Astronomy:885 Ulrike
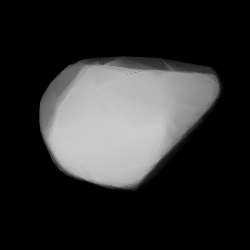 Modelled shape of Ulrike from its lightcurve | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | S. Belyavskyj |
| Discovery site | Simeiz Obs. |
| Discovery date | 23 September 1917 |
| Designations | |
| (885) Ulrike | |
| Named after | Ulrike von Levetzow [2] (friend and love of Goethe) |
| 1917 CX · 1933 QQ 1934 XL · A906 SE 1917 CX · 1906 SE | |
| Minor planet category | main-belt [1][3] · (outer) background [4] · Themis [5] |
| Orbital characteristics [3] | |
| Epoch 31 May 2020 (JD 2459000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 112.98 yr (41,267 d) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 3.6720 AU |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.5253 AU |
| 3.0987 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.1850 |
| Orbital period | 5.45 yr (1,992 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 318.39° |
| Mean motion | 0° 10m 50.52s / day |
| Inclination | 3.3056° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 148.90° |
| 203.78° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | |
| Rotation period | 4.90±0.05 h[9][10] |
| Pole ecliptic latitude | |
| Geometric albedo | |
| C (assumed)[9] | |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 10.7[1][3][7][8] |
885 Ulrike (prov. designation: A917 SV or 1917 CX) is an elongated Themistian asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 23 September 1917, by Soviet astronomer Sergey Belyavsky at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula.[1] The presumed C-type asteroid has a short rotation period of 4.9 hours and measures approximately 33 kilometers (21 miles) in diameter. It was likely named after Ulrike von Levetzow, last love of Goethe.[2]
Orbit and classification
When applying the synthetic hierarchical clustering method (HCM) by Zappalà, Milani and Knežević (AstDys), Ulrike is a core member of the Themis family (602), a large asteroid family of carbonaceous asteroids named after 24 Themis. However, according to another HCM-analysis by Nesvorný, it is a background asteroid.[4][5][12]:23 It orbits the Sun in the outer main-belt at a distance of 2.5–3.7 AU once every 5 years and 5 months (1,992 days; semi-major axis of 3.1 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.19 and an inclination of 3° with respect to the ecliptic.[3] The asteroid was first observed at Lowell Observatory in August 1906. The body's observation arc begins at Heidelberg Observatory on 27 September 1906, more than a decade prior to its official discovery observation at Simeiz.[1]
Naming
This minor planet was allegedly named after Ulrike von Levetzow (1804–1899), a friend and last love of the German poet Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, who met Ulrike during summertime 1821–1823 in Marienbad, Bohemia.[2] After she declined to marry him, Goethe started writing Marienbad Elegy, one of his finest poems. Lutz Schmadel, the author of the Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, considers this interpretation the most likely because the discoverer, who studied at Göttingen University, was an expert in German literature.[2]
Physical characteristics
Ulrike' spectral type is unknown. It is an assumed carbonaceous C-type asteroid,[9] which agrees with the overall spectral type assigned to members of the Themis family.[12]:23
Rotation period
In September 2010, a rotational lightcurve of Ulrike was obtained from photometric observations by John Menke at the Menke Observatory. Lightcurve analysis gave a rotation period of 4.90±0.05 hours with a high brightness variation of 0.55±0.05 magnitude, indicative of an elongated shape ({{{1}}}).[9][10] An alternative period determination of 4.9268±0.0002 hours with an even higher amplitude of 0.72±0.12 was made by Laurent Bernasconi one month later in October 2010 ({{{1}}}).[13] A modeled lightcurve using photometric data from the Lowell Photometric Database gave a sidereal period of 4.906164±0.000001 and two spin axes at (13.0°, −64.0°) and (207.0°, −60.0°) in ecliptic coordinates (λ, β).[11]
Diameter and albedo
