Step function: Difference between revisions
imported>Dennis Ross linkage |
correction |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Linear combination of indicator functions of real intervals}} | {{Short description|Linear combination of indicator functions of real intervals}} | ||
{{About|a piecewise constant function|the unit step function|Heaviside step function}} | |||
In mathematics, a [[Function (mathematics)|function]] on the [[Real number|real number]]s is called a '''step function''' if it can be written as a [[Finite set|finite]] [[Linear combination|linear combination]] of [[Indicator function|indicator function]]s of [[Interval (mathematics)|interval]]s. Informally speaking, a step function is a [[Piecewise|piecewise]] [[Constant function|constant function]] having only finitely many pieces. | In mathematics, a [[Function (mathematics)|function]] on the [[Real number|real number]]s is called a '''step function''' if it can be written as a [[Finite set|finite]] [[Linear combination|linear combination]] of [[Indicator function|indicator function]]s of [[Interval (mathematics)|interval]]s. Informally speaking, a step function is a [[Piecewise|piecewise]] [[Constant function|constant function]] having only finitely many pieces. | ||
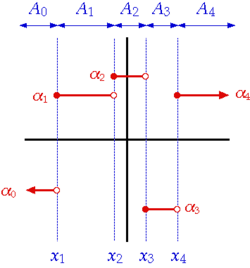
[[Image:StepFunctionExample.png|thumb|right|250px|An example of step functions (the red graph). In this function, each constant subfunction with a function value ''α<sub>i</sub>'' (''i'' = 0, 1, 2, ...) is defined by an interval ''A<sub>i</sub>'' and intervals are distinguished by points ''x<sub>j</sub>'' (''j'' = 1, 2, ...). This particular step function is right-continuous.]] | [[Image:StepFunctionExample.png|thumb|right|250px|An example of step functions (the red graph). In this function, each constant subfunction with a function value ''α<sub>i</sub>'' (''i'' = 0, 1, 2, ...) is defined by an interval ''A<sub>i</sub>'' and intervals are distinguished by points ''x<sub>j</sub>'' (''j'' = 1, 2, ...). This particular step function is [[Continuous function#Directional and semi-continuity|right-continuous]].]] | ||
==Definition and first consequences== | ==Definition and first consequences== | ||
:<math>f(x) = \sum\limits_{i=0}^n \alpha_i \chi_{A_i}(x)</math>, for all real numbers <math>x</math> | :<math>f(x) = \sum\limits_{i=0}^n \alpha_i \chi_{A_i}(x)</math>, for all real numbers <math>x</math> | ||
where <math>n\ge 0</math>, <math>\alpha_i</math> are real numbers, <math>A_i</math> are intervals, and <math>\ | where <math>n\ge 0</math>, <math>\alpha_i</math> are real numbers, <math>A_i</math> are intervals, and <math>\chi_{A_{i}}</math> is the [[Indicator function|indicator function]] of <math>A_{i}</math>: | ||
:<math>\ | :<math>\chi_{A_{i}}(x) = \begin{cases} | ||
1 & \text{if } x \in | 1 & \text{if } x \in A_{i} \\ | ||
0 & \text{if } x \notin | 0 & \text{if } x \notin A_{i} \\ | ||
\end{cases}</math> | \end{cases}</math> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
===Variations in the definition=== | ===Variations in the definition=== | ||
Sometimes, the intervals are required to be right-open<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://mathworld.wolfram.com/StepFunction.html|title = Step Function}}</ref> or allowed to be singleton.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://mathonline.wikidot.com/step-functions|title = Step Functions - Mathonline}}</ref> The condition that the collection of intervals must be finite is often dropped, especially in school mathematics,<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.mathwords.com/s/step_function.htm|title=Mathwords: Step Function}}</ref><ref>https://study.com/academy/lesson/step-function-definition-equation-examples.html | Sometimes, the intervals are required to be right-open<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://mathworld.wolfram.com/StepFunction.html|title = Step Function}}</ref> or allowed to be singleton.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://mathonline.wikidot.com/step-functions|title = Step Functions - Mathonline}}</ref> The condition that the collection of intervals must be finite is often dropped, especially in school mathematics,<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.mathwords.com/s/step_function.htm|title=Mathwords: Step Function}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web | title=Archived copy | url=https://study.com/academy/lesson/step-function-definition-equation-examples.html | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150912010951/http://study.com:80/academy/lesson/step-function-definition-equation-examples.html | access-date=2024-12-16 | archive-date=2015-09-12}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.varsitytutors.com/hotmath/hotmath_help/topics/step-function|title = Step Function}}</ref> though it must still be [[Locally finite collection|locally finite]], resulting in the definition of piecewise constant functions. | ||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
[[Image:Dirac distribution CDF.svg|325px|thumb|The [[ | [[Image:Dirac distribution CDF.svg|325px|thumb|The [[Heaviside step function]] is an often-used step function.]] | ||
* A [[Constant function|constant function]] is a trivial example of a step function. Then there is only one interval, <math>A_0=\mathbb R.</math> | * A [[Constant function|constant function]] is a trivial example of a step function. Then there is only one interval, <math>A_0=\mathbb R.</math> | ||
* The [[Sign function|sign function]] {{math|sgn(''x'')}}, which is −1 for negative numbers and +1 for positive numbers, and is the simplest non-constant step function. | * The [[Sign function|sign function]] {{math|sgn(''x'')}}, which is −1 for negative numbers and +1 for positive numbers, and is the simplest non-constant step function. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
* A step function takes only a finite number of values. If the intervals <math>A_i,</math> for <math>i=0, 1, \dots, n</math> in the above definition of the step function are disjoint and their union is the real line, then <math>f(x)=\alpha_i</math> for all <math>x\in A_i.</math> | * A step function takes only a finite number of values. If the intervals <math>A_i,</math> for <math>i=0, 1, \dots, n</math> in the above definition of the step function are disjoint and their union is the real line, then <math>f(x)=\alpha_i</math> for all <math>x\in A_i.</math> | ||
* The definite integral of a step function is a [[Piecewise linear function|piecewise linear function]]. | * The definite integral of a step function is a [[Piecewise linear function|piecewise linear function]]. | ||
* The Lebesgue integral of a step function <math>\textstyle f = \sum_{i=0}^n \alpha_i \chi_{A_i}</math> is <math>\textstyle \int f\,dx = \sum_{i=0}^n \alpha_i \ell(A_i),</math> where <math>\ell(A)</math> is the length of the interval <math>A</math>, and it is assumed here that all intervals <math>A_i</math> have finite length. In fact, this equality (viewed as a definition) can be the first step in constructing the Lebesgue integral.<ref>{{Cite book | author=Weir, Alan J | title=Lebesgue integration and measure | date= 10 May 1973| publisher=Cambridge University Press, 1973 | isbn=0-521-09751-7 |chapter= 3}}</ref> | * The [[Lebesgue integral]] of a step function <math>\textstyle f = \sum_{i=0}^n \alpha_i \chi_{A_i}</math> is <math>\textstyle \int f\,dx = \sum_{i=0}^n \alpha_i \ell(A_i),</math> where <math>\ell(A)</math> is the length of the interval <math>A</math>, and it is assumed here that all intervals <math>A_i</math> have finite length. In fact, this equality (viewed as a definition) can be the first step in constructing the Lebesgue integral.<ref>{{Cite book | author=Weir, Alan J | title=Lebesgue integration and measure | date= 10 May 1973| publisher=Cambridge University Press, 1973 | isbn=0-521-09751-7 |chapter= 3}}</ref> | ||
* A discrete random variable is sometimes defined as a [[Random variable|random variable]] whose [[Cumulative distribution function|cumulative distribution function]] is piecewise constant.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|title=Introduction to Probability|last=Bertsekas|first=Dimitri P.|date=2002|publisher=Athena Scientific|others=Tsitsiklis, John N., Τσιτσικλής, Γιάννης Ν.|isbn=188652940X|location=Belmont, Mass.|oclc=51441829}}</ref> In this case, it is locally a step function (globally, it may have an infinite number of steps). Usually however, any random variable with only countably many possible values is called a discrete random variable, in this case their cumulative distribution function is not necessarily locally a step function, as infinitely many intervals can accumulate in a finite region. | * A discrete random variable is sometimes defined as a [[Random variable|random variable]] whose [[Cumulative distribution function|cumulative distribution function]] is piecewise constant.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|title=Introduction to Probability|last=Bertsekas|first=Dimitri P.|date=2002|publisher=Athena Scientific|others=Tsitsiklis, John N., Τσιτσικλής, Γιάννης Ν.|isbn=188652940X|location=Belmont, Mass.|oclc=51441829}}</ref> In this case, it is locally a step function (globally, it may have an infinite number of steps). Usually however, any random variable with only countably many possible values is called a discrete random variable, in this case their cumulative distribution function is not necessarily locally a step function, as infinitely many intervals can accumulate in a finite region. | ||
Latest revision as of 20:52, 11 February 2026
In mathematics, a function on the real numbers is called a step function if it can be written as a finite linear combination of indicator functions of intervals. Informally speaking, a step function is a piecewise constant function having only finitely many pieces.
