Social:Puppet state
This article includes a list of references, but its sources remain unclear because it has insufficient inline citations. (July 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Part of the Politics series | ||||||||
| Basic forms of government | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power structure | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Power source | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Power ideology | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Politics portal | ||||||||
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government[1] is a state that is de jure independent but de facto completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.[2] Puppet states have nominal sovereignty, except that a foreign power effectively exercises control through economic or military support.[3] By leaving a local government in existence the outside power evades all responsibility, while at the same time successfully paralysing the local government they tolerate.[1]
Puppet states differ from allies, who choose their actions of their own initiative or in accordance with treaties they have voluntarily entered. Puppet states are forced into legally endorsing actions already taken by a foreign power.
Characteristics
Puppet states are "endowed with the outward symbols of authority",[4] such as a name, flag, anthem, constitution, law codes, motto, and government, but in reality, are appendages of another state which creates,[5] sponsors or otherwise controls the puppet government. International law does not recognise occupied puppet states as legitimate.[6]
Puppet states can cease to be puppets through:
- military defeat of the "master" state (as in Europe and Asia in 1945),
- absorption into the master state (as in the early Soviet Union),
- achievement of independence
Terminology
The term is a metaphor which compares a state or government to a puppet controlled by a puppeteer with strings.[7] The first recorded use of the term "puppet government" was in 1884, in reference to the Khedivate of Egypt.[8] In the Middle Ages, vassal states existed based on delegation of the rule of a country by a king to noble men of lower rank. Since the Peace of Westphalia of 1648, the concept of a nation came into existence where sovereignty was connected more to the people who inhabited the land than to the nobility who owned the land.
Nineteenth-century examples
French revolutionary and Napoleon/Napoleonic clients
The Batavian Republic was established in the Netherlands under French revolutionary protection.
In Italy, the French First Republic encouraged a proliferation of small republics in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, known as sister republics.
In Eastern Europe, Napoleon's First French Empire established the Polish client state of the Duchy of Warsaw.[9]
British Empire
In 1896, Britain established a state in Zanzibar.
Early twentieth-century examples
Established by the German Empire
 Kingdom of Poland (1917–1918) – The Central Powers' forces occupied Russian Congress Poland in 1915 and in 1916, Germany and Austria-Hungary created a Polish monarchy to exploit the occupied territories in an easier way and mobilise the Poles against the Russians (see Polish Legions). In 1918 the state became independent and formed the backbone of the new internationally recognised Second Polish Republic.
Kingdom of Poland (1917–1918) – The Central Powers' forces occupied Russian Congress Poland in 1915 and in 1916, Germany and Austria-Hungary created a Polish monarchy to exploit the occupied territories in an easier way and mobilise the Poles against the Russians (see Polish Legions). In 1918 the state became independent and formed the backbone of the new internationally recognised Second Polish Republic. Kingdom of Lithuania (1918) – After Russia's defeat and the territorial cessions of the 1918 Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, the Germans established a Lithuanian kingdom. However, it became an independent republic with Germany's defeat.
Kingdom of Lithuania (1918) – After Russia's defeat and the territorial cessions of the 1918 Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, the Germans established a Lithuanian kingdom. However, it became an independent republic with Germany's defeat. Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1918) – In 1915, German forces occupied the Russian Courland Governorate and the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk ended the war in the east, so the local ethnic Baltic Germans established a duchy under the German crown in that part of Ober Ost, with a common return of civil administration in favour of the military.[clarification needed] This state was swiftly merged with the Baltic State Duchy and the German-occupied territories of the Russian Empire in Livonia and Estonia, into a multi-ethnic United Baltic Duchy.
Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1918) – In 1915, German forces occupied the Russian Courland Governorate and the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk ended the war in the east, so the local ethnic Baltic Germans established a duchy under the German crown in that part of Ober Ost, with a common return of civil administration in favour of the military.[clarification needed] This state was swiftly merged with the Baltic State Duchy and the German-occupied territories of the Russian Empire in Livonia and Estonia, into a multi-ethnic United Baltic Duchy.
By others
 Provisional National Government of the Southwestern Caucasus and
Provisional National Government of the Southwestern Caucasus and  Provisional Government of Western Thrace were provisional republics established by the Turkish minorities of Thrace and Caucasia after the Ottoman Empire lost its lands in these regions. Both were the products of the Ottoman Intelligence agency, Teşkilat-ı Mahsusa, in terms of organisational structure and organisers, and they had remarkably common[clarification needed] features.[10]
Provisional Government of Western Thrace were provisional republics established by the Turkish minorities of Thrace and Caucasia after the Ottoman Empire lost its lands in these regions. Both were the products of the Ottoman Intelligence agency, Teşkilat-ı Mahsusa, in terms of organisational structure and organisers, and they had remarkably common[clarification needed] features.[10] Donetsk-Krivoy Rog Republic (1918) – The state, remotely controlled by the Russian Soviet Republic,[11] was founded by Joseph Stalin's close friend Fyodor Sergeyev.[12] However, the DKRR was disliked by Vladimir Lenin. The capital of the republic was soon overthrown by the Germans again, and after the Soviet Red Army regained control of the territory, the country was dissolved at Lenin's request.
Donetsk-Krivoy Rog Republic (1918) – The state, remotely controlled by the Russian Soviet Republic,[11] was founded by Joseph Stalin's close friend Fyodor Sergeyev.[12] However, the DKRR was disliked by Vladimir Lenin. The capital of the republic was soon overthrown by the Germans again, and after the Soviet Red Army regained control of the territory, the country was dissolved at Lenin's request. Republic of Central Lithuania (1920–1922) – Dependent and fully incorporated by the Second Polish Republic in 1922.
Republic of Central Lithuania (1920–1922) – Dependent and fully incorporated by the Second Polish Republic in 1922.
World War II
Imperial Japan
During Japan's imperial period, and particularly during the Pacific War (parts of which are considered the Pacific theatre of World War II), the Imperial Japanese government established a number of dependent states.
Nominally sovereign states


- Template:Country data Azad Hind Azad Hind (1943–1945), officially known as Provisional Government of Free India – established by Indian nationalists in Singapore in October 1943 by Subhas Chandra Bose and was in charge of Indian expatriates and military personnel in Japanese Southeast Asia. It had nominal sovereignty over Axis controlled Indian territories and would enjoy the prospective control of Indian territory to be captured in a future invasion of British India. Of the territory of post-independence India, the government took charge of Kohima (after it fell to the Japanese-INA offensive), parts of Manipur that fell to both the Japanese 15th Army and the INA, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The government had diplomatic relationships with eleven countries including Germany, Italy, Japan, Philippines, and the Soviet Union. It was headed by Subhas Chandra Bose, who was the Head of the State and Prime Minister, who was also the Supreme Commander of the Indian National Army. The government had its own cabinet and banks.
- Template:Country data State of Burma State of Burma (1942–1945) – Head of State: Ba Maw
- Template:Country data Second Philippine Republic Second Philippine Republic (1943–1945) – Headed by Jose P. Laurel as President
 Empire of Vietnam (1945) – Emperor Bảo Đại's regime with Trần Trọng Kim as Prime Minister after proclaiming independence from France
Empire of Vietnam (1945) – Emperor Bảo Đại's regime with Trần Trọng Kim as Prime Minister after proclaiming independence from France Kingdom of Kampuchea (1945) – King Norodom Sihanouk's regime with Son Ngoc Thanh as Prime Minister after proclaiming independence from France
Kingdom of Kampuchea (1945) – King Norodom Sihanouk's regime with Son Ngoc Thanh as Prime Minister after proclaiming independence from France Kingdom of Luang Prabang (1945) – King Sisavang Vong's regime with Prince Phetsarath as Prime Minister after proclaiming independence from France
Kingdom of Luang Prabang (1945) – King Sisavang Vong's regime with Prince Phetsarath as Prime Minister after proclaiming independence from France
In China
 Manchukuo (1932–1945) – Set up in Manchuria under the leadership of the last Chinese Emperor, Puyi[13]
Manchukuo (1932–1945) – Set up in Manchuria under the leadership of the last Chinese Emperor, Puyi[13] North Shanxi Autonomous Government (1937–1939) – Formed in northern Shanxi with its capital at Datong on October 15, 1937. The state was then merged into Mengjiang along with the South Chahar Autonomous Government and the Mongol United Autonomous Government.
North Shanxi Autonomous Government (1937–1939) – Formed in northern Shanxi with its capital at Datong on October 15, 1937. The state was then merged into Mengjiang along with the South Chahar Autonomous Government and the Mongol United Autonomous Government. South Chahar Autonomous Government (1937–1939) – Formed in South Chahar with its capital at Kalgan (modern day Zhangjiakou) on September 4, 1937. The state was merged with the North Shanxi Autonomous Government as well as the Mongol United Autonomous Government to create Mengjiang.
South Chahar Autonomous Government (1937–1939) – Formed in South Chahar with its capital at Kalgan (modern day Zhangjiakou) on September 4, 1937. The state was merged with the North Shanxi Autonomous Government as well as the Mongol United Autonomous Government to create Mengjiang. Mongol Military Government (1936–1937) and Mongol United Autonomous Government (1937–1939) – Established in Inner Mongolia as puppet states with local collaborators. This state formed the large basis of what was to become Mengjiang.
Mongol Military Government (1936–1937) and Mongol United Autonomous Government (1937–1939) – Established in Inner Mongolia as puppet states with local collaborators. This state formed the large basis of what was to become Mengjiang.- Template:Country data Mengjiang Mengjiang (1936–1945) – Set up in Inner Mongolia on May 12, 1936, as the Mongol Military Government was renamed in October 1937 as the Mongol United Autonomous Government. On September 1, 1939, the predominantly Han Chinese governments of the South Chahar and North Shanxi Autonomous Governments were merged with the Mongol Autonomous Government, creating the new Mengjiang United Autonomous Government. All of these were headed by De Wang.[14]
 East Hebei Autonomous Council (1935–1938) – A state in northeast China
East Hebei Autonomous Council (1935–1938) – A state in northeast China Great Way (Dadao) Government (1937–1938) – A short-lived regime based in Shanghai. This provisional government was established as a preliminary collaboration state as the Japanese took control of all of Shanghai and advanced towards Nanjing. This was then merged with the Reformed Government of China as well as the Provisional Government of China into the Reorganised Nationalist Government of the Republic of China under the leadership of Wang Jingwei.
Great Way (Dadao) Government (1937–1938) – A short-lived regime based in Shanghai. This provisional government was established as a preliminary collaboration state as the Japanese took control of all of Shanghai and advanced towards Nanjing. This was then merged with the Reformed Government of China as well as the Provisional Government of China into the Reorganised Nationalist Government of the Republic of China under the leadership of Wang Jingwei. Reformed Government of the Republic of China (1938–1940) – First regime established in Nanjing after the Battle of Nanjing. Later fused into the Provisional Government of China
Reformed Government of the Republic of China (1938–1940) – First regime established in Nanjing after the Battle of Nanjing. Later fused into the Provisional Government of China Provisional Government of China (1937–1940) – Incorporated into the Nanjing Nationalist Government on March 30, 1940[15]
Provisional Government of China (1937–1940) – Incorporated into the Nanjing Nationalist Government on March 30, 1940[15]- 23px Reorganised Nationalist Government of the Republic of China (1940–1945) – Established in Nanjing under the leadership of Wang Jingwei[16]
Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy
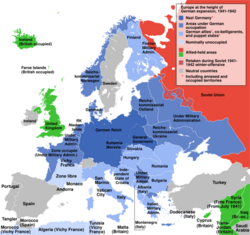
Several European governments under the domination of Germany and Italy during World War II have been described as "puppet régimes". The formal means of control in occupied Europe varied greatly. These states fall into several categories.
Existing states in alliance with Germany and Italy
 Hungarian Government of National Unity (1944–1945) – The pro-Nazi regime of Prime Minister Ferenc Szálasi supported by the pro-German, antisemitic fascist Arrow Cross Party was a German puppet regime. Szálasi was installed by the Germans after Adolf Hitler launched Operation Panzerfaust and had the Hungarian Regent, Admiral Miklós Horthy, removed and placed under house arrest. Horthy was forced to abdicate in favor of Szálasi. Szálasi fought on even after Budapest fell and Hungary was completely overrun.
Hungarian Government of National Unity (1944–1945) – The pro-Nazi regime of Prime Minister Ferenc Szálasi supported by the pro-German, antisemitic fascist Arrow Cross Party was a German puppet regime. Szálasi was installed by the Germans after Adolf Hitler launched Operation Panzerfaust and had the Hungarian Regent, Admiral Miklós Horthy, removed and placed under house arrest. Horthy was forced to abdicate in favor of Szálasi. Szálasi fought on even after Budapest fell and Hungary was completely overrun.
Existing states under German or Italian rule
 Albania under Nazi Germany (1943–1944) – The Kingdom of Albania was an Italian protectorate and puppet regime. Italy invaded Albania in 1939 and ended the rule of King Zog I. King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy added King of Albania to his titles and Zog was exiled. King Victor Emmanuel and Shefqet Bej Verlaci, Albanian Prime Minister and Head of State, controlled the Italian protectorate. Verlaci was replaced by Mustafa Merlika Kruja on December 3, 1941. The Germans occupied Albania when Italy exited the war in 1943 and Ibrahim Bej Biçaku, Mehdi Bej Frashëri, and Rexhep Bej Mitrovica became successive Prime Minister under the Nazis.
Albania under Nazi Germany (1943–1944) – The Kingdom of Albania was an Italian protectorate and puppet regime. Italy invaded Albania in 1939 and ended the rule of King Zog I. King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy added King of Albania to his titles and Zog was exiled. King Victor Emmanuel and Shefqet Bej Verlaci, Albanian Prime Minister and Head of State, controlled the Italian protectorate. Verlaci was replaced by Mustafa Merlika Kruja on December 3, 1941. The Germans occupied Albania when Italy exited the war in 1943 and Ibrahim Bej Biçaku, Mehdi Bej Frashëri, and Rexhep Bej Mitrovica became successive Prime Minister under the Nazis. Vichy France (1940–1942/4) – The Vichy French regime of Philippe Pétain had limited autonomy from 1940 to 1942, and depended heavily on Germany. The Vichy government controlled many of France's colonies and the unoccupied part of France and enjoyed international recognition. In 1942, the Germans occupied the portion of France administered by the Vichy government in Case Anton and installed a new leadership under Pierre Laval, ending much of Vichy France's international legitimacy.
Vichy France (1940–1942/4) – The Vichy French regime of Philippe Pétain had limited autonomy from 1940 to 1942, and depended heavily on Germany. The Vichy government controlled many of France's colonies and the unoccupied part of France and enjoyed international recognition. In 1942, the Germans occupied the portion of France administered by the Vichy government in Case Anton and installed a new leadership under Pierre Laval, ending much of Vichy France's international legitimacy. Monaco (1942–1944) – In 1943, the Italian Army invaded and occupied Monaco, setting up a fascist administration. Shortly thereafter, following Benito Mussolini's deposal in Italy, the German Army occupied Monaco and began deporting the Jewish population. Among them was René Blum, founder of Monaco's Ballet de l'Opera, who died in a Nazi extermination camp.
Monaco (1942–1944) – In 1943, the Italian Army invaded and occupied Monaco, setting up a fascist administration. Shortly thereafter, following Benito Mussolini's deposal in Italy, the German Army occupied Monaco and began deporting the Jewish population. Among them was René Blum, founder of Monaco's Ballet de l'Opera, who died in a Nazi extermination camp.
New states formed to reflect national aspirations
- Template:Country data Slovak Republic (1939–1945) Slovak Republic under the Slovak People's Party (1939–1945) – The Slovak Republic was a German client state. The Slovak People's Party was a clerofascist nationalist movement associated with the Roman Catholic Church. Monsignor Jozef Tiso became president in a nominally independent Slovakia.
 Independent State of Croatia (1941–1945) – The Independent State of Croatia (Nezavisna Država Hrvatska or NDH) was a German and Italian puppet regime. On paper, the NDH was a kingdom under King Tomislav II (Aimone, Duke of Spoleto) of the House of Savoy,[17] but Tomislav II was only a figurehead in Croatia who never exercised any real power, with Ante Pavelić a somewhat independent leader (Poglavnik), though staying obedient to Rome and Berlin.
Independent State of Croatia (1941–1945) – The Independent State of Croatia (Nezavisna Država Hrvatska or NDH) was a German and Italian puppet regime. On paper, the NDH was a kingdom under King Tomislav II (Aimone, Duke of Spoleto) of the House of Savoy,[17] but Tomislav II was only a figurehead in Croatia who never exercised any real power, with Ante Pavelić a somewhat independent leader (Poglavnik), though staying obedient to Rome and Berlin.
States and governments under the control of Germany and Italy
 Hellenic State (1941–1944) – The Hellenic State administration of Georgios Tsolakoglou, Konstantinos Logothetopoulos, and Ioannis Rallis was a "collaborationist" puppet government[18] during the Axis occupation of Greece. Germany, Italy, and Bulgaria occupied different portions of Greece at different times during these regimes.
Hellenic State (1941–1944) – The Hellenic State administration of Georgios Tsolakoglou, Konstantinos Logothetopoulos, and Ioannis Rallis was a "collaborationist" puppet government[18] during the Axis occupation of Greece. Germany, Italy, and Bulgaria occupied different portions of Greece at different times during these regimes. Government of National Salvation (1941–1944) – The government of General Milan Nedić and sometimes known as Nedić's Serbia was a German puppet regime operating in the Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia[19] during the Axis occupation of Serbia.
Government of National Salvation (1941–1944) – The government of General Milan Nedić and sometimes known as Nedić's Serbia was a German puppet regime operating in the Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia[19] during the Axis occupation of Serbia. Lokot Republic (1941–1943) – The Lokot Republic under Konstantin Voskoboinik and Bronislav Kaminski was a semi-autonomous region in Nazi-occupied Russia under a collaborationist administration. The republic covered the area of several raions of Oryol and Kursk Oblasts. It was directly associated with the Russian Liberation People's Army (Russkaya Osvoboditelnaya Narodnaya Armiya or RONA), known as the Kaminski Brigade.
Lokot Republic (1941–1943) – The Lokot Republic under Konstantin Voskoboinik and Bronislav Kaminski was a semi-autonomous region in Nazi-occupied Russia under a collaborationist administration. The republic covered the area of several raions of Oryol and Kursk Oblasts. It was directly associated with the Russian Liberation People's Army (Russkaya Osvoboditelnaya Narodnaya Armiya or RONA), known as the Kaminski Brigade. Norwegian National government (1942–1945) – The occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany started with all authority held by German Reich Commissioner (Reichskommissar) Josef Terboven, who exercised this through the Reichskommissariat Norwegen. The Norwegian pro-German fascist Vidkun Quisling attempted a coup d'état against the Norwegian government during the German invasion on 9 April 1940, but was not appointed by the Germans to head another native government until 1 February 1942.
Norwegian National government (1942–1945) – The occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany started with all authority held by German Reich Commissioner (Reichskommissar) Josef Terboven, who exercised this through the Reichskommissariat Norwegen. The Norwegian pro-German fascist Vidkun Quisling attempted a coup d'état against the Norwegian government during the German invasion on 9 April 1940, but was not appointed by the Germans to head another native government until 1 February 1942.
Italian Social Republic
 Italian Social Republic (1943–1945, known also as the Republic of Salò) – General Pietro Badoglio and King Victor Emmanuel III withdrew Italy from the Axis powers and moved the government to Southern Italy, already controlled by the Allies. In response, the Germans occupied Northern Italy and founded the Italian Social Republic (Repubblica Sociale Italiana or RSI) with Benito Mussolini as its "Head of State" and "Minister of Foreign Affairs". While the RSI government had some trappings of an independent state, it was completely dependent both economically and politically on Germany.
Italian Social Republic (1943–1945, known also as the Republic of Salò) – General Pietro Badoglio and King Victor Emmanuel III withdrew Italy from the Axis powers and moved the government to Southern Italy, already controlled by the Allies. In response, the Germans occupied Northern Italy and founded the Italian Social Republic (Repubblica Sociale Italiana or RSI) with Benito Mussolini as its "Head of State" and "Minister of Foreign Affairs". While the RSI government had some trappings of an independent state, it was completely dependent both economically and politically on Germany.
British examples during and after World War II
The Axis demand for oil and the concern of the Allies that Germany would look to the oil-rich Middle East for a solution, caused the invasion of Iraq by the United Kingdom and the invasion of Iran by the UK and the Soviet Union. Pro-Axis governments in both Iraq and Iran were removed and replaced with Allied-dominated governments.
- Template:Country data Kingdom of Iraq Kingdom of Iraq (1941–1947) – Iraq was important to the United Kingdom because of its position on the route to India. Iraq also could provide strategic oil reserves. But due to the UK's weakness early in the war, Iraq backed away from the pre-war Anglo-Iraqi Alliance. On 1 April 1941, the Hashemite monarchy in Iraq was overthrown by a pro-German coup d'état under Rashid Ali. The Rashid Ali regime began negotiations with the Axis powers and military aid was quickly sent to Mosul via Vichy French-controlled Syria. The Germans provided a squadron of twin-engine fighters and a squadron of medium bombers. The Italians provided a squadron of biplane fighters. In mid-April 1941, a brigade of the 10th Indian Infantry Division landed at Basra (Operation Sabine). On 30 April, British forces at RAF Habbaniya were besieged by a numerically inferior Iraqi force. On 2 May, the British launched pre-emptive airstrikes against the Iraqis and the Anglo-Iraqi War began. By the end of May, the siege of RAF Habbaniya was lifted, Fallujah was taken, Baghdad was surrounded by British forces, and the pro-German government of Rashid Ali collapsed. Rashid Ali and his supporters fled the country. The Hashemite monarchy under King Faisal II was restored, and declared war on the Axis powers in January 1942. British and Commonwealth forces remained in Iraq until 26 October 1947.[20]
 Imperial State of Iran (1941–1943) – German workers in Iran caused both the UK and the Soviet Union to question Iran's neutrality. In addition, Iran's geographical position was important to the Allies. As a result, the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran (Operation Countenance) was launched in August 1941. The following month, Reza Shah Pahlavi was forced to abdicate his throne and went into exile. He was replaced by his son Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, who was willing to declare war on the Axis powers. By January 1942, the UK and the Soviet Union agreed to end their occupation of Iran six months after the end of the war.
Imperial State of Iran (1941–1943) – German workers in Iran caused both the UK and the Soviet Union to question Iran's neutrality. In addition, Iran's geographical position was important to the Allies. As a result, the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran (Operation Countenance) was launched in August 1941. The following month, Reza Shah Pahlavi was forced to abdicate his throne and went into exile. He was replaced by his son Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, who was willing to declare war on the Axis powers. By January 1942, the UK and the Soviet Union agreed to end their occupation of Iran six months after the end of the war.
Soviet examples after 1939
Puppet states later absorbed into the Soviet Union
- Template:Country data Tuvan People's Republic Tuvan People's Republic[disputed ] (1921–1944) – Achieved independence from China by means of local nationalist revolutions only to come under the domination of the Soviet Union in the 1920s. In 1944, Tannu Tuva was absorbed into the USSR.
 Finnish Democratic Republic (1939–1940) – The Finnish Democratic Republic was a short-lived republic in the parts of Finland that were occupied by the Soviet Union during the Winter War. It was also known as the "Terijoki Government", as Terijoki was the first town captured by the Soviets. The Finnish Democratic Republic was intended to govern Finland after Soviet conquest.[21][22]
Finnish Democratic Republic (1939–1940) – The Finnish Democratic Republic was a short-lived republic in the parts of Finland that were occupied by the Soviet Union during the Winter War. It was also known as the "Terijoki Government", as Terijoki was the first town captured by the Soviets. The Finnish Democratic Republic was intended to govern Finland after Soviet conquest.[21][22]- Template:Country data Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic (1940) – In June 1940, the Republic of Latvia was occupied by the Soviet Union and in July a government proclaimed Soviet power.[23] In August 1940, Latvia was illegally annexed by the USSR.[24]
- Template:Country data Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (1940) – In June 1940, the Republic of Lithuania was occupied by the Soviet Union and in July a government proclaimed Soviet power.[23] In August 1940, Lithuania was illegally annexed by the USSR.[24]
- Template:Country data Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic (1940) – In June 1940, the Republic of Estonia was occupied by the Soviet Union and in July a government proclaimed Soviet power.[23][25] In August 1940, Estonia was illegally annexed by the USSR.[24]
Soviet puppet states in Central Asia
 Azerbaijan People's Government (1945–1946) – A short-lived state in Iranian Azerbaijan after World War II.[26]
Azerbaijan People's Government (1945–1946) – A short-lived state in Iranian Azerbaijan after World War II.[26]- Template:Country data Republic of Mahabad Republic of Mahabad (1946–1947) – Officially known as the Republic of Kurdistan and established in several provinces of northwestern Iran, or what is known as Iranian Kurdistan and was a short-lived republic that sought Kurdish autonomy within the limits of the Iranian state. Iran retook control in December and the leaders of the state were executed in March 1947 in Mahabad.
Other states under Soviet influence
Yugoslavia was a communist state closely linked to the Soviet Union, but Yugoslavia retained autonomy within its own borders. After the Tito–Stalin split in 1948, the relationship between the two countries deteriorated significantly. Yugoslavia was expelled from the international organisations of the Eastern Bloc. After Stalin's death and a period of de-Stalinization by Nikita Khrushchev, peace was restored, but the relationship between the two countries was never completely mended. Yugoslavia continued to pursue independent policies and became the founding member of the Non-Aligned Movement.[citation needed]
The Soviet Union continued to exert some influence over the People's Republic of China before the Sino-Soviet split in 1961.
Examples before and during decolonisation
In some cases, the process of decolonisation has been managed by the decolonising power to create a neo-colony, that is a nominally independent state whose economy and politics permits continued foreign domination. Neo-colonies are not normally considered puppet states.[citation needed]
Dutch East Indies
The Netherlands formed several puppet states in the former Dutch East Indies as part of its effort to quell the Indonesian National Revolution.[citation needed]
 East Indonesia
East Indonesia East Java
East Java East Sumatra
East Sumatra Madura
Madura Pasundan
Pasundan South Sumatra
South Sumatra Banjar
Banjar- Bangka Island
- Biliton
- Central Java
- East Kalimantan
 Great Dayak
Great Dayak- Southeast Borneo Federation
 West Kalimantan
West Kalimantan
Congo crisis
Following the Belgian Congo's independence as Congo-Leopoldville in 1960, Belgian interests supported the short-lived breakaway State of Katanga (1960–1963).[27]
East Timor
Indonesia established a Provisional Government of East Timor following its invasion of East Timor in December 1975.[28][29][30]
South Africa's Bantustans

During the 1970s and 1980s, four ethnic Bantustans - some of which were extremely fragmented - called "homelands" by the government of the time, were carved out of South Africa and given nominal sovereignty. Mostly Xhosa people resided in the Ciskei and Transkei, Tswana people in Bophuthatswana, and Venda people in the Venda.[31][unreliable source?]
The principal purpose of these states was to remove South African citizenship from the Xhosa, Tswana, and Venda peoples, and so provide grounds for denying them their democratic rights. All four Bantustans were reincorporated into a democratic South Africa on 27 April 1994, under a new constitution.[citation needed]
The South African authorities established ten Bantustans in South West Africa (present-day Namibia), then illegally occupied by South Africa, in the late 1960s and early 1970s in accordance with the Odendaal Commission. Three of them were granted self-rule. These Bantustans were replaced with separate ethnicity-based governments in 1980.[citation needed]
Post-Cold War examples
Republic of Kuwait
The Republic of Kuwait was a short-lived pro-Iraqi state in the Persian Gulf that only existed three weeks before it was annexed by Iraq in 1990.
Republic of Serbian Krajina
The Republic of Serbian Krajina was a self-proclaimed territory ethnically cleansed[clarification needed] by Serbian forces during the Croatian War (1991–95). It was completely dependent on the Serbian regime of Slobodan Milošević,[32] and was not recognised internationally.
Recent and current examples
Multiple often unrecognised states had been described or accused of being a puppet state of other countries.
United States
 Islamic Republic of Afghanistan – Many, including the Taliban who now comprise the country's current government,[33] considered the former Islamic Republic of Afghanistan to have been a U.S. puppet state.[34]
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan – Many, including the Taliban who now comprise the country's current government,[33] considered the former Islamic Republic of Afghanistan to have been a U.S. puppet state.[34]- Template:Country data Republic of Iraq (Interim Government and Coalition Provisional Authority) – Critics of the Iraqi Interim Government argued that it existed only at the pleasure of the United States and other coalition countries and considered it a U.S. puppet government.[35] This criticism was also extended to politicians active within the Interim Government, with the media suggesting that Ayad Allawi, was Washington's puppet.[36][37] The CPA's economy was dominated by American influence. The CPA began to dismantle Iraq's centrally planned economy. Paul Bremer, chief executive of the CPA, planned to restructure Iraq's state owned economy with free market thinking. Bremer dropped the corporate tax rate from around 45% to a flat tax rate of 15% and allowed foreign corporations to repatriate all profits earned in Iraq. Opposition from senior Iraqi officials, together with the poor security situation, meant that Bremer's privatisation plan was not implemented during his tenure,[38] though his orders remained in place. CPA Order 39 laid out the framework for full privatisation in Iraq and permitted 100% foreign ownership of Iraqi assets and strengthened the positions of foreign businesses and investors. Critics like Naomi Klein argued that CPA Order 39 was designed to create as favourable an environment for foreign investors as possible, which would allow U.S. corporations to dominate Iraq's economy.[39] Also controversial was CPA Order 17 which granted all foreign contractors operating in Iraq immunity from "Iraqi legal process," effectively granting immunity from any kind of suit, civil or criminal, for actions the contractors engaged in within Iraq.[40] CPA Order 49 also provided significant tax cuts for corporations operating within Iraq by reducing the rate from a maximum of 40% to a maximum of just 15% on income. Furthermore, corporations who collaborated with the CPA were exempted from having to pay any tax.[41]
Armenia
 Artsakh – A former self-declared independent state heavily populated by Armenians, it was internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Russian peacekeepers controlled the Lachin corridor that allowed traffic to reach Armenia, on which it was heavily dependent.[42][43]
Artsakh – A former self-declared independent state heavily populated by Armenians, it was internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Russian peacekeepers controlled the Lachin corridor that allowed traffic to reach Armenia, on which it was heavily dependent.[42][43]
China
- [[File:|23x15px|border |alt=|link=]] Wa State – The de facto independent Wa State in Myanmar is considered a puppet state linked to China.[44][45]
Russia

 Abkhazia is considered a puppet state that is dependent on Russia.[46][47] The economy of Abkhazia is heavily integrated with Russia and uses the Russian ruble as its currency. About half of Abkhazia's state budget is financed with aid money from Russia.[48] Most Abkhazians have Russian passports.[49] Russia maintains a 3,500-strong force in Abkhazia with its headquarters in Gudauta, a former Soviet military base on the Black Sea coast[50] and the borders of Abkhazia are protected by Russian paratroopers.[51]
Abkhazia is considered a puppet state that is dependent on Russia.[46][47] The economy of Abkhazia is heavily integrated with Russia and uses the Russian ruble as its currency. About half of Abkhazia's state budget is financed with aid money from Russia.[48] Most Abkhazians have Russian passports.[49] Russia maintains a 3,500-strong force in Abkhazia with its headquarters in Gudauta, a former Soviet military base on the Black Sea coast[50] and the borders of Abkhazia are protected by Russian paratroopers.[51] South Ossetia has declared independence but its ability to maintain independence is solely based on Russian troops deployed on its territory. As South Ossetia is landlocked between Russia and Georgia, from which it seceded, it has relied on Russia for economic and logistical support, as all of its exports and imports and air and road traffic is only with Russia. Former President of South Ossetia Eduard Kokoity claimed he would like South Ossetia eventually to become a part of the Russian Federation through reunification with North Ossetia.[52]
South Ossetia has declared independence but its ability to maintain independence is solely based on Russian troops deployed on its territory. As South Ossetia is landlocked between Russia and Georgia, from which it seceded, it has relied on Russia for economic and logistical support, as all of its exports and imports and air and road traffic is only with Russia. Former President of South Ossetia Eduard Kokoity claimed he would like South Ossetia eventually to become a part of the Russian Federation through reunification with North Ossetia.[52]- The
 Donetsk People's Republic (DPR) and the
Donetsk People's Republic (DPR) and the  Luhansk People's Republic (LPR) were self-proclaimed republics in eastern Ukraine following the fallout from the Euromaidan protests and widely considered to be Russian puppet states.[53][54] Russia annexed the DPR and LPR on September 30, 2022, following the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Luhansk People's Republic (LPR) were self-proclaimed republics in eastern Ukraine following the fallout from the Euromaidan protests and widely considered to be Russian puppet states.[53][54] Russia annexed the DPR and LPR on September 30, 2022, following the Russian invasion of Ukraine.  Transnistria, a conservative holdover of pro-Soviet forces from the Transnistria War, is considered a puppet state sponsored by Russia.[55][56][57][58]
Transnistria, a conservative holdover of pro-Soviet forces from the Transnistria War, is considered a puppet state sponsored by Russia.[55][56][57][58]
Turkey
 Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus – According to the European Court of Human Rights, the Republic of Cyprus remains the sole legitimate government in Cyprus, and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus should be considered as a puppet state under Turkish control.[59][60] Its isolation, Turkish military presence, and heavy dependence on Turkish support mean that Turkey has a high level of control over the country's decision-making processes. That has led to some experts stating that it runs as an effective puppet state of Turkey.[61][62][63] Other experts, however, have pointed out the independent nature of elections and appointments in Northern Cyprus and disputes between the Turkish Cypriot and Turkish governments and concluded that "puppet state" is not an accurate description for Northern Cyprus.[64][65]
Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus – According to the European Court of Human Rights, the Republic of Cyprus remains the sole legitimate government in Cyprus, and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus should be considered as a puppet state under Turkish control.[59][60] Its isolation, Turkish military presence, and heavy dependence on Turkish support mean that Turkey has a high level of control over the country's decision-making processes. That has led to some experts stating that it runs as an effective puppet state of Turkey.[61][62][63] Other experts, however, have pointed out the independent nature of elections and appointments in Northern Cyprus and disputes between the Turkish Cypriot and Turkish governments and concluded that "puppet state" is not an accurate description for Northern Cyprus.[64][65]- Template:Country data Syrian opposition Syrian Interim Government – Originally founded in 2013, before the Turkish occupation of northern Syria, SIG became more dependent of Turkey in recent years and accused of being a puppet government[66] with their Syrian National Army being described as "Turkish-backed",[67] as "funded by Turkey"[68] or as "mercenaries".[69] The SNA was also reported to have being used to support the GNA in the Second Libyan Civil War[68] and to support Azerbaijan in the Second Nagorno-Karabakh War by the Turkish government.[69]
Israel
- Template:Country data Palestinian Authority – The Palestinian Authority, an autonomous administration which exercises partial civil control over the Palestinian enclaves in the Israeli-occupied West Bank, was created in 1994 as a result of the Oslo Accords. It is widely viewed by Palestinians as subservient to Israel, and the two have coordinated security.[70][71]
 Popular Forces administration in the Gaza Strip – after the successful Rafah offensive, the Israeli-backed Popular Forces militia led by Yasser Abu Shabab has had control over parts of the Rafah Governorate. Critics consider it a puppet state of Israel.[72][73]
Popular Forces administration in the Gaza Strip – after the successful Rafah offensive, the Israeli-backed Popular Forces militia led by Yasser Abu Shabab has had control over parts of the Rafah Governorate. Critics consider it a puppet state of Israel.[72][73]
In Yemen
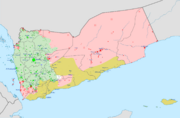
Iran
 Yemen – The Houthi government is considered by some[74] to be a puppet state which is supported by Iran.[75]
Yemen – The Houthi government is considered by some[74] to be a puppet state which is supported by Iran.[75]
Saudi Arabia
 Yemen – The Alimi government is sometimes considered a puppet state which is supported by Saudi Arabia.[76]
Yemen – The Alimi government is sometimes considered a puppet state which is supported by Saudi Arabia.[76]
United Arab Emirates
 Yemen – The Southern Transitional Council is sometimes considered a puppet state which is supported by the United Arab Emirates.[77][78]
Yemen – The Southern Transitional Council is sometimes considered a puppet state which is supported by the United Arab Emirates.[77][78]
See also
- Banana republic
- Buffer state
- Client state
- Co-belligerence
- Failed state
- List of World War II puppet states
- Princely state
- Protectorate
- Satellite state
- Satrapy
- Sphere of influence
- Suzerainty
- Tributary state
- Vassal state
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Morgan Shuster. "The Strangling of Persia: A Story of European Diplomacy and Oriental Intrigue". p. 221. http://www.magepublishers.com/the-strangling-of-persia-a-story-of-european-diplomacy-and-oriental-intrigue/.
- ↑ Compare: Marek, Krystyna (1968). Identity and Continuity of States in Public International Law. Library Droz. p. 178. ISBN 9782600040440. https://books.google.com/books?id=QaF7mnj9igkC. "[...] an allegedly independent, but 'actually' dependent, i.e. puppet State [...]."
- ↑ McNeely, Connie L. (1995). Constructing the Nation-state: International Organization and Prescriptive Action. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-313-29398-6. https://archive.org/details/constructingnati00mcne. Retrieved 13 September 2017. "The term 'puppet state' is used to describe nominal sovereigns under effective foreign control..."
- ↑ Puppet government, Merriam-Webster
- ↑ Raič, David (2002). Statehood and the Law of Self-Determination. Kluwer Law International. p. 81. ISBN 90-411-1890-X. https://books.google.com/books?id=L7UOyPGYBkwC&pg=PA81. Retrieved 13 September 2017. "In most cases, puppet States are created by the occupant during occupation of a State, for the purpose of circumventing the former's international responsibility regarding the violation of the rights of the occupied State."
- ↑ Axis Rule in Occupied Europe: Laws of Occupation, Analysis of Government, Proposals for Redress. The Lawbook Exchange, Ltd.. 2008. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-58477-901-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=y0in2wOY-W0C&pg=PA11. Retrieved 30 June 2019. "The creation of puppet states or of puppet governments does not give them any special status under international law in the occupied territory. Therefore the puppet governments and puppet states have no greater rights in the occupied territory than the occupant himself. Their actions should be considered as actions of the occupant and hence subject to the limitations of the Hague Regulations."
- ↑ Shapiro, Stephen (2003). Ultra Hush-hush. Annick Press. p. 38. ISBN 1-55037-778-7. https://archive.org/details/ultrahushhushesp00step. "Puppet state: a country whose government is being controlled by the government of another country, much as a puppeteer controls the strings on a marionette"
- ↑ Harper, Douglas. "puppet (n.)". http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=puppet&allowed_in_frame=0.
- ↑ Stanley, John (1989). "The Adaptation of the Napoleonic Political Structure in the Duchy of Warsaw (1807–1813)". Canadian Slavonic Papers / Revue Canadienne des Slavistes 31 (2): 128–145. doi:10.1080/00085006.1989.11091911. https://www.jstor.org/stable/40869047.
- ↑ Şirin, İbrahim (February 2014). "İki Hükümet Bir Teşkilat: Garbî Trakya Hükümet-i Muvakkatesi'nden Cenub-î Garbî Kafkas Hükümeti Muvakkate- î Milliyesi'ne" (in tr). History Studies (historystudies.net) 6 (2): 125–142. doi:10.9737/historys1130. ISSN 1309-4688. http://www.historystudies.net/dergi/tar201512901a7.pdf. See translated abstract on page 125.
- ↑ Serhii Plokhii (2022-02-27). "Casus Belli: Did Lenin Create Modern Ukraine?". Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute. https://huri.harvard.edu/news/serhii-plokhii-casus-belli-did-lenin-create-modern-ukraine.
- ↑ Yekaterina Sinelschikova (2021-08-03). "USSR's first AEROWAGON - and the dark story behind it (PHOTOS + VIDEO)". RBTH. https://www.rbth.com/history/334071-ussrs-first-aerowagon-story.
- ↑ Jowett, Phillip S., Rays of The Rising Sun, Armed Forces of Japan’s Asian Allies 1931–45, Volume I: China & Manchuria, 2004. Helion & Co. Ltd., 26 Willow Rd., Solihull, West Midlands, England, pp. 7–36.
- ↑ Jowett, Phillip S., Rays of The Rising Sun, Armed Forces of Japan’s Asian Allies 1931–45, Volume I: China & Manchuria, 2004. Helion & Co. Ltd., 26 Willow Rd., Solihull, West Midlands, England, pp. 49–57, 88–89.
- ↑ Jowett, Phillip S., Rays of The Rising Sun, Armed Forces of Japan’s Asian Allies 1931–45, Volume I: China & Manchuria, 2004. Helion & Co. Ltd., 26 Willow Rd., Solihull, West Midlands, England, pp. 44–47, 85–87.
- ↑ Jowett, Phillip S., Rays of The Rising Sun, Armed Forces of Japan’s Asian Allies 1931–45, Volume I: China & Manchuria, 2004. Helion & Co. Ltd., 26 Willow Rd., Solihull, West Midlands, England, pp. 63–89.
- ↑ Friedman, Francine (2004). Bosnia and Herzegovina: a polity on the brink. Routledge. p. 130. ISBN 0415274354. "...nominally Croatia was ruled by the Italian Duke of Spoleto styled as King"
- ↑ ...managed to see the puppet Greek Prime Minister Ioannis Rallis through @ Sephardi Jewry: A History of the Judeo-Spanish Community, 14th–20th Centuries, p. 168
- ↑ Serbia also had a Nazi puppet regime headed by Milan Nedic @ The Balkanization of the West: The Confluence of Postmodernism and Postcommunism, p. 198
- ↑ Taqoosh, Muhammad Sahil (2015) (in ar). تاريخ العراق (الحديث والمعاصر). Dar Al-Nafaes. pp. 190–191.
- ↑ Tanner, Väinö (1956). The Winter War: Finland Against Russia, 1939–1940, Volume 312. Palo Alto: Stanford University Press. p. 114.
- ↑ Trotter, William (2013). A Frozen Hell: The Russo-Finnish Winter War of 1939–1940. Algonquin Books. pp. 58, 61.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 The Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania (Postcommunist States and Nations) David J. Smith from Front Matter ISBN 0-415-28580-1
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Mälksoo, Lauri (2003). Illegal Annexation and State Continuity: The Case of the Incorporation of the Baltic States by the USSR. Leiden – Boston: Brill. ISBN 90-411-2177-3.
- ↑ Estonia: Identity and Independence: Translated into English (On the Boundary of Two Worlds: Identity, Freedom, and Moral Imagination in the Baltics) Jean-Jacques Subrenat, David Cousins, Alexander Harding, Richard C. Waterhouse. p. 246. ISBN 90-420-0890-3
- ↑ Arfa, Hassan. "Reza Shah Pahlavi: Shah of Iran: Policies as Shah". Encyclopædia Britannica online. Britannica.com. http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-6144/Reza-Shah-Pahlavi. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ↑ Mockler, Antony (1987). The New Mercenaries: The History of the Hired Soldier from the Congo to the Seychelles. New York: Paragon House Publishers. pp. 37–55. ISBN 0-913729-72-8.
- ↑ "Declaration of Independence". http://timor-leste.gov.tl/?p=29&lang=en.
- ↑ Rourke, Alison (29 August 2019). "East Timor: Indonesia's invasion and the long road to independence". The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/aug/30/east-timor-indonesias-invasion-and-the-long-road-to-independence.
- ↑ Febrian, Ramdan (28 November 2019). "A Piece Of The Story Of East Timor's Independence From Portugal Then Indonesia Was "annexed"". VOI. https://voi.id/en/memori/473/a-piece-of-the-story-of-east-timors-independence-from-portugal-then-indonesia-was-annexed.
- ↑ "Trump's Plan for Palestine Looks a Lot Like Apartheid". Foreign Policy. 27 February 2020. https://foreignpolicy.com/2020/02/27/trumps-plan-for-palestine-looks-a-lot-like-apartheid/.
- ↑ Shattuck, John (2009). Freedom on Fire. Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674043480. https://books.google.com/books?id=-t2p8irU2okC&q=krajina+puppet+state&pg=PA186. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- ↑ Crocker, Ryan (17 November 2021). "Afghanistan 2001–2021: U.S. Policy Lessons Learned" (in en). https://carnegieendowment.org/posts/2021/11/afghanistan-2001-2021-us-policy-lessons-learned?lang=en.
- ↑ Dreyfuss, Bob (28 April 2010). "Hamid Karzai: Revenge of the Puppet" (in en). Rolling Stone. https://www.rollingstone.com/politics/politics-news/revenge-of-the-puppet-rolling-stones-2010-story-on-hamid-karzai-193925/. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ↑ "Iraqis rise up against 16 years of 'made in the USA' corruption" (in en). https://www.opendemocracy.net/en/oureconomy/iraqis-rise-against-16-years-made-usa-corruption/.
- ↑ "Iraq's New S.O.B.". Newsweek. July 2004.
- ↑ Dowd, Maureen (26 September 2004). "Dance of the Marionettes". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2004/09/26/opinion/26dowd.html?_r=0.
- ↑ Weisman, Steven R. (2004-01-05). "The Struggle for Iraq: Northern Region; Kurdish Region in Northern Iraq Will Get to Keep Special Status". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2004/01/05/world/struggle-for-iraq-northern-region-kurdish-region-northern-iraq-will-get-keep.html?scp=3&sq=privatization&st=nyt.
- ↑ The Shock Doctrine, Naomi Klein
- ↑ "iraqcoalition.org/~Status_of_Coalition_Rev_with_Annex_A.pdf". http://www.iraqcoalition.org/regulations/20040627_CPAORD_17_Status_of_Coalition__Rev__with_Annex_A.pdf.
- ↑ "iraqcoalition.org/~Tax_Strategy_of_2004_with_Annex_and_Ex_Note.pdf". http://www.iraqcoalition.org/regulations/20040220_CPAORD_49_Tax_Strategy_of_2004_with_Annex_and_Ex_Note.pdf.
- ↑ "The Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict and the Exercise of 'Self-Defense' to Recover Occupied Land". 10 November 2020. https://www.justsecurity.org/73310/the-nagorno-karabakh-conflict-and-the-exercise-of-self-defense-to-recover-occupied-land/.
- ↑ Sassounian, Harut (2 November 2020). "Putin Finally Reveals His Solution to the Artsakh Conflict". https://armenianweekly.com/2020/11/02/putin-finally-reveals-his-solution-to-the-artsakh-conflict/.
- ↑ Slodkowski, Antoni; Lee, Yimou (28 December 2016). "Through reclusive Wa, a China's reach extends into Suu Kyi's Myanmar". Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/article/amp/idUSKBN14H1V8.
- ↑ Linter, Bertil (18 September 2019). "Why Myanmar's Wa always get what they want". https://asiatimes.com/2019/09/why-myanmars-wa-always-get-what-they-want.
- ↑ Coffey, Luke (1 June 2012). "Georgia and Russia: The occupation too many have forgotten". thecommentator.com. http://www.thecommentator.com/article/1272/georgia_and_russia_the_occupation_too_many_have_forgotten.
- ↑ Francis, Céline (2011). Conflict Resolution and Status: The Case of Georgia and Abkhazia (1989–2008). VUBPRESS Brussels University Press. pp. 92–97. ISBN 978-90-5487-899-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=M0HYNMc3cOIC&pg=PA92. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ↑ Nikolaus von Twickel (26 August 2011). "No Clear Frontrunner as Abkhazia Goes to Poll". The Moscow Times. http://www.themoscowtimes.com/news/article/no-clear-frontrunner-as-abkhazia-goes-to-poll/442702.html.
- ↑ "BBC News – Regions and territories: Abkhazia". BBC News (London: BBC). 22 November 2011. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-18175030.
- ↑ "Russian Troops in Abkhazia to Get Air-Conditioned APCs". RIA Novosti. 19 April 2013. http://en.ria.ru/military_news/20130419/180735302.html.
