Earth:List of tectonic plate interactions
From HandWiki
Short description: Movements of Earth's lithosphere
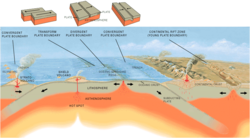
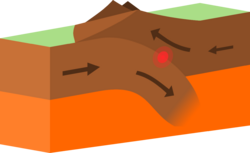
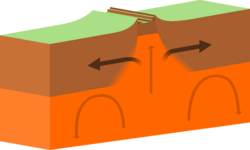
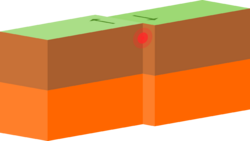
Tectonic plate interactions are classified into three basic types:[1]
- Convergent boundaries are areas where plates move toward each other and collide. These are also known as compressional or destructive boundaries.
- Obduction zones occurs when the continental plate is pushed under the oceanic plate, but this is unusual as the relative densities of the tectonic plates favours subduction of the oceanic plate. This causes the oceanic plate to buckle and usually results in a new mid-ocean ridge forming and turning the obduction into subduction.[citation needed]
- Orogenic belts occur where two continental plates collide and push upwards to form large mountain ranges. These are also known as collision boundaries.
- Subduction zones occur where an oceanic plate meets a continental plate and is pushed underneath it. Subduction zones are marked by oceanic trenches. The descending end of the oceanic plate melts and creates pressure in the mantle, causing volcanoes to form.
- Back-arc basins can form from extension in the overriding plate, in response to the displacement of the subducting slab at some oceanic trenches. This paradoxically results in divergence which was only incorporated in the theory of plate tectonics in 1970, but still results in net destruction when summed over major plate boundaries.[2]
- Divergent boundaries are areas where plates move away from each other, forming either mid-ocean ridges or rift valleys. These are also known as constructive boundaries.
- Transform boundaries occur when two plates grind past each other with only limited convergent or divergent activity.
Convergent boundaries (subduction zones)
- The oceanic Nazca Plate subducts beneath the continental South American Plate at the Peru–Chile Trench.
- Just north of the Nazca Plate, the oceanic Cocos Plate subducts under the Caribbean Plate and forms the Middle America Trench.
- The Cascadia subduction zone is where the oceanic Juan de Fuca, Gorda and Explorer Plates subduct under the continental North American plate.
- The oceanic Pacific Plate subducts under the North American Plate (composed of both continental and oceanic sections) forming the Aleutian Trench.
- The oceanic Pacific Plate subducts beneath the continental Okhotsk Plate at the Japan Trench.
- The oceanic Philippine Sea Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate at the Ryukyu Trench.
- The oceanic Pacific Plate subducts under the oceanic Philippine Sea Plate forming the Mariana Trench.
- The oceanic Philippine Sea Plate is subducting under the Philippine Mobile Belt forming the Philippine Trench and the East Luzon Trench.
- The Eurasian Plate is subducting under the Philippine Mobile Belt at the Manila Trench.
- The Sunda Plate is subducting under the Philippine Mobile Belt at the Negros Trench and the Cotobato Trench.
- The oceanic Australian Plate is subducted beneath the continental Sunda Plate along the Sunda Trench.
- The oceanic Solomon Sea Plate is subducting beneath the South Bismarck Plate and the New Hebrides Plate driven by the mutual movements of the Australian and Pacific plates and local spreading centres.
- The oceanic Pacific Plate is subducting under the Tonga Plate at the Tonga Trench driven by the mutual movements of the Australian and Pacific plates and local spreading centres.
- The oceanic Pacific Plate is subducting under the Kermadec Plate at the Kermadec Trench north and east of New Zealand but the direction of subduction reverses south of the Alpine Fault where the Australian Plate starts subducting under the Pacific Plate at the Puysegur Trench.
- The South American Plate is subducting under the South Sandwich Plate, forming the South Sandwich Trench.
- The oceanic Australian Plate is subducting underneath the New Hebrides Plate forming the New Hebrides Trench.
Back arc basins
- These are often associated with minor plates and include:
- The Tyrrhenian Basin
- The Mariana Trough
- The North Fiji Basin
- The Lau Basin
Orogenic belts
- The most dramatic orogenic belt on the planet is the one between the African Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate on one side (to the south) and the Eurasian Plate on the other side (to the north). This belt runs from New Zealand in the east-south-east, through Indonesia, along the Himalayas, through the Middle East up to the Mediterranean in the west-north-west. It is also called the "Tethyan" Zone, as it constitutes the zone along which the ancient Tethys Ocean was deformed and disappeared. The following mountain belts can be distinguished:
- The Andes orogenic belt is the latest of a series of orogenies along the western margin of the South American Plate.
Divergent boundaries
- The East African Rift (Great Rift Valley) in eastern Africa
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge system separates the North American Plate and the South American Plate in the west from the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate in the east
- The Gakkel Ridge is a slow spreading ridge located in the Arctic Ocean
- The East Pacific Rise, extending from the South Pacific to the Gulf of California
- The Baikal Rift Zone in eastern Russia
- The Red Sea Rift
- The Aden Ridge along the southern shore of the Arabian Peninsula
- The Carlsberg Ridge in the eastern Indian Ocean
- The Woodlark Basin undergoing transition from continental rifting to sea floor spreading to the east of New Guinea
- The Gorda Ridge off the northwest coast of North America
- The Explorer Ridge off the northwest coast of North America
- The Juan de Fuca Ridge off the northwest coast of North America
- The Chile Rise off the southeast Pacific
Transform boundaries
- The San Andreas Fault in California is an active transform boundary. The Pacific Plate (carrying the city of Los Angeles ) is moving northwards with respect to the North American Plate.
- The Queen Charlotte Fault on the Pacific Northwest coast of North America
- The Motagua Fault, which crosses through Guatemala, is a transform boundary between the southern edge of the North American Plate and the northern edge of the Caribbean Plate.
- New Zealand's Alpine Fault is another active transform boundary.
- The Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault which runs through the Jordan River Valley in the Middle East.
- The Owen Fracture Zone along the southeastern boundary of the Arabian Plate.
- The East Anatolian and North Anatolian faults run across much of Turkey and cause large and deadly earthquakes such as the 1999 İzmit earthquake
See also
- Earth:Triple junction – Meeting point of three tectonic plates
References
- ↑ "Tectonic Plates and Plate Boundaries". http://www.gns.cri.nz/Home/Learning/Science-Topics/Earthquakes/Earthquakes-at-a-Plate-Boundary/Tectonic-Plates-and-Plate-Boundaries.
- ↑ Karig, Daniel E (1970). "Ridges and basins of the Tonga-Kermadec island arc system". Journal of Geophysical Research 75 (2): 239–254. doi:10.1029/JB075i002p00239. Bibcode: 1970JGR....75..239K.
 |
