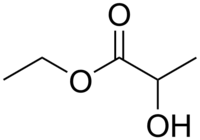
Chemistry:Ethyl lactate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate
| |
| Other names
Ethyl lactate; Lactic acid ethyl ester; 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid ethyl ester; Actylol; Acytol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1192 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 118.132 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.03 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −26 °C (−15 °F; 247 K) |
| Boiling point | 151 to 155 °C (304 to 311 °F; 424 to 428 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Solubility in ethanol and most alcohols |
Miscible |
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
−11.3° |
| -72.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| 3.46 D[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H318, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P271, P280, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P370+378, P403+233, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 46 °C (115 °F; 319 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Lactic acid, Methyl lactate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl lactate, also known as lactic acid ethyl ester, is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CO2CH2CH3. It is the ethyl ester of lactic acid. A colorless liquid, it is a chiral ester. Being naturally derived, it is readily available as a single enantiomer. It is commonly used as a solvent.[4] This compound is considered biodegradable and can be used as a water-rinsible degreaser. Ethyl lactate is found naturally in small quantities in a wide variety of foods including wine, chicken, and various fruits. The odor of ethyl lactate when dilute is mild, buttery, creamy, with hints of fruit and coconut.[5]
Production
Ethyl lactate is produced from biological sources, and can be either the levo (S) form or dextro (R) form, depending on the organism that is the source of the lactic acid. Most biologically sourced ethyl lactate is ethyl (−)-L-lactate (ethyl (S)-lactate). Ethyl lactate is also produced industrially from petrochemical stocks, and this ethyl lactate consists of the racemic mixture of levo and dextro forms.
Applications
Because both enantiomers are found in nature, and because ethyl lactate is easily biodegradable, it is considered to be a "green solvent." Ethyl lactate and its aqueous solutions are used as sustainable media for organic synthesis.[6] Due to its relatively low toxicity, ethyl lactate is used commonly in pharmaceutical preparations, food additives,[7] and fragrances. Ethyl lactate is also used as solvent for nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate, and cellulose ethers.[8]
Further reading
- Jacqueline S. Bennett; Kaitlyn L. Charles; Matthew R. Miner; Caitlin F. Heuberger; Elijah J. Spina; Michael F. Bartels; Taylor Foreman (2009). "Ethyl lactate as a tunable solvent for the synthesis of aryl aldimines". Green Chem. 11 (2): 166–168. doi:10.1039/b817379f.
References
- ↑ Aparicio, Santiago; Alcalde, Rafael (2009). "The green solvent ethyl lactate: an experimental and theoretical characterization". Green Chemistry 11 (1): 65–78. doi:10.1039/b811909k.
- ↑ "Ethyl lactate". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ethyl-lactate#datasheet=LCSS.
- ↑ "ETHYL LACTATE | CAMEO Chemicals | NOAA". https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/700.
- ↑ Stoye, Dieter (2000). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a24_437.
- ↑ Pereira, Carla S. M.; Silva, Viviana M. T. M.; Rodrigues, Alírio E. (2011). "Ethyl lactate as a solvent: Properties, applications and production processes – a review". Green Chemistry 13 (10): 2658. doi:10.1039/C1GC15523G.
- ↑ Dolzhenko, Anton V. (2020). "Ethyl lactate and its aqueous solutions as sustainable media for organic synthesis" (in en). Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy 18: 100322. doi:10.1016/j.scp.2020.100322. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352554120305611.
- ↑ [1] U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition
- ↑ "Industrial Solvents Handbook" by Ernest W. Flick. 5th Edition. William Andrew Inc., 1998. ISBN:0-8155-1413-1, ISBN:978-0-8155-1413-8
 |


