Astronomy:882 Swetlana
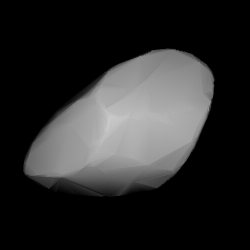 Modelled shape of Swetlana from its lightcurve | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | G. Neujmin |
| Discovery site | Simeiz Obs. |
| Discovery date | 15 August 1917 |
| Designations | |
| (882) Swetlana | |
| Named after | unknown [2] |
| A917 PB · 1967 TQ 1917 CM | |
| Minor planet category | |
| Orbital characteristics [3] | |
| Epoch 31 May 2020 (JD 2459000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 102.46 yr (37,424 d) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 3.9571 AU |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.2903 AU |
| 3.1237 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.2668 |
| Orbital period | 5.52 yr (2,016 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 151.70° |
| Mean motion | 0° 10m 42.6s / day |
| Inclination | 6.1256° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 256.30° |
| 126.44° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | |
| Rotation period | 29.867±0.009 h[9] |
| Geometric albedo | |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 10.7[1][3] |
882 Swetlana (prov. designation: A917 PB or 1917 CM) is a dark background asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 15 August 1917, by Russian astronomer Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula.[1] The X-type asteroid has a longer-than average rotation period of 29.9 hours and measures approximately 42 kilometers (26 miles) in diameter. The origin of the asteroid's name remains unknown.[2]
Orbit and classification
Swetlana is a non-family asteroid of the main belt's background population when applying the hierarchical clustering method to its proper orbital elements.[4][5] It orbits the Sun in the outer asteroid belt at a distance of 2.3–4.0 AU once every 5 years and 6 months (2,016 days; semi-major axis of 3.12 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.27 and an inclination of 6° with respect to the ecliptic.[3] The body's observation arc begins on 18 August 1917, with its independent discovery at Heidelberg Observatory by Max Wolf, just three nights after its official discovery observation by Grigory Neujmin at Simeiz.[1]
Naming
This minor planet is named after a Feminine Russian first name. Any reference of this name to a person or occurrence is unknown.[2]
Unknown meaning
Among the many thousands of named minor planets, Swetlana is one of 120 asteroids, for which no official naming citation has been published. All of these low-numbered asteroids have numbers between 164 Eva and 1514 Ricouxa and were discovered between 1876 and the 1930s, predominantly by astronomers Auguste Charlois, Johann Palisa, Max Wolf and Karl Reinmuth.[11]
Physical characteristics
In both the Tholen- and SMASS-like taxonomy of the Small Solar System Objects Spectroscopic Survey (S3OS2), Swetlana is an X-type asteroid.[5][10]
Rotation period
In September 2017, a rotational lightcurve of Swetlana was obtained from photometric observations by Thomas A. Polakis at the Command Module Observatory (V02) in Arizona. Lightcurve analysis gave a well-defined rotation period of 29.867±0.009 hours with a brightness variation of 0.38±0.02 magnitude ({{{1}}}).[9] The result supersedes an observations by Italian amateur astronomers Roberto Crippa and Federico Manzini at the Sozzago Astronomical Station (A12) from September 2006, which tentatively determined a period of more than 20 hours and an amplitude of 0.17±0.05 magnitude ({{{1}}}).[12][13]
Diameter and albedo
According to the surveys carried out by the NEOWISE mission of NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), the Infrared Astronomical Satellite IRAS, and the Japanese Akari satellite, Swetlana measures (42.440±0.313), (43.55±2.2) and (44.94±0.50) kilometers in diameter and its surface has an albedo of (0.062±0.011), (0.0588±0.006) and (0.056±0.002), respectively.[6][7][8] The Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link derives an albedo of 0.0491 and a diameter of 43.47 kilometers based on an absolute magnitude of 10.7.[13] Alternative measurements published by the WISE team include mean-diameters of (39.014±0.412 km) and (39.346±0.766 km) with corresponding albedos of (0.0733±0.0177) and (0.072±0.012).[5][13]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedMPC-object - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Schmadel, Lutz D. (2007). "(882) Swetlana". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 80. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29925-7_883. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 882 Swetlana (A917 PB)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2000882.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Asteroid 882 Swetlana – Proper Elements". AstDyS-2, Asteroids – Dynamic Site. https://newton.spacedys.com/astdys/index.php?pc=1.1.6&n=882.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "Asteroid 882 Swetlana". Small Bodies Data Ferret. https://sbntools.psi.edu/ferret/SimpleSearch/results.action?targetName=882+Swetlana.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Masiero, Joseph R.; Grav, T.; Mainzer, A. K.; Nugent, C. R.; Bauer, J. M.; Stevenson, R. et al. (August 2014). "Main-belt Asteroids with WISE/NEOWISE: Near-infrared Albedos". The Astrophysical Journal 791 (2): 11. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/791/2/121. Bibcode: 2014ApJ...791..121M.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Tedesco, E. F.; Noah, P. V.; Noah, M.; Price, S. D. (October 2004). "IRAS Minor Planet Survey V6.0". NASA Planetary Data System 12: IRAS-A-FPA-3-RDR-IMPS-V6.0. Bibcode: 2004PDSS...12.....T. https://sbnarchive.psi.edu/pds3/iras/IRAS_A_FPA_3_RDR_IMPS_V6_0/data/diamalb.tab. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Usui, Fumihiko; Kuroda, Daisuke; Müller, Thomas G.; Hasegawa, Sunao; Ishiguro, Masateru; Ootsubo, Takafumi et al. (October 2011). "Asteroid Catalog Using Akari: AKARI/IRC Mid-Infrared Asteroid Survey". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 63 (5): 1117–1138. doi:10.1093/pasj/63.5.1117. Bibcode: 2011PASJ...63.1117U. (online, AcuA catalog p. 153)
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Polakis, Tom (April 2018). "Lightcurve Analysis for Seven Main-belt Asteroids". Minor Planet Bulletin 45 (2): 112–115. ISSN 1052-8091. Bibcode: 2018MPBu...45..112P. http://www.minorplanet.info/MPB/issues/MPB_45-2.pdf. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Lazzaro, D.; Angeli, C. A.; Carvano, J. M.; Mothé-Diniz, T.; Duffard, R.; Florczak, M. (November 2004). "S3OS2: the visible spectroscopic survey of 820 asteroids". Icarus 172 (1): 179–220. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2004.06.006. Bibcode: 2004Icar..172..179L. http://sirrah.troja.mff.cuni.cz/yarko-site/tmp/eos/NEW/spectral_type_figure/s3os2.pdf. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedDOMPN-unknown - ↑ Behrend, Raoul. "Asteroids and comets rotation curves – (882) Swetlana". Geneva Observatory. http://obswww.unige.ch/~behrend/page3cou.html#000882.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 "LCDB Data for (882) Swetlana". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). http://www.minorplanet.info/PHP/generateOneAsteroidInfo.php?AstInfo=882.
External links
- Lightcurve Database Query (LCDB), at www.minorplanet.info
- Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, Google books
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Geneva Observatory, Raoul Behrend
- Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets (1)-(5000) – Minor Planet Center
- 882 Swetlana at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 882 Swetlana at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |

