Astronomy:(308242) 2005 GO21
 | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Siding Spring Srvy. |
| Discovery site | Siding Spring Obs. |
| Discovery date | 1 April 2005 |
| Designations | |
| (308242) 2005 GO21 | |
| Minor planet category | Aten · NEO · PHA[2] |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 3385 days (9.27 yr) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 1.0093 astronomical unit|AU (150.99 Gm) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 0.49720 AU (74.380 Gm) |
| 0.75324 AU (112.683 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.33992 |
| Orbital period | 0.65 yr (238.8 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 19.462° |
| Mean motion | 1.5077°/day |
| Inclination | 24.926° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 272.70° |
| 156.62° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0452219 AU (6.76510 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | ~1.6 km[3] |
| Rotation period | 11.00 h[2][3] |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 16.5[2] |
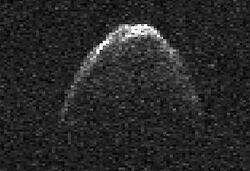
(308242) 2005 GO21 is a large Aten near-Earth asteroid and potentially hazardous object.[2] It has a well determined orbit with an observation arc of 7 years and an uncertainty parameter of 0.[2] It was discovered on 1 April 2005 by the Siding Spring Survey at an apparent magnitude of 18.1 using the 0.5-metre (20 in) Uppsala Southern Schmidt Telescope.[1]
Based on an absolute magnitude of 16.4,[2] the asteroid has an estimated diameter of 1.6 km (within a factor of two).[3] (308242) 2005 GO21 is the largest potentially hazardous asteroid (PHA) discovered in 2005.[4] On 21 June 2012 it passed Earth at a distance of 0.043963 astronomical unit|AU (6,576,800 km; 4,086,600 mi).[5] The 2012 passage was studied with radar using Goldstone and Arecibo.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "MPEC 2005-G31 : 2005 GO21". IAU Minor Planet Center. 2005-04-05. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/mpec/K05/K05G31.html. Retrieved 2012-06-18. (K05G21O)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 308242 (2005 GO21)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2005GO21. Retrieved 7 April 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Dr. Lance A. M. Benner (2012-06-18). "(308242) 2005 GO21 Goldstone Radar Observations Planning". NASA/JPL Asteroid Radar Research. http://echo.jpl.nasa.gov/asteroids/2005GO21/2005GO21_planning.html. Retrieved 2012-06-18.
- ↑ "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine: PHAs and H < 17 (mag)". JPL Solar System Dynamics. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb_query.cgi?obj_group=pha;obj_kind=all;obj_numbered=all;OBJ_field=0;ORB_field=0;c1_group=OBJ;c1_item=Ai;c1_op=%3C;c1_value=17;table_format=HTML;max_rows=100;format_option=comp;c_fields=AcBhBgBjBiBnBsCkCqAi;.cgifields=format_option;.cgifields=obj_kind;.cgifields=obj_group;.cgifields=obj_numbered;.cgifields=ast_orbit_class;.cgifields=table_format;.cgifields=com_orbit_class&query=1&c_sort=AcA. Retrieved 2011-11-20.
- ↑ "JPL Close-Approach Data: 308242 (2005 GO21)". https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2005GO21;cad=1#cad. Retrieved 2012-06-18.
External links
- (308242) 2005 GO21 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- (308242) 2005 GO21 at ESA–space situational awareness
- (308242) 2005 GO21 at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |

