Astronomy:HD 143183
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Norma |
| Right ascension | 16h 01m 22.2226s[1] |
| Declination | −54° 08′ 35.6066″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.3 - 8.6[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Red supergiant |
| Spectral type | M3 Ia[3] |
| U−B color index | +0.75[4] |
| B−V color index | +2.10[4] |
| Variable type | LB[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −39.67±0.66[1] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −1.1[5] mas/yr Dec.: 13.1[5] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.5559 ± 0.1021[1] mas |
| Distance | 6,850±650[6] ly (2,100±200[6] pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −7.5[7] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 20[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 1,147[8][lower-alpha 1] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 167,000[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | −0.6[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,443 – 3,605[8] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
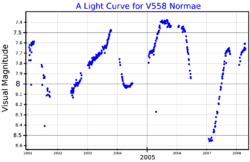
HD 143183 is a red supergiant variable star of spectral type M3Ia in constellation Norma. It is a member of the Norma OB1 association, at a distance of about 2 kiloparsecs. It is one of the most luminous red supergiants with a luminosity over 100,000 times greater than the Sun (L☉), and is as well one of the largest stars with a radius more than a thousand times that of the Sun (R☉). Older studies frequently calculated higher luminosities and radii.[6][10] It has an estimated mass loss rate of 5×10−5 M☉ per year[6] and has been once described as a cool hypergiant.[11] It is surrounded by a dozen early-type stars and a circumstellar nebula which extends 0.12 parsecs (0.39 ly).
HD 143183 is catalogued with the variable star designation V558 Normae as its brightness varies irregularly between apparent magnitudes 7.3 and 8.6.[2]
It is possible that HD 143183 is a spectroscopic binary with an OB+ companion but this is considered doubtful.[6] HD 143183 lies approximately 1' from the 10th-magnitude O-class bright giant CD-53 6363, the second-brightest star in the cluster.
Notes
- ↑ Applying the Stefan-Boltzmann Law with a nominal solar effective temperature of 5,772 K:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{(5772/10^{3.537})^4 * 10^{5.222}} = 1147.23\ R\odot }[/math]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1: B/gcvs. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Messineo, M.; Brown, A. G. A. (2019). "A Catalog of Known Galactic K-M Stars of Class I Candidate Red Supergiants in Gaia DR2". The Astronomical Journal 158 (1): 20. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab1cbd. Bibcode: 2019AJ....158...20M.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Klare, G.; Neckel, T. (1977). "UBV, Hβ and polarization measurements of 1660 southern OB stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 27: 215. Bibcode: 1977A&AS...27..215K.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Høg, E; Fabricius, C; Makarov, V. V; Urban, S; Corbin, T; Wycoff, G; Bastian, U; Schwekendiek, P et al. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 355: L27. Bibcode: 2000A&A...355L..27H.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Moffat, A. F. J. (August 1976). "Mass loss from the M 3 supergiant HD 143183 in a young compact star cluster in Norma". Astronomy and Astrophysics 50 (3): 429–434. Bibcode: 1976A&A....50..429M.
- ↑ Humphreys, R. M (1978). "Studies of luminous stars in nearby galaxies. I. Supergiants and O stars in the Milky Way". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 38: 309. doi:10.1086/190559. Bibcode: 1978ApJS...38..309H.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Dorn-Wallenstein, Trevor Z.; Levesque, Emily M.; Neugent, Kathryn F.; Davenport, James R. A.; Morris, Brett M.; Gootkin, Keyan (2020). "Short Term Variability of Evolved Massive Stars with TESS II: A New Class of Cool, Pulsating Supergiants". The Astrophysical Journal 902 (1): 24. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abb318. Bibcode: 2020ApJ...902...24D.
- ↑ "ASAS All Star Catalogue". The All Sky Automated Survey. http://www.astrouw.edu.pl/asas/?page=aasc.
- ↑ Blum, R. D; Ramirez, Solange V; Sellgren, K; Olsen, K (2003). "Really Cool Stars and the Star Formation History at the Galactic Center". The Astrophysical Journal 597 (1): 323–346. doi:10.1086/378380. Bibcode: 2003ApJ...597..323B.
- ↑ Stickland, D. J. (1985). "IRAS observations of the cool galactic hypergiants". The Observatory 105: 229. Bibcode: 1985Obs...105..229S.
 |


