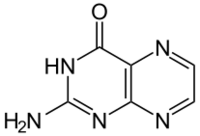
Chemistry:Pterin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
2-Aminopteridin-4(3H)-one
(one of many tautomers; see text) | |
| Other names
Pteridoxamine
Pterine 4-Oxopterin 2-Amino-4-pteridone 2-Amino-4-hydroxypteridine 2-Amino-4-oxopteridine 2-aminopteridin-4-ol 2-Amino-4-pteridinol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5N5O | |
| Molar mass | 163.137 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Pterin is a heterocyclic compound composed of a pteridine ring system, with a "keto group" (a lactam) and an amino group on positions 4 and 2 respectively. It is structurally related to the parent bicyclic heterocycle called pteridine. Pterins, as a group, are compounds related to pterin with additional substituents. Pterin itself is of no biological significance.
Pterins were first discovered in the pigments of butterfly wings[1] (hence the origin of their name, from the Greek pteron (πτερόν),[2] wing) and perform many roles in coloration in the biological world.
Chemistry
Pterins exhibit a wide range of tautomerism in water, beyond what is assumed by just keto-enol tautomerism. For the unsubstituted pterin, at least five tautomers are commonly cited.[3] For 6-methylpterin, seven tautomers are theoretically predicted to be important in solution.[4]
The pteridine ring system contains four nitrogen atoms, reducing its aromaticity to the point that it can be attacked by nucleophile. Pterins can take three oxidation states on the ring system: the unprefixed oxidized form, the 7,8-dihydro semi-reduced form (among other, less stable tautomers), and finally the 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro fully-reduced form. The latter two are more common in biological systems.[5]
Biosynthesis
Pterin rings are either salvaged from existing ones or produced de novo in living organisms. The ring comes from rearrangement of guanosine in bacteria[6] and humans.[7]
Pterin cofactors
Pterin derivatives are common cofactors in all domains of life.
Folates
One important family of pterin derivatives are folates. Folates are pterins that contain p-aminobenzoic acid connected to the methyl group at position 6 of the pteridine ring system (known as pteroic acid) conjugated with one or more L-glutamates. They participate in numerous biological group transfer reactions. Folate-dependent biosynthetic reactions include the transfer of methyl groups from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate to homocysteine to form L-methionine, and the transfer of formyl groups from 10-formyltetrahydrofolate to L-methionine to form N-formylmethionine in initiator tRNAs. Folates are also essential for the biosynthesis of purines and one pyrimidine.
Substituted pteridines are intermediates in the biosynthesis of dihydrofolic acid in many microorganisms.[9] The enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase converts pteridine and 4-aminobenzoic acid to dihydrofolic acid in the presence of glutamate. The enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase is inhibited by sulfonamide antibiotics.
Molybdopterin
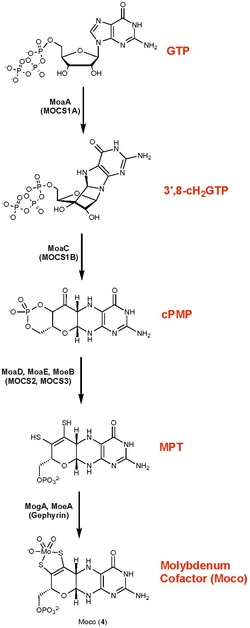
Molybdopterin is a cofactor found in virtually all molybdenum and tungsten-containing proteins.[6] It binds molybdenum to yield redox cofactors involved in biological hydroxylations, reduction of nitrate, and respiratory oxidation.[11]
Molybdopterin biosynthesis does not use the conventional GTPCH-1 pathway. It occurs in four steps:[10]
- the radical-mediated cyclization of nucleotide, guanosine 5′-triphosphate (GTP), to (8S)‑3′,8‐cyclo‑7,8‑dihydroguanosine 5′-triphosphate (3′,8‑cH2GTP),
- the formation of cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate (cPMP) from the 3′,8‑cH2GTP,
- the conversion of cPMP into molybdopterin (MPT),
- the insertion of molybdate into MPT to form Moco (molybdenum cofactor).
Tetrahydrobiopterin
Tetrahydrobiopterin, the major unconjugated pterin in vertebrates, is involved in three families of enzymes that effect hydroxylation. The aromatic amino acid hydroxylases include phenylalanine hydroxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase, and tryptophan hydroxylases. They are involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters catecholamine and serotonin. Tetrahydrobiopterin is also required for the functioning of alkylglycerol monooxygenase, whereby monoalkylglycerols are broken down to glycerol and an aldehyde. In the synthesis of nitric oxide the pterin-dependent nitric oxide synthase converts arginine to its N-hydroxy derivative, which in turn releases nitric oxide.[12]
Other pterins
Tetrahydromethanopterin is a cofactor in methanogenesis, which is a metabolism adopted by many organisms, as a form of anaerobic respiration.[13] It carries the C1 substrate in the course of the formation or production of methane. It is structurally similar to folate.
Pterin pigments
Cyanopterin[15] is a glycosylated version of pteridine of unknown function in cyanobacteria.
See also
References
- ↑ "Colors and pterin pigmentation of pierid butterfly wings". Journal of Insect Physiology 53 (12): 1206–1217. December 2007. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2007.06.016. PMID 17669418. https://pure.rug.nl/ws/files/6712123/2007JInsectPhysiolWijnen.pdf.
- ↑ πτερόν. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project
- ↑ "Correct protonation states and relevant waters = better computational simulations?". Current Pharmaceutical Design 19 (23): 4291–4309. 2013. doi:10.2174/1381612811319230011. PMID 23170888.
- ↑ "Theoretical study on the relative energies of cationic pterin tautomers". Pteridines 26 (1): 13–22. 1 March 2015. doi:10.1515/pterid-2014-0011.
- ↑ "Pterin chemistry and its relationship to the molybdenum cofactor". Coordination Chemistry Reviews 255 (9–10): 1016–1038. May 2011. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.02.010. PMID 21607119.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Pterin function in bacteria". Pteridines 28 (1): 23–36. 1 May 2017. doi:10.1515/pterid-2016-0012. http://iu.tind.io/record/732/files/0448_Pterin-function-in-bacteria.pdf.
- ↑ "Tetrahydrobiopterin: biochemistry and pathophysiology". The Biochemical Journal 438 (3): 397–414. September 2011. doi:10.1042/BJ20110293. PMID 21867484.
- ↑ "Analysis of Catecholamines and Pterins in Inborn Errors of Monoamine Neurotransmitter Metabolism-From Past to Future". Cells 8 (8): 867. August 2019. doi:10.3390/cells8080867. PMID 31405045.
- ↑ Biochemistry (3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. 2004. ISBN 0-471-39223-5.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis and molybdenum enzymes". Annual Review of Plant Biology 57: 623–647. 2006. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105437. PMID 16669776.
- ↑ "Molybdenum cofactors, enzymes and pathways". Nature 460 (7257): 839–847. August 2009. doi:10.1038/nature08302. PMID 19675644. Bibcode: 2009Natur.460..839S.
- ↑ "Three classes of tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent enzymes" (in en). Pteridines 24 (1): 7–11. 2013-01-01. doi:10.1515/pterid-2013-0003. ISSN 2195-4720.
- ↑ "Biochemistry of methanogenesis: a tribute to Marjory Stephenson. 1998 Marjory Stephenson Prize Lecture". Microbiology 144 (9): 2377–2406. September 1998. doi:10.1099/00221287-144-9-2377. PMID 9782487.
- ↑ "Colors and pterin pigmentation of pierid butterfly wings". Journal of Insect Physiology 53 (12): 1206–1217. December 2007. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2007.06.016. PMID 17669418. https://pure.rug.nl/ws/files/6712123/2007JInsectPhysiolWijnen.pdf.
- ↑ "Characterization of a novel unconjugated pteridine glycoside, cyanopterin, in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1410 (1): 61–70. January 1999. doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(98)00175-3. PMID 10076015.
External links
- "Photochemistry and Reactivity of Pteridines Research Group". La Plata, Argentina: Universidad Nacional De La Plata. https://web.archive.org/web/20131202231508/http://grupoargentinodefotobiologia.info/grupos/pteridinas/e_index.html.
 |




