Astronomy:NGC 6782
| NGC 6781 | |
|---|---|
 A Hubble Space Telescope (HST) image of NGC 6782. | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Pavo |
| Right ascension | 19h 23m 57.935s[1] |
| Declination | −59° 55′ 21.04″[1] |
| Redshift | 0.012462±0.000123[2] |
| Helio radial velocity | 3,736 km/s[3] |
| Distance | 173 Mly (53 Mpc)[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.8[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | (R1R′2)SB(r)a[5] |
| Apparent size (V) | 1′.197 × 0′.814[1] (NIR) |
| Other designations | |
| LEDA 63168, ESO 142-1, 2MASX J19235793-5955210, NGC 6782, PGC 63168[6] | |
NGC 6782 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the southern constellation of Pavo, at a distance of approximately 173 megalight-years from the Milky Way.[3] It was discovered on July 12, 1834 by English astronomer John Herschel. John L. E. Dreyer described it as, "considerably faint, considerably small, round, a little brighter middle, 9th magnitude star to south".[7] The morphological classification of NGC 6782 is (R1R′2)SB(r)a, indicating a barred spiral galaxy with a multiple ring system and tightly-wound spiral arms.[5] It is seen nearly face-on,[8] being inclined by an angle of 27.2°±0.2° to the line of sight from the Earth.[5]
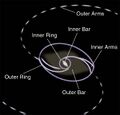
At the galactic core is an almost circular nuclear ring at the inner Lindblad resonance. This is attached to the primary bar, which extends out to a somewhat pointy, diamond-shaped inner ring. It is actually a double-barred galaxy, with an interior bar inside the nuclear ring. A pair of faint spiral arms extend out from the inner ring to the outer parts of the galaxy, where it joints a double outer ring system.[5] Both inner rings of the galaxy are undergoing star formation, producing hot OB stars, with little star formation occurring in the remainder.[8]
Gallery
NGC 6782 with legacy survey
See also
- Messier 94 - a similar spiral galaxy
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Skrutskie, Michael F.; Cutri, Roc M.; Stiening, Rae; Weinberg, Martin D.; Schneider, Stephen E.; Carpenter, John M.; Beichman, Charles A.; Capps, Richard W. et al. (1 February 2006). "The Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS)". The Astronomical Journal 131 (2): 1163–1183. doi:10.1086/498708. ISSN 0004-6256. Bibcode: 2006AJ....131.1163S. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2006AJ....131.1163S/abstract.
- ↑ de Vaucouleurs, G. et al. (1976). Second Reference Catalog of Bright Galaxies. Austin: University of Texas Press. ISBN 978-0-292-75509-3.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Crook, Aidan C. et al. (February 2007). "Groups of Galaxies in the Two Micron All Sky Redshift Survey". The Astrophysical Journal 655 (2): 790–813. doi:10.1086/510201. Bibcode: 2007ApJ...655..790C.
- ↑ "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". Results for NGC 6782. http://nedwww.ipac.caltech.edu/.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Lin, Lien-Hsuan et al. (September 2008). "Hydrodynamical Simulations of the Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 6782". The Astrophysical Journal 684 (2): 1048–1061. doi:10.1086/590247. Bibcode: 2008ApJ...684.1048L.
- ↑ "NGC 6782". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=NGC+6782.
- ↑ Seligman, Courtney. "NGC Objects: NGC 6750 - 6799". https://cseligman.com/text/atlas/ngc67a.htm#6783.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Eskridge, Paul B. et al. (April 2003). "Ultraviolet-Optical Pixel Maps of Face-on Spiral Galaxies: Clues for Dynamics and Star Formation Histories". The Astrophysical Journal 586 (2): 923–938. doi:10.1086/367820. Bibcode: 2003ApJ...586..923E.
External links
 |