Astronomy:2021 SG
From HandWiki
Short description: Near-Earth asteroid
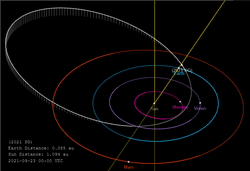 Orbit of 2021 SG | |
| Discovery [1][2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Zwicky Transient Facility |
| Discovery site | Palomar Obs. |
| Discovery date | 17 September 2020 |
| Designations | |
| 2021 SG | |
| ZTF0MtF [3] | |
| Minor planet category | NEO · Apollo [4] |
| Orbital characteristics [4] | |
| Epoch 21 January 2022 (JD 2459600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 7 | |
| Observation arc | 7 days |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.953 AU |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 0.4730 AU |
| 1.713 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.7238 |
| Orbital period | 2.24 yr (818.77 days) |
| Mean anomaly | 76.606° |
| Mean motion | 0° 26m 22.869s / day |
| Inclination | 3.176° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 352.203° |
| 256.579° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.00157 AU (235,000 km) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | 42–94 m [5] |
| Apparent magnitude | 13.4 (discovery) [2] |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 24.01±0.24 [4][1] |
2021 SG is a near-Earth asteroid, with an estimated diameter of 42 to 94 meters, that passed about half a lunar distance from Earth on 16 September 2021. It approached from the direction of the Sun, so it was invisible until a day later.[6] It completes its highly eccentric orbit in 2.24 years. 2021 SG is an Apollo asteroid with a 1.71 AU semimajor axis, and a 0.473 AU perihelion (near Mercury at perihelion) out to a 2.95 AU aphelion (between Mars and Jupiter). With an absolute magnitude (H) of 24.0, it is possibly the largest asteroid to pass within 1 lunar distance of Earth during 2021.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "2021 SG". Minor Planet Center. International Astronomical Union. http://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?object_id=2021+SG. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "MPEC 2021-S24 : 2021 SG". Minor Planet Electronic Circular. Minor Planet Center. 17 September 2021. https://minorplanetcenter.net/mpec/K21/K21S24.html. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ↑ "2021 SG". NEO Exchange. Las Cumbres Observatory. 17 September 2021. https://neoexchange.lco.global/target/78847/. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2021 SG)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=54198375&view=OPC. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ↑ "NEO Earth Close Approaches". Center for Near Earth Asteroid Studies. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://cneos.jpl.nasa.gov/ca/. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ↑ "EarthSky | Asteroid 2021 SG came from the sun's direction". 20 September 2021. https://earthsky.org/space/asteroid-2021-sg-closest-to-earth-sep21-2021/.
External links
- 2021 SG at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |

