Astronomy:4954 Eric
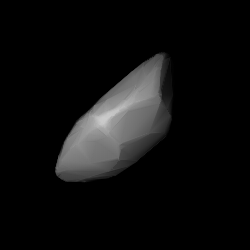 Shape model of Eric from its lightcurve | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Brian P. Roman |
| Discovery site | Palomar Obs. |
| Discovery date | 23 September 1990 |
| Designations | |
| (4954) Eric | |
| 1990 SQ | |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 14681 days (40.19 yr) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.8993 astronomical unit|AU (433.73 Gm) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 1.10393 AU (165.146 Gm) |
| 2.0016 AU (299.44 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.44848 |
| Orbital period | 2.83 yr (1034.4 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 314.18° |
| Mean motion | 0° 20m 52.944s / day |
| Inclination | 17.4461° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 358.52° |
| 52.429° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.194843 AU (29.1481 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 10.8 km |
| Mean radius | 5.4 km |
| Rotation period | 12.052[3] hours |
| S (SMASSII) | |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 12.6 |
4954 Eric (prov. designation: 1990 SQ) is an eccentric, stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Amor group, approximately 11 kilometers (6.8 miles) in diameter. It was discovered by American astronomer Brian Roman at Palomar Observatory on 23 September 1990.[4] The asteroid was named after its discoverer's son, Eric Roman.
It is the largest near-Earth asteroid discovered since 3552 Don Quixote in 1983.[2] On 2007 October 11 the asteroid passed 0.2865 AU (42,860,000 km; 26,630,000 mi) from Earth.[4] It currently makes closer approaches to Mars than it does Earth. The asteroid has a rotation period of 12.05 hours.[3]
Other large near-Earth asteroids include 1036 Ganymed (32 km), 3552 Don Quixote (19 km), 433 Eros (17 km), and 1866 Sisyphus (8.5 km).[2][5]

References
- ↑ "(4954) Eric = 1990 SQ". Minor Planet Center. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?utf8=%E2%9C%93&object_id=4954.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine: asteroids and NEOs and H < 13 (mag)". JPL Solar System Dynamics. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb_query.cgi?obj_group=neo;obj_kind=ast;obj_numbered=all;OBJ_field=0;ORB_field=0;c1_group=OBJ;c1_item=Ai;c1_op=%3C;c1_value=13;table_format=HTML;max_rows=100;format_option=comp;c_fields=AcBhBgBjBiBnBsCkCqAiAp;.cgifields=format_option;.cgifields=obj_kind;.cgifields=obj_group;.cgifields=obj_numbered;.cgifields=ast_orbit_class;.cgifields=table_format;.cgifields=com_orbit_class&query=1&c_sort=ApA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hanus, J.; Durech, J.; Broz, M.; Marciniak, A.; Warner, B. D.; Pilcher, F. et al. (March 2013). "Asteroids' physical models from combined dense and sparse photometry and scaling of the YORP effect by the observed obliquity distribution". Astronomy and Astrophysics 551: 16. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201220701. Bibcode: 2013A&A...551A..67H.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "JPL Close-Approach Data: 4954 Eric (1990 SQ)". https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=4954;cad=1#cad.
- ↑ Philip A. Bland; Elaine A. Moore; Ian Wright; Mike Widdowson (2004). An Introduction to the Solar System. Cambridge University Press. p. 394. ISBN 978-0-521-54620-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=CsX_E3gDaIoC&pg=PA394.
External links
- 4954 Eric at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- 4954 Eric at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |
