Astronomy:QU Normae
From HandWiki
Short description: Star in the constellation Norma
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Norma |
| Right ascension | 16h 29m 42.32668s[1] |
| Declination | −46° 14′ 35.6022″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.37[2] (5.27 - 5.41[3]) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B1.5 Iap[4] |
| U−B color index | −0.44[2] |
| B−V color index | +0.62[2] |
| Variable type | α Cyg[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −14.80 ± 3.2[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −4.54[1] mas/yr Dec.: −1.51[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 1.79 ± 0.70[1] mas |
| Distance | approx. 1,800 ly (approx. 600 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −7.50[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 43[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 58[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 417,000[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.00[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 17,000[7] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 44[7] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
QU Normae, also known as HR 6131, is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Norma. It is also a variable star, thought to be an α Cyg variable.
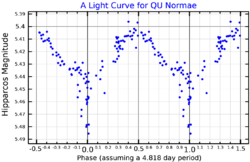
The apparent magnitude of QU Normae varies somewhat irregularly between 5.27 and 5.41. The General Catalogue of Variable Stars quotes a period of 4.818 days,[3] but other research only shows likely periods longer than 10 days.[9]
QU Normae has a spectral type B1.5 Ia, a luminous supergiant that has swollen and cooled off the main sequence. Surface abundances suggest that it has not yet passed through a red supergiant phase.[6] Around 1,820 light-years distant, it shines with a luminosity approximately 417,000 times that of the Sun and has a diameter around 58 times that of the Sun.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues 2237. Bibcode: 2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Chini, R.; Hoffmeister, V. H.; Nasseri, A.; Stahl, O.; Zinnecker, H. (2012). "A spectroscopic survey on the multiplicity of high-mass stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 424 (3): 1925. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21317.x. Bibcode: 2012MNRAS.424.1925C.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Lennon, D. J.; Dufton, P. L. (1986). "Evolutionary effects on the surface abundances of an early-type supergiant". Astronomy and Astrophysics 155: 79. Bibcode: 1986A&A...155...79L.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Fraser, M.; Dufton, P. L.; Hunter, I.; Ryans, R. S. I. (2010). "Atmospheric parameters and rotational velocities for a sample of Galactic B-type supergiants". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 404 (3): 1306. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16392.x. Bibcode: 2010MNRAS.404.1306F.
- ↑ Wesselink, A. J.; Paranya, K.; Devorkin, K. (1972). "Catalogue of stellar dimensions". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement 7: 257. Bibcode: 1972A&AS....7..257W.
- ↑ Van Leeuwen, F.; Van Genderen, A. M.; Zegelaar, I. (1998). "Hipparcos photometry of 24 variable massive stars (α Cygni variables)". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 128: 117–129. doi:10.1051/aas:1998129. Bibcode: 1998A&AS..128..117V.
- ↑ "Hipparcos Tools Interactive Data Access". ESA. https://www.cosmos.esa.int/web/hipparcos/interactive-data-access.
 |