Astronomy:R Volantis
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox (celestial coordinates) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Volans |
| Right ascension | 07h 05m 36.2081s[2] |
| Declination | −73° 00′ 52.0345″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.78 - 11.50[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | AGB[4] |
| Spectral type | Ce[5] |
| Variable type | Mira[6] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −4.7[7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −14.298[2] mas/yr Dec.: +19.462[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 1.3931 ± 0.0631[2] mas |
| Distance | 2,300 ± 100 ly (720 ± 30 pc) |
| Details | |
| Radius | 41.92+1.23−3.03[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 196±22[8] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,335+128−48[8] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
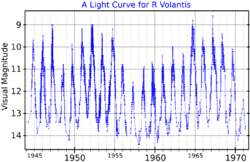
R Volantis is a single variable star in the southern circumpolar constellation Volans. It has an average apparent magnitude of 8.7,[9] making it readily visible in amateur telescopes but not to the naked eye. The object is relatively far at a distance of about 2,300 light years but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −5 km/s.
R Volantis' peculiarity was first observed in 1954 when it was found to have emission lines in its spectrum.[10] Observations from 1955 to 1967 reveal that the star was a probable Mira variable[11] and was given its current designation. However, its nature as a carbon star wasn't discovered until 1968 by Pik-Sin The. In the paper, R Volantis and V1163 Centauri (HD 114586) had their spectrums studied and revealed that the former is a carbon star while the latter is an S-type star.[12]
R Volantis has a stellar classification of Ce,[5] indicating that it is a carbon star with emission lines. It is a giant star on the asymptotic giant branch,[4] meaning that it is generating energy via hydrogen and helium shells around an inert carbon core. As a result, it has expanded to 41.92 times the radius of the Sun and now radiates a luminosity of 196 solar luminosity.[8] R Vol has an effective temperature of 3,335 K, giving a deep red hue.[8]
It fluctuates between magnitude 8.7 and 15.4 and has a period of 445 days.[3]
References
- ↑ "Download Data". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/data-download.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G. Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Vogt, N.; Contreras-Quijada, A.; Fuentes-Morales, I.; Vogt-Geisse, S.; Arcos, C.; Abarca, C.; Agurto-Gangas, C.; Caviedes, M. et al. (10 November 2016). "Determination of Pulsation Periods and Other Parameters of 2875 Stars Classified as MIRA in the All Sky Automated Survey (ASAS)". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 227 (1): 6. doi:10.3847/0067-0049/227/1/6. Bibcode: 2016ApJS..227....6V.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Montez, Rodolfo; Ramstedt, Sofia; Kastner, Joel H.; Vlemmings, Wouter; Sanchez, Enmanuel (22 May 2017). "A Catalog of GALEX Ultraviolet Emission from Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars". The Astrophysical Journal 841 (1): 33. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa704d. Bibcode: 2017ApJ...841...33M.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Henize, K. G. (April 1976). "Observations of southern emission-line stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 30: 491. doi:10.1086/190369. ISSN 0067-0049. Bibcode: 1976ApJS...30..491H.
- ↑ Samus’, N. N.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Durlevich, O. V.; Kireeva, N. N.; Pastukhova, E. N. (January 2017). "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1". Astronomy Reports 61 (1): 80–88. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. ISSN 1063-7729. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ Menzies, John W.; Feast, Michael W.; Whitelock, Patricia A. (5 May 2006). "Carbon-rich Mira variables: radial velocities and distances". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 369 (2): 783–790. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10323.x. ISSN 0035-8711. Bibcode: 2006MNRAS.369..783M.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues 2237. Bibcode: 2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ↑ Bidelman, William P. (November 1954). "Catalogue and Bibliography of Emission-Line Stars of Types Later than B.". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 1: 175. doi:10.1086/190007. ISSN 0067-0049. Bibcode: 1954ApJS....1..175B.
- ↑ Feuchter, A. Ch. (August 1967). "On several statistical characteristics of Mira variables.". The Astronomical Journal 72: 702. doi:10.1086/110295. ISSN 0004-6256. Bibcode: 1967AJ.....72..702F.
- ↑ The, Pik-Sin (February 1968). "The Spectrum of the Variables R Vol and HD 114586". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 80 (472): 104. doi:10.1086/128597. ISSN 0004-6280. Bibcode: 1968PASP...80..104T.
 |