Astronomy:T Normae
From HandWiki
Short description: Variable star in the constellation Norma
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Norma |
| Right ascension | 1 5h 44m 03.83966s[2] |
| Declination | −54° 59′ 12.5184″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.2-13.6[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M3e-M6e[3] (-M9[4]) |
| U−B color index | +0.76 - +1.09[5] |
| B−V color index | +1.42 - +1.87 |
| Variable type | Mira |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −10.02[2] mas/yr Dec.: −11.55[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.61 ± 1.25[2] mas |
| Distance | 500[6] pc |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.01 - 3.63[6] |
| Details | |
| Luminosity | 760[7] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,234 K[7] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
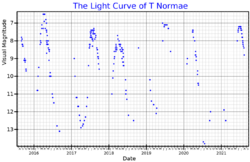
T Normae is a Mira variable star. It is located midway between Eta Normae and Gamma Circini.[8] It ranges from magnitude 6.2 to 13.6 and a period of 244 days.[3] Located around 900 light-years distant, it shines with a luminosity 760 times that of the Sun and has a surface temperature of 3234 K.[7]
References
- ↑ "Download Data". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/data-download.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the New Hipparcos Reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–64. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Otero, Sebastian Alberto (19 March 2011). "T Normae". AAVSO Website. American Association of Variable Star Observers. http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=19963. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ↑ Crowe, Richard A.; Garrison, Robert F. (1988). "The visible spectra of Southern Hemisphere Mira variable stars". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 66: 69. doi:10.1086/191247. Bibcode: 1988ApJS...66...69C.
- ↑ Celis s., L. (1986). "UBVRI photometry of red stars". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 60: 879. doi:10.1086/191103. Bibcode: 1986ApJS...60..879C.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Celis, L. (1995). "Lumnosity attenuation and distances of red giant stars". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 98: 701. doi:10.1086/192175. Bibcode: 1995ApJS...98..701C.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (2012). "Fundamental Parameters and Infrared Excesses of Hipparcos Stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 427 (1): 343–57. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x. Bibcode: 2012MNRAS.427..343M.
- ↑ Arnold, H.J.P.; Doherty, Paul; Moore, Patrick (1999). The Photographic Atlas of the Stars. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. 176. ISBN 978-0-7503-0654-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=YjcvJUfnWBAC&pg=PA148.
 |