- ↑ Stephen Dowling (May 31, 2018). "Abkhazia: The 'country' living in a Soviet time warp". BBC. https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20190530-abkhazia-the-country-living-in-a-soviet-time-warp.
- ↑ McLaughlin, Daniel (12 September 2008). "Russia insists it has no imperial ambitions for ex-Soviet neighbours". The Irish Times. https://www.irishtimes.com/news/russia-insists-it-has-no-imperial-ambitions-for-ex-soviet-neighbours-1.937994.
- ↑ "Russian Analytical Digest No 214: The Armed Conflict in Eastern Ukraine". https://css.ethz.ch/en/services/digital-library/articles/article.html/7b91e171-a779-43d3-9f24-35e8a88d8974.
- ↑ Tymur Korotkyi, Nataliia Hendel (2018). The Legal Status of the Donetsk and Luhansk "Peoples' Republics". pp. 145–170. doi:10.1007/978-94-6265-222-4_7. ISBN 978-94-6265-221-7. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-6265-222-4_7.
- ↑ Robertson, Dylan C. (5 March 2014). "Is Transnistria the ghost of Crimea's future?". The Christian Science Monitor. https://www.csmonitor.com/World/Europe/2014/0305/Is-Transnistria-the-ghost-of-Crimea-s-future-video.
- ↑ Ivanel, Bogdan (2016). "Puppet States: A Growing Trend of Covert Occupation". Yearbook of International Humanitarian Law Volume 18, 2015. 18. pp. 43–65. doi:10.1007/978-94-6265-141-8_2. ISBN 978-94-6265-140-1. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-6265-141-8_2.
- ↑ "Neopatrimonialism and Regime Endurance in Transnistria". https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/bitstream/handle/10919/35153/Owen_JD_T_2009.pdf.
- ↑ Beaucillon, Charlotte (17 August 2021). "The European Unions position and practice with regard to unilateral and extraterritorial sanctions". Research Handbook on Unilateral and Extraterritorial Sanctions: 110–129. doi:10.4337/9781839107856.00014. ISBN 9781839107856. https://www.elgaronline.com/view/edcoll/9781839107849/9781839107849.00014.xml.
- ↑ Milano, Enrico (2006). Unlawful Territorial Situations in International Law: Reconciling Effectiveness, Legality And Legitimacy. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. p. 146. ISBN 9004149392. https://books.google.com/books?id=4ph_D_aYHNMC&q=puppet+state+trnc&pg=PA146.
- ↑ Terry.D., Gill (2016). Yearbook of International Humanitarian Law 2015. Springer. p. 58. ISBN 9789462651418. https://books.google.com/books?id=ENeSDQAAQBAJ&q=puppet+state+trnc&pg=PA58.
- ↑ James, A. Sovereign statehood: The basis of international society. p. 142 [1]. Taylor and Francis, 1986, 288 pages. ISBN 0-04-320191-1.
- ↑ Kurtulus, E. State sovereignty: concept, phenomenon and ramifications. p. 136 [2]. Macmillan, 2005, 232 pages. ISBN 1-4039-6988-4.
- ↑ Kaczorowska, A. Public International Law. p. 190 [3]. Taylor and Francis, 2010, 944 pages. ISBN 0-415-56685-1.
- ↑ Bartmann, Barry (2004). Bahcheli, Tozun; Bartmann, Barry; Srebrnik, Henry. eds. De Facto States: The Quest for Sovereignty. Routledge. p. 24. ISBN 9781135771218. https://books.google.com/books?id=Gk2QAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA24.
- ↑ Dodd, Clement Henry (1993). The political, social and economic development of Northern Cyprus. Eothen Press. p. 377. ISBN 9780906719183. "In short, the electorate of Northern Cyprus votes freely for its political leaders and gives them substantial support. Nor is Northern Cyprus a Turkish puppet state. Mr Denktas and the Turkish-Cypriot case have a powerful following in Turkey..."
- ↑ Croitoru, Joseph (13 March 2019). "Die kleine Türkei in Nordsyrien". Neue Zürcher Zeitung. https://www.nzz.ch/international/die-kleine-tuerkei-in-nordsyrien-ld.1463513.
- ↑ Gritten, David (29 November 2024). "Syria rebels launch major offensive in north-west and gain territory". BBC. https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cn5w0ype0vlo.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 McKernan, Bethan; Akoush, Hussein (15 January 2020). "Exclusive: 2,000 Syrian fighters deployed to Libya to support government". The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/jan/15/exclusive-2000-syrian-troops-deployed-to-libya-to-support-regime.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 Alasaad, Daham; Perrier, Guillaume; Popp, Maximilian (5 October 2020). "Syrische Söldner im Bergkarabach-Konflikt: Erdogans Schattenkrieger". Der Spiegel. https://www.spiegel.de/ausland/bergkarabach-tuerkische-regierung-schickt-gezielt-syrische-soeldner-a-432ebced-23b0-4fdf-a566-ae830f96905d.
- ↑ "Who Governs the Palestinians? | Council on Foreign Relations" (in en). https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/who-governs-palestinians.
- ↑ DC, Arab Center Washington (2024-11-07). "Fending for Themselves: The Palestinians and the Palestinian Authority" (in en-US). https://arabcenterdc.org/resource/fending-for-themselves-the-palestinians-and-the-palestinian-authority/.
- ↑ Ynetnews (2025-07-27). "In Gaza's Rafah, rebel commander claims war already over—and offers alternative to Hamas" (in en). Ynetnews. https://www.ynetnews.com/article/sjju8qqdge.
- ↑ "Is the UAE involved in Israel's Gaza 'concentration camp' scheme? Here's what we know." (in en-US). 2025-07-31. https://mondoweiss.net/2025/07/is-the-uae-involved-in-israels-gaza-concentration-camp-scheme-heres-what-we-know/.
- ↑ Juneau, Thomas (16 May 2016). "No, Yemen's Houthis actually aren't Iranian puppets" (in en). Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/monkey-cage/wp/2016/05/16/contrary-to-popular-belief-houthis-arent-iranian-proxies/?outputType=amp.
- ↑ "Yemen president calls Houthis 'Iran's puppet'" (in en). Reuters. 28 March 2015. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-yemen-security-hadi-puppet-idUSKBN0MO0G220150328.
- ↑ "ANALYSIS: Saudi Arabia plays puppet master as Yemen slowly breaks apart". Middle East Eye. 2 February 2018. https://www.middleeasteye.net/news/analysis-saudi-arabia-plays-puppet-master-yemen-slowly-breaks-apart.
- ↑ Browning, Noah (11 May 2018). "UAE extends military reach in Yemen and Somalia". https://uk.reuters.com/article/uk-uae-security-yemen-somalia/uae-extends-military-reach-in-yemen-and-somalia-idUKKBN1IC12B.
- ↑ "Yemen on the brink: how the UAE is profiting from the chaos of civil war". The Guardian. 21 December 2018. https://www.theguardian.com/news/2018/dec/21/yemen-uae-united-arab-emirates-profiting-from-chaos-of-civil-war.
Further reading
- Crawford, James (1979). The Creation of States in International Law. ISBN 978-0-199-22842-3
 |