Definition and first consequences
- , for all real numbers
where , are real numbers, are intervals, and is the indicator function of :
In this definition, the intervals can be assumed to have the following two properties:
- The intervals are pairwise disjoint: for
- The union of the intervals is the entire real line:
Indeed, if that is not the case to start with, a different set of intervals can be picked for which these assumptions hold. For example, the step function
can be written as
Variations in the definition
Sometimes, the intervals are required to be right-open[1] or allowed to be singleton.[2] The condition that the collection of intervals must be finite is often dropped, especially in school mathematics,[3][4][5] though it must still be locally finite, resulting in the definition of piecewise constant functions.
Examples

- A constant function is a trivial example of a step function. Then there is only one interval,
- The sign function sgn(x), which is −1 for negative numbers and +1 for positive numbers, and is the simplest non-constant step function.
- The Heaviside function H(x), which is 0 for negative numbers and 1 for positive numbers, is equivalent to the sign function, up to a shift and scale of range (). It is the mathematical concept behind some test signals, such as those used to determine the step response of a dynamical system.
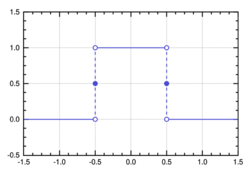
- The rectangular function, the normalized boxcar function, is used to model a unit pulse.
Non-examples
- The integer part function is not a step function according to the definition of this article, since it has an infinite number of intervals. However, some authors[6] also define step functions with an infinite number of intervals.[6]
Properties
- The sum and product of two step functions is again a step function. The product of a step function with a number is also a step function. As such, the step functions form an algebra over the real numbers.
- A step function takes only a finite number of values. If the intervals for in the above definition of the step function are disjoint and their union is the real line, then for all
- The definite integral of a step function is a piecewise linear function.
- The Lebesgue integral of a step function is where is the length of the interval , and it is assumed here that all intervals have finite length. In fact, this equality (viewed as a definition) can be the first step in constructing the Lebesgue integral.[7]
- A discrete random variable is sometimes defined as a random variable whose cumulative distribution function is piecewise constant.[8] In this case, it is locally a step function (globally, it may have an infinite number of steps). Usually however, any random variable with only countably many possible values is called a discrete random variable, in this case their cumulative distribution function is not necessarily locally a step function, as infinitely many intervals can accumulate in a finite region.
See also
- Crenel function
- Piecewise
- Sigmoid function
- Simple function
- Step detection
- Heaviside step function
- Piecewise-constant valuation
References
- ↑ "Step Function". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/StepFunction.html.
- ↑ "Step Functions - Mathonline". http://mathonline.wikidot.com/step-functions.
- ↑ "Mathwords: Step Function". https://www.mathwords.com/s/step_function.htm.
- ↑ "Archived copy". https://study.com/academy/lesson/step-function-definition-equation-examples.html.
- ↑ "Step Function". https://www.varsitytutors.com/hotmath/hotmath_help/topics/step-function.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Bachman, Narici, Beckenstein (5 April 2002). "Example 7.2.2". Fourier and Wavelet Analysis. Springer, New York, 2000. ISBN 0-387-98899-8.
- ↑ Weir, Alan J (10 May 1973). "3". Lebesgue integration and measure. Cambridge University Press, 1973. ISBN 0-521-09751-7.
- ↑ Bertsekas, Dimitri P. (2002). Introduction to Probability. Tsitsiklis, John N., Τσιτσικλής, Γιάννης Ν.. Belmont, Mass.: Athena Scientific. ISBN 188652940X. OCLC 51441829.
 |