According to the survey carried out by the Infrared Astronomical Satellite IRAS, the Japanese Akari satellite, and the NEOWISE mission of NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), Ulrike measures (30.537±0.756), (33.43±5.3) and (44.69±1.06) kilometers in diameter and its surface has an albedo of (0.109±0.025), (0.083±0.034) and (0.047±0.003), respectively.[6][7][8] The Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link adopts the results from IRAS, that is an albedo of 0.083 and a diameter of 33.43 kilometers based on an absolute magnitude of 10.7.[9] The WISE team also published an alternative mean-diameter of (42.20±14.76 km) with an albedo of (0.08±0.06).[4][9]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "885 Ulrike (1917 CX)". Minor Planet Center. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?object_id=885.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Schmadel, Lutz D. (2007). "(885) Ulrike". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 80. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29925-7_886. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3. https://archive.org/details/dictionaryminorp00schm.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 885 Ulrike (A917 SV)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2000885.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "Asteroid 885 Ulrike". Small Bodies Data Ferret. https://sbntools.psi.edu/ferret/SimpleSearch/results.action?targetName=885+Ulrike.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Asteroid 885 Ulrike – Proper Elements". AstDyS-2, Asteroids – Dynamic Site. https://newton.spacedys.com/astdys/index.php?pc=1.1.6&n=885.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Mainzer, A. K.; Bauer, J. M.; Cutri, R. M.; Grav, T.; Kramer, E. A.; Masiero, J. R. et al. (June 2016). "NEOWISE Diameters and Albedos V1.0". NASA Planetary Data System: EAR-A-COMPIL-5-NEOWISEDIAM-V1.0. Bibcode: 2016PDSS..247.....M. https://sbnarchive.psi.edu/pds3/non_mission/EAR_A_COMPIL_5_NEOWISEDIAM_V1_0/data/neowise_mainbelt.tab. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Tedesco, E. F.; Noah, P. V.; Noah, M.; Price, S. D. (October 2004). "IRAS Minor Planet Survey V6.0". NASA Planetary Data System 12: IRAS-A-FPA-3-RDR-IMPS-V6.0. Bibcode: 2004PDSS...12.....T. https://sbnarchive.psi.edu/pds3/iras/IRAS_A_FPA_3_RDR_IMPS_V6_0/data/diamalb.tab. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Usui, Fumihiko; Kuroda, Daisuke; Müller, Thomas G.; Hasegawa, Sunao; Ishiguro, Masateru; Ootsubo, Takafumi et al. (October 2011). "Asteroid Catalog Using Akari: AKARI/IRC Mid-Infrared Asteroid Survey". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 63 (5): 1117–1138. doi:10.1093/pasj/63.5.1117. Bibcode: 2011PASJ...63.1117U. (online, AcuA catalog p. 153)
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 "LCDB Data for (885) Ulrike". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). http://www.minorplanet.info/PHP/generateOneAsteroidInfo.php?AstInfo=885.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Menke, John (December 2005). "Asteroid lightcurve results from Menke Observatory". Minor Planet Bulletin 32 (4): 85–88. ISSN 1052-8091. Bibcode: 2005MPBu...32...85M. http://www.minorplanet.info/MPB/issues/MPB_32-4.pdf.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Ďurech, J.; Hanuš, J.; Oszkiewicz, D.; Vančo, R. (March 2016). "Asteroid models from the Lowell photometric database". Astronomy and Astrophysics 587: A48. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2016A&A...587A..48D.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Nesvorný, D.; Broz, M.; Carruba, V. (December 2014). "Identification and Dynamical Properties of Asteroid Families". Asteroids IV: 297–321. doi:10.2458/azu_uapress_9780816532131-ch016. Bibcode: 2015aste.book..297N.
- ↑ Behrend, Raoul. "Asteroids and comets rotation curves – (885) Ulrike". Geneva Observatory. http://obswww.unige.ch/~behrend/page3cou.html#000885.
External links
- Lightcurve Database Query (LCDB), at www.minorplanet.info
- Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, Google books
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Geneva Observatory, Raoul Behrend
- Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets (1)-(5000) – Minor Planet Center
- 885 Ulrike at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 885 Ulrike at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |

