Chemistry:Indium acetylacetonate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(Z)-4-bis[(Z)-1-methyl-3-oxobut-1-enoxy]indiganyloxypent-3-en-2-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H21InO6 | |
| Molar mass | 412.145 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white |
| Density | 1.52 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
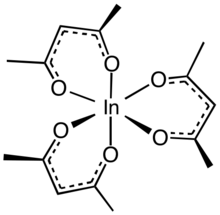
Indium acetylacetonate, also known as In(acac)3, is a compound with formula In(C5H7O2)3. It is a colorless solid. It adopts an octahedral structure.[2]
Uses
Indium acetylacetonate and tin(II) acetylacetonate can be used to prepare indium tin oxide thin films with an atmospheric‐pressure chemical vapor deposition method. The resulting thin films are transparent and conductive, with a thickness of about 200 nanometers.[3] Copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) can also be produced with indium acetylacetonate. Thin-film CIGS solar cells are synthesized with atomic layer chemical vapour deposition (ALCVD) using In(acac)3 and hydrogen sulfide.[4]
References
- ↑ Indium acetylacetonate at American Elements
- ↑ Palenik, G. J.; Dymock, K. R. (1980). "The structure of tris(2,4-pentanedionato)indium(III)". Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry 36 (9): 2059–2063. doi:10.1107/S0567740880007935.
- ↑ "Indium‐tin oxide thin films prepared by chemical vapor deposition"
- ↑ "High-efficiency copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) solar cells with indium sulfide buffer layers deposited by atomic layer chemical vapor deposition (ALCVD)"
 |

