Chemistry:Molybdenite
| Molybdenite | |
|---|---|
 Euhedral molybdenite on quartz, Molly Hill mine, Quebec, Canada. The large crystal is 15 mm across | |
| General | |
| Category | Sulfide mineral |
| Formula (repeating unit) | Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) |
| Strunz classification | 2.EA.30 |
| Crystal system | Common, 2H polytype: hexagonal 3R polytype: trigonal |
| Crystal class | 2H polytype: dihexagonal dipyramidal (6/mmm) 3R polytype: Ditrigonal pyramidal (3m) |
| Space group | 2H polytype: P63/mmc 3R polytype: R3m |
| Unit cell | 2H polytype: a = 3.16 Å, c = 12.3 Å; Z = 2 3R polytype: a = 3.16 Å, c = 18.33 Å; Z = 3 |
| Identification | |
| Color | Black, lead-silvery gray |
| Crystal habit | Thin, platy hexagonal crystals terminated by pinacoidal faces, also as tapering six-sided pyramids that can be truncated by the pinacoids. Also massive, lamellar and in small grains in sulfide ore bodies |
| Cleavage | Perfect on [0001] |
| Tenacity | Lamellae flexible, not elastic |
| Mohs scale hardness | 1–1.5 |
| |re|er}} | Metallic |
| Streak | Bluish gray |
| Diaphaneity | Nearly opaque; translucent in thin flakes |
| Specific gravity | 4.73 |
| Pleochroism | Very strong |
| Fusibility | Infusible (decomposes at 1185 °C) |
| Other characteristics | It has a greasy feel and leaves marks on fingers |
| References | [1][2][3][4][5] |
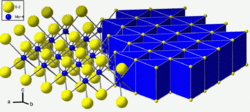
Molybdenite is a mineral of molybdenum disulfide, MoS2. Similar in appearance and feel to graphite, molybdenite has a lubricating effect that is a consequence of its layered structure. The atomic structure consists of a sheet of molybdenum atoms sandwiched between sheets of sulfur atoms. The Mo-S bonds are strong, but the interaction between the sulfur atoms at the top and bottom of separate sandwich-like tri-layers is weak, resulting in easy slippage as well as cleavage planes. Molybdenite crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system as the common polytype 2H and also in the trigonal system as the 3R polytype.[2][3][7]
Description
Occurrence
Molybdenite occurs in high temperature hydrothermal ore deposits. Its associated minerals include pyrite, chalcopyrite, quartz, anhydrite, fluorite, and scheelite. Important deposits include the disseminated porphyry molybdenum deposits at Questa, New Mexico and the Henderson and Climax mines in Colorado. Molybdenite also occurs in porphyry copper deposits of Arizona, Utah, and Mexico.
The element rhenium is always present in molybdenite as a substitute for molybdenum, usually in the parts per million (ppm ) range, but often up to 1–2%. High rhenium content results in a structural variety detectable by X-ray diffraction techniques. Molybdenite ores are essentially the only source for rhenium. The presence of the radioactive isotope rhenium-187 and its daughter isotope osmium-187 provides a useful geochronologic dating technique.
Features
Molybdenite is extremely soft with a metallic luster, and is superficially almost identical to graphite, to the point where it is not possible to positively distinguish between the two minerals without scientific equipment. It marks paper in much the same way as graphite. Its distinguishing feature from graphite is its higher specific gravity, as well as its tendency to occur in a matrix.
Uses
Molybdenite is an important ore of molybdenum, and is the most common source of the metal.[3] While molybdenum is rare in the Earth's crust, molybdenite is relatively common and easy to process, and accounts for much of the metal's economic viability. Molybdenite is purified by froth flotation, and then oxidized to form soluble molybdate. Reduction of ammonium molybdate yields pure molybdenum metal, which is used for fertilizer, as a catalyst, and in battery electrodes. By far the most common use of molybdenum is as an alloy with iron. Ferromolybdenum is an important component of high strength and corrosion-resistant steel.
Semiconductor
Multilayer molybdenite flakes are semiconductors with an indirect bandgap. In contrast, monolayer flakes have a direct gap.[8] In the early years of the 20th century, molybdenite was used in some of the first crude semiconductor diodes, called cat's whisker detectors, which served as a demodulator in early crystal radios. Monolayer molybdenite shows good charge carrier mobility and can be used to create small or low-voltage transistors.[9] The transistors can detect and emit light and may have future use in optoelectronics.[10]
See also
- Powellite (calcium molybdate: CaMoO4)
- Rheniite (rhenium sulfide: ReS2)
- Wulfenite (lead molybdate: PbMoO4)
References
- ↑ Mineralienatlas
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Handbook of Mineralogy
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Mindat.org
- ↑ Webmineral data for Molybdenite
- ↑ Dana's Manual of Mineralogy ISBN:0-471-03288-3
- ↑ Warr, L.N. (2021). "IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols". Mineralogical Magazine 85 (3): 291–320. doi:10.1180/mgm.2021.43. Bibcode: 2021MinM...85..291W.
- ↑ Molybdenite 3R on Mindat
- ↑ Mak, Kin Fai; Lee, Changgu; Hone, James; Shan, Jie; Heinz, Tony F. (24 Sep 2010). "Atomically Thin MoS2: A New Direct-Gap Semiconductor". Physical Review Letters 105 (13). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.136805. http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.136805.
- ↑ "Molybdenite transistor is a first". 8 Feb 2011. http://physicsworld.com/cws/article/news/45056.
- ↑ First light from molybdenite transistors. 19 Apr 2013
External links
{{Navbox |name = Ores |title = Ore minerals, mineral mixtures and ore deposits |listclass = hlist
|group1 = Ores |list1 =
{{Navbox|subgroup
|groupwidth = 7.0em
|group1 = Oxides |list1 =
- Cassiterite (tin)
- Chromite (chromium)
- Coltan (niobium and tantalum)
- Columbite (niobium)
- Hematite (iron)
- Ilmenite (titanium)
- Magnetite (iron)}}
- Pyrolusite (manganese)
- Tantalite (tantalum)
- Uraninite (uranium)
 |