Astronomy:2019 BZ3
 Orbit of 2019 BZ3, before and after 2019 flyby with 30 day motion | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | MLS |
| Discovery site | Mount Lemmon Obs. |
| Discovery date | 28 January 2019 (first observed only) |
| Designations | |
| 2019 BZ3 | |
| Minor planet category | NEO · Apollo [1][2] |
| Orbital characteristics [2] | |
| Epoch 27 April 2019 (JD 2458600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 7[2] · 5[1] | |
| Observation arc | 8 days |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 3.6251 AU |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 0.9591 AU |
| 2.2921 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.5815 |
| Orbital period | 3.47 yr (1,268 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 30.064° |
| Mean motion | 0° 17m 2.4s / day |
| Inclination | 10.631° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 127.44° |
| 338.22° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0004575 AU (0.18 LD) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | 6 m (est. at 0.15)[3] |
| Apparent magnitude | 17.9 (brightest)[1] |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 28.8[1] 28.719[2] |
2019 BZ3 is a very small near-Earth asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 6 meters (20 feet) in diameter. It was first observed by the Mount Lemmon Survey on 28 January 2019, just hours after the asteroid's sub-lunar flyby of Earth at less than 0.12 lunar distance.[1][4]
Orbit and classification
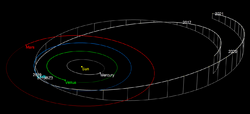
2019 BZ3 is an Apollo asteroid, the largest subgroup of near-Earth objects. It orbits the Sun at a distance of 0.96–3.6 AU once every 3 years and 6 months (1,268 days; semi-major axis of 2.29 AU). Its orbit has a high eccentricity of 0.58 and an inclination of 11° with respect to the ecliptic.[2] The body still has a high orbital uncertainty of 5 and 7, respectively.[1][2] Its observation arc of only 8 days begins with its official first observation at Mount Lemmon Observatory on 28 January 2019.[1]
Close approaches
2019 BZ3 has an Earth minimum orbital intersection distance of 0.000457 AU (68,000 km), which corresponds to 0.18 lunar distances (LD).[2] Due to its very small size, however, 2019 BZ3 is not a potentially hazardous asteroid, which are required to be approximately 140 meters (460 ft) in diameter, that is, to be brighter than an absolute magnitude of 22.
- Flybys
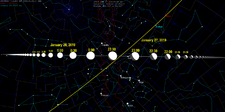
On 27 January 2019 at UTC 23:29, 2019 BZ3 passed Earth at a nominal distance of 48,130 km (0.125 LD) with a relative velocity of 11.37 km. Six hours later, it flew by the Moon at 350400 km.[2][4] The object's next close approaches will occur on 17 December 2025 at a much greater distance of 56 LD (0.143 AU), and on 29 January 2085 at 5.5 LD (0.0142 AU).[5]
Numbering and naming
This minor planet has not yet been numbered by the Minor Planet Center and remains unnamed.[1]
Physical characteristics
2019 BZ3 has an undetermined spectral type. Based on a generic magnitude-to-diameter conversion, the asteroid measures approximately 6 meter in diameter for an assumed albedo of 0.15 and absolute magnitude 28.8.[3] The estimated diameter may vary between 5 and 10 meters depending on whether an albedo for a dark carbonaceous (0.05) or a bright stony (0.25) asteroid is assumed.[3]
See also
- List of asteroid close approaches to Earth in 2019
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "2019 BZ3". Minor Planet Center. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?object_id=2019+BZ3. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2019 BZ3)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=3838044;cad=1. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Asteroid Size Estimator". CNEOS NASA/JPL. https://cneos.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/ast_size_est.html. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Blašković, Teo (29 January 2019). "Asteroid 2019 BZ3 flew past Earth at 0.13 lunar distances". https://watchers.news/2019/01/29/asteroid-2019-bz3/. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ↑ "Asteroid 2019 BZ3 – Close approaches". AstDyS-2, Asteroids – Dynamic Site. https://newton.spacedys.com/neodys/index.php?pc=1.1.8&n=2019BZ3.
External links
- 2019 BZ3 -- Very small Apollo-class Asteroid, spacereference.org
- 2019 BZ3 Geometry, International Asteroid Warning Network
- MPEC 2019-B142: 2019 BZ3, MPC, 2019 Jan. 29, 12:24 UT
- Near-Earth Object Observations Program, 24 NASA, June 2019
- Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB), query form (info )
- 2019 BZ3 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- 2019 BZ3 at ESA–space situational awareness
- 2019 BZ3 at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |