141(01)00120-1. Bibcode: 2002JSG....24..651W. http://earthsciences.stanford.edu/research/geomech/Software/publications/Willsey_JSG_2002.pdf. Retrieved 2011-01-09.
- ↑ Finch, E.; Hardy, S.; Gawthorpe, R. (2003). "Discrete element modelling of contractional fault-propagation folding above rigid basement fault blocks". Journal of Structural Geology 25 (4): 515–528. doi:10.1016/S0191-8141(02)00053-6. Bibcode: 2003JSG....25..515F.
- ↑ "Geology". Capitol Reef National Park. National Park Service. 23 December 2017. https://www.nps.gov/care/learn/nature/geology.htm.
- ↑ "Comb Ridge, Utah" (in en). 2019-11-24. https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/145913/comb-ridge-utah.
- ↑ Abbott, Lon; Cook, Terri (2004). Hiking the Grand Canyon's Geology. Seattle: The Mountaineers Books. pp. 99–114. ISBN 978-0-89886-895-1.
- ↑ Murray, Frederick N. (1967). "Jointing in Sedimentary Rocks along the Grand Hogback Monocline, Colorado". The Journal of Geology 75 (3): 340–350. doi:10.1086/627261. Bibcode: 1967JG.....75..340M.
- ↑ Klausen, M.B. (2009). "The Lebombo monocline and associated feeder dyke swarm: Diagnostic of a successful and highly volcanic rifted margin?". Tectonophysics 468 (1–4): 42–62. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2008.10.012. Bibcode: 2009Tectp.468...42K.
- ↑ "L001 : Lapstone Monocline". Heritage places and items. Office of Environment and Heritage, Government of New South Wales. http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/heritageapp/ViewHeritageItemDetails.aspx?ID=1170643.
- ↑ "61. Beaumaris Cliffs 3 - Monocline". Sites of Geological and Geomorphological Significance. Agriculture Victoria. 8 June 2017. http://vro.agriculture.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/portregn.nsf/pages/port_lf_sig_sites_beaumaris3.
- ↑ Nowell, D.A.G. (1997). "Structures affecting the coast around Lulworth Cove, Dorset and syn-sedimentary Wealden faulting". Proceedings of the Geologists' Association 108 (4): 257–268. doi:10.1016/S0016-7878(97)80011-9.
- ↑ Kluska, B.; Rospondek, M.J.; Marynowski, L.; Schaeffer, P. (2013). "The Werra cyclotheme (Upper Permian, Fore-Sudetic Monocline, Poland): Insights into fluctuations of the sedimentary environment from organic geochemical studies". Applied Geochemistry 29: 73–91. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.09.010. Bibcode: 2013ApGC...29...73K.
- ↑ Memon, A.D.; Siddiqui, I.; Memon, A. (1999). "Tectonics of the Sindh monocline, Pakistan and their effects on hydrocarbons". Mehran University Research Journal of Engineering and Technology 18 (2): 87–96. https://inis.iaea.org/search/searchsinglerecord.aspx?recordsFor=SingleRecord&RN=30035671.
- ↑ Seth, H. (2018). Tectonic Deformation of Flood Basalt Provinces. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-67704-0. https://www.springerprofessional.de/en/tectonic-deformation-of-flood-basalt-provinces/15254768.
 |