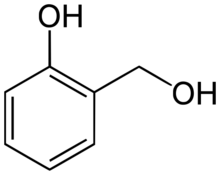
Chemistry:Salicyl alcohol
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(Hydroxymethyl)phenol | |
| Other names
2-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol, Salicain, Diathesin, Saligenin, Saligenol, Salicyl alcohol, α,2-Toluenediol, o-Methylolphenol, 2-Methylolphenol, Salicylic alcohol[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 124.139 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.16 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 86 °C (187 °F; 359 K) |
| Boiling point | 267 °C (513 °F; 540 K) |
| 67g/L at 22 °C[2] | |
| -76.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| HH315Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, H319, H335 | |
| PP261Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 134 °C[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Salicyl alcohol (saligenin) is an organic compound with the formula C
6HOH(CH
2OH. It is a white solid that is used as a precursor in organic synthesis.[3]
Synthesis and applications
Salicyl alcohol is produced by the hydroxymethylation of phenol using formaldehyde:[4]
- C
6H
5OH + CH
2O → C
6H
4OH(CH
2OH
Air oxidation of salicyl alcohol gives salicylaldehyde.
- C
6H
4OH(CH
2OH + O → C
6H
4OH(CHO) +H
2O
Chemical sweeteners are formed by acetal formation with e.g. isovanillin (Cmp4).[5]
Salicyl alcohol appears as a pharmacophore in several notable β2-adrenoceptor agonists (e.g. salbutamol), as well as in synthetic estrone analogs, e.g. CID:22940780 or CID:154236944.
Biosynthesis
Salicyl alcohol is the precursor of salicylic acid.[6] It is formed from salicin by enzymatic hydrolysis by Salicyl-alcohol beta-D-glucosyltransferase or by acid hydrolysis.
See also
- Gastrodigenin (4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol)
- Discovery and development of beta2 agonists
References
- ↑ "2-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol". chemicalbook.com. http://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB9303076.htm.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "salicylic alcohol". chemspider.com. http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.4962.html.
- ↑ Vishwakarma Singh, Mini Porinchu, Punitha Vedantham, Pramod K. Sahu1 (2005). "Synthesis of 9-Spiroepoxy-endo-Tricyclo[5.2.2.0]undeca-4,10-dien-8-one". Organic Syntheses 81: 171. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.081.0171.
- ↑ Maliverney, Christian; Mulhauser, Michel (2000). "Hydroxybenzaldehydes". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0825041813011209.a01. ISBN 978-0-471-48494-3.
- ↑ Bassoli, Angela; Merlini, Lucio; Morini, Gabriella (2002). "Isovanillyl sweeteners. From molecules to receptors". Pure and Applied Chemistry 74 (7): 1181–1187. doi:10.1351/pac200274071181. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ↑ Seo, Eun-Seong; Lee, Jin-Ha; Park, Ji-Young; Kim, Doman; Han, Ho-Jae; Robyt, John F. (2005). "Enzymatic synthesis and anti-coagulant effect of salicin analogs by using the Leuconostoc mesenteroides glucansucrase acceptor reaction". Journal of Biotechnology 117 (1): 31–38. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.10.013. PMID 15831245.
 |

