Astronomy:NGC 6884
| Emission nebula | |
|---|---|
| Planetary nebula | |
 | |
| Observation data: J2000 epoch | |
| Right ascension | 20h 10m 23.64012s[1] |
| Declination | +46° 27′ 39.5478″[1] |
| Distance | 12.5 kly (3.830 kpc)[2] ly |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 0.127′[2] |
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Radius | 0.23 ly |
| Designations | PNG 082.1+07.0[3], NGC 6766[4] |
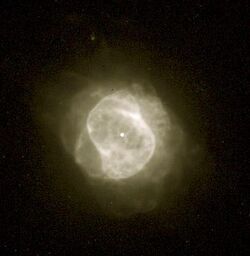
NGC 6884 is a planetary nebula[4] located in the constellation Cygnus, less than a degree to the southwest of the star Ο1 Cygni.[5] It lies at a distance of approximately 12.5 kly from the Sun.[2] The nebula was discovered on May 8, 1883, by American astronomer Edward C. Pickering.[6]
This nebula consists of the cast-off outer atmosphere of an aging star. It is young and compact with a kinematic age of 720 years.[7] The nebula is point-symmetric with arcs forming an S-shaped inner core;[8] the shape is likely explained by bipolar outflows with a velocity of 55 km/s.[7] The core is surrounded by a filamentary ring structure that is inclined at an angle of around 40–45° to the line of sight from the Earth. The core has an overall shape of a prolate ellipsoid with axis ratios of 1.6:1 and is inclined by 40°.[8] The expansion velocity of the nebula ranges over 19–25 km/s. The central star has a temperature of ~100,000 K[7] and a class of WN b?.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Stanghellini, Letizia et al. (December 10, 2008). "The Magellanic Cloud Calibration of the Galactic Planetary Nebula Distance Scale". The Astrophysical Journal 689 (1): 194–202. doi:10.1086/592395. Bibcode: 2008ApJ...689..194S.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Weidmann, W. A.; Gamen, R. (February 2011). "Central stars of planetary nebulae: New spectral classifications and catalogue". Astronomy and Astrophysics 526: 16. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913984. A6. Bibcode: 2011A&A...526A...6W.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "NGC 6884". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=NGC+6884.
- ↑ Sinnott, Roger W.; Perryman, Michael A. C. (1997). Millennium Star Atlas. 3. Sky Publishing Corporation and the European Space Agency. p. 1108. ISBN 0-933346-84-0.
- ↑ Seligman, Courtney. "NGC Objects: NGC 6850 - 6899". https://cseligman.com/text/atlas/ngc68a.htm#6884.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Miranda, Luis F. et al. (March 1999). "Multiwavelength Imaging and Long-Slit Spectroscopy of the Planetary Nebula NGC 6884: The Discovery of a Fast Precessing, Bipolar Collimated Outflow". The Astronomical Journal 117 (3): 1421–1432. doi:10.1086/300774. Bibcode: 1999AJ....117.1421M.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Palen, Stacy et al. (May 2002). "Hubble Space Telescope Expansion Parallaxes of the Planetary Nebulae NGC 6578, NGC 6884, NGC 6891, and IC 2448". The Astronomical Journal 123 (5): 2666–2675. doi:10.1086/339838. Bibcode: 2002AJ....123.2666P.
External links
 |
