Biology:R.EcoRII
Restriction endonuclease (REase) EcoRII (pronounced "eco R two") is an enzyme of restriction modification system (RM) naturally found in Escherichia coli, a Gram-negative bacteria. Its molecular mass is 45.2 kDa, being composed of 402 amino acids.[1]
Mode of action
EcoRII is a bacterial Type IIE[2] REase that interacts with two[3] or three[4] copies of the pseudopalindromic DNA recognition sequence 5'-CCWGG-3' (W = A or T), one being the actual target of cleavage, the other(s) serving as the allosteric activator(s). EcoRII cuts the target DNA sequence CCWGG, generating sticky ends.[5]
Cut diagram
| Recognition site | Cut results |
5' NNCCWGGNN 3' NNGGWCCNN |
5' NN CCWGGNN 3' NNGGWCC NN |
Structure
| Restriction endonuclease EcoRII, N-terminal | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 crystal structure of restriction endonuclease ecorii mutant r88a | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | EcoRII-N | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09217 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0405 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015300 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1na6 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| EcoRII C terminal | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 crystal structure of restriction endonuclease ecorii mutant r88a | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | EcoRII-C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09019 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0236 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015109 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
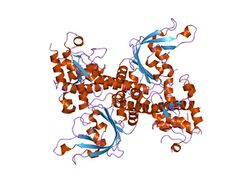
The apo crystal structure of EcoRII mutant R88A (PDB: 1NA6)[6] has been solved at 2.1 Å resolution. The EcoRII monomer has two domains, N-terminal and C-terminal, linked through a hinge loop.
Effector-binding domain
The N-terminal effector-binding domain has an archetypal DNA-binding pseudobarrel fold (SCOP 101936) with a prominent cleft. Structural superposition showed it is evolutionarily related to:
- B3 DNA binding domain (SCOP 117343) from the transcription factors in higher plants (PDB: 1WID)[7]
- C-terminal domain of restriction endonuclease BfiI[8] (PDB: 2C1L)[9]
Catalytic domain
The C-terminal catalytic domain has a typical[10] restriction endonuclease-like fold (SCOP 52979) and belongs to the large (more than 30 members) restriction endonuclease superfamily (SCOP 52980).
Autoinhibition/activation mechanism
Structure-based sequence alignment and site-directed mutagenesis identified the putative PD..D/EXK active sites of the EcoRII catalytic domain dimer that in apo structure are spatially blocked by the N-terminal domains.[6]
See also
- EcoRI, another nuclease enzyme from Escherichia coli.
- EcoRV, another nuclease enzyme from Escherichia coli.
- B3 DNA binding domain from higher plants is evolutionary related to EcoRII
- FokI, another nuclease enzyme from Flavobacterium okeanokoites
External links
- EcoRII in Restriction Enzyme Database REBASE
References
- ↑ Richard J. Roberts. "EcoRII". REBASE - The Restriction Enzyme Database. http://rebase.neb.com/rebase/enz/EcoRII.html.
- ↑ "A nomenclature for restriction enzymes, DNA methyltransferases, homing endonucleases and their genes". Nucleic Acids Res. 31 (7): 1805–12. 2003. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg274. PMID 12654995. PDF[|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ "Imaging DNA loops induced by restriction endonuclease EcoRII. A single amino acid substitution uncouples target recognition from cooperative DNA interaction and cleavage". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (39): 30631–7. 2000. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003904200. PMID 10903314.PDF[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ "Direct visualization of the EcoRII-DNA triple synaptic complex by atomic force microscopy". Biochemistry 46 (39): 11128–36. 2007. doi:10.1021/bi701123u. PMID 17845057.
- ↑ Griffiths, Anthony J. F. (1999). An Introduction to genetic analysis. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-3520-5.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Crystal structure of type IIE restriction endonuclease EcoRII reveals an autoinhibition mechanism by a novel effector-binding fold". J. Mol. Biol. 335 (1): 307–19. 2004. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.030. PMID 14659759.
- ↑ "Solution structure of the B3 DNA binding domain of the Arabidopsis cold-responsive transcription factor RAV1". Plant Cell 16 (12): 3448–59. 2004. doi:10.1105/tpc.104.026112. PMID 15548737.PDF
- ↑ Richard J. Roberts. "BfiI". REBASE - The Restriction Enzyme Database. http://rebase.neb.com/rebase/enz/BfiI.html.
- ↑ "Structure of the metal-independent restriction enzyme BfiI reveals fusion of a specific DNA-binding domain with a nonspecific nuclease". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (44): 15797–802. 2005. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507949102. PMID 16247004. PMC 1266039. Bibcode: 2005PNAS..10215797G. http://bib-pubdb1.desy.de/record/138680/files/2005_Grazulis_15797.pdf. PDF
- ↑ "Topology of Type II REases revisited; structural classes and the common conserved core". Nucleic Acids Research 35 (7): 2227–37. 2007. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm045. PMID 17369272.
 |


