Snub icosidodecadodecahedron
| Snub icosidodecadodecahedron | |
|---|---|
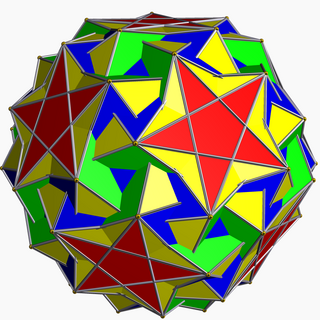
| |
| Type | Uniform star polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 104, E = 180 V = 60 (χ = −16) |
| Faces by sides | (20+60){3}+12{5}+12{5/2} |
| Wythoff symbol | | 5/3 3 5 |
| Symmetry group | I, [5,3]+, 532 |
| Index references | U46, C58, W112 |
| Dual polyhedron | Medial hexagonal hexecontahedron |
| Vertex figure | 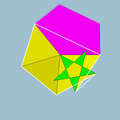 3.3.3.5.3.5/3 |
| Bowers acronym | Sided |
File:Snub icosidodecadodecahedron.stl In geometry, the snub icosidodecadodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U46. It has 104 faces (80 triangles, 12 pentagons, and 12 pentagrams), 180 edges, and 60 vertices.[1] As the name indicates, it belongs to the family of snub polyhedra.
The circumradius of the snub icosidodecadodecahedron with unit edge length is [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{\frac{2\rho - 1}{\rho - 1}}, }[/math] where ρ is the plastic constant, or the unique real root of ρ3 = ρ + 1.[2]
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a snub icosidodecadodecahedron are all the even permutations of [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{array}{crrrc} \Bigl(& \pm\,2\alpha,& \pm\,2\gamma,& \pm\,2\beta &\Bigr), \\ \Bigl(& \pm \bigl[\alpha+\frac{\beta}{\varphi}+\gamma\varphi\bigr],& \pm \bigl[-\alpha\varphi+\beta+\frac{\gamma}{\varphi}\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\frac{\alpha}{\varphi}+\beta\varphi-\gamma\bigr] &\Bigr), \\ \Bigl(& \pm \bigl[-\frac{\alpha}{\varphi}+\beta\varphi+\gamma\bigr],& \pm \bigl[-\alpha+\frac{\beta}{\varphi}-\gamma\varphi\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\alpha\varphi+\beta-\frac{\gamma}{\varphi}\bigr] &\Bigr), \\ \Bigl(& \pm \bigl[-\frac{\alpha}{\varphi}+\beta\varphi-\gamma\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\alpha-\frac{\beta}{\varphi}-\gamma\varphi\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\alpha\varphi+\beta+\frac{\gamma}{\varphi}\bigr] &\Bigr), \\ \Bigl(& \pm \bigl[\alpha+\frac{\beta}{\varphi}-\gamma\varphi\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\alpha\varphi-\beta+\frac{\gamma}{\varphi}\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\frac{\alpha}{\varphi}+\beta\varphi+\gamma\bigr] &\Bigr), \end{array} }[/math]
with an even number of plus signs, where [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi = \tfrac{1+\sqrt 5}{2} }[/math] is the golden ratio; ρ is the plastic ratio, or the unique real solution to ρ3 = ρ + 1; [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \alpha &= \rho + 1 = \rho^3, \\[4pt] \beta &= \varphi^2\rho^4 + \varphi, \\[4pt] \gamma &= \rho^2 + \varphi\rho. \end{align} }[/math] Taking the odd permutations of the above coordinates with an odd number of plus signs gives another form, the enantiomorph of the other one.[3]
Related polyhedra
Medial hexagonal hexecontahedron
| Medial hexagonal hexecontahedron | |
|---|---|
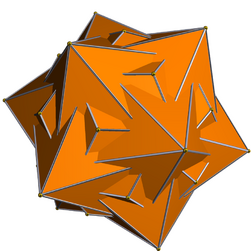
| |
| Type | Star polyhedron |
| Face | 
|
| Elements | F = 60, E = 180 V = 104 (χ = −16) |
| Symmetry group | I, [5,3]+, 532 |
| Index references | DU46 |
| dual polyhedron | Snub icosidodecadodecahedron |
File:Medial hexagonal hexecontahedron.stl The medial hexagonal hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the uniform snub icosidodecadodecahedron.
See also
References
- ↑ Maeder, Roman. "46: snub icosidodecadodecahedron". https://www.mathconsult.ch/static/unipoly/46.html.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Snub icosidodecadodecahedron". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/SnubIcosidodecadodecahedron.html.
- ↑ Skilling, John (1975), "The complete set of uniform polyhedra", Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A 278 (1278): 111–135, doi:10.1098/rsta.1975.0022.
- Wenninger, Magnus (1983), Dual Models, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-54325-5
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Medial hexagonal hexecontahedron". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/MedialHexagonalHexecontahedron.html.
 |

