Astronomy:9905 Tiziano
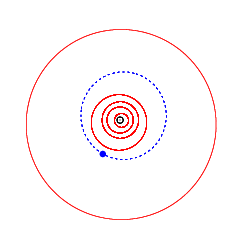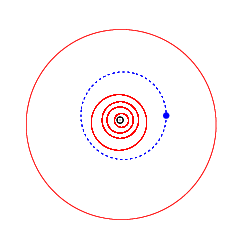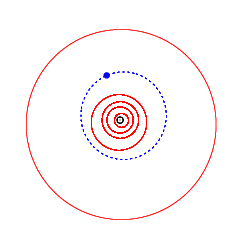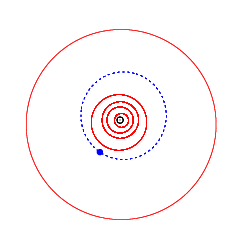 Orbit of Tiziano (blue), with the inner planets and Jupiter (outermost) | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | C. J. van Houten I. van Houten-G. T. Gehrels |
| Discovery site | Palomar Obs. |
| Discovery date | 24 September 1960 |
| Designations | |
| (9905) Tiziano | |
| Pronunciation | [titˈtsjaːno] |
| Named after | Titian – Tiziano Vecellio (Renaissance painter)[2] |
| 4611 P-L · 1990 TD10 | |
| Minor planet category | main-belt [1][3] · (inner) |
| Orbital characteristics [1] | |
| Epoch 4 September 2017 (JD 2458000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 56.35 yr (20,581 days) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.7157 AU |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.0914 AU |
| 2.4035 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.1299 |
| Orbital period | 3.73 yr (1,361 days) |
| Mean anomaly | 333.40° |
| Mean motion | 0° 15m 52.2s / day |
| Inclination | 12.723° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 9.1406° |
| 130.73° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 5.239±0.040 km[4] |
| Geometric albedo | 0.099±0.016[4] |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 14.4[1] |
9905 Tiziano (Italian pronunciation: [titˈtsjaːno]), provisional designation 4611 P-L, is an asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter. Discovered during the Palomar–Leiden survey in 1960, the asteroid was named after Italian Renaissance painter Titian.
Discovery
Tiziano was discovered on 24 September 1960, by Dutch astronomer couple Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten, as well as Dutch–American astronomer Tom Gehrels. The asteroid was spotted during the Palomar–Leiden survey by examining photographic plates taken at Palomar Observatory, California, United States.[3]
The survey designation "P-L" stands for Palomar–Leiden, named after Palomar Observatory and Leiden Observatory, which collaborated on the fruitful Palomar–Leiden survey in the 1960s. Gehrels used Palomar's Samuel Oschin telescope (also known as the 48-inch Schmidt Telescope), and shipped the photographic plates to Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten at Leiden Observatory where astrometry was carried out. The trio are credited with the discovery of several thousand minor planets.[5]
Orbit and classification
Tiziano orbits the Sun in the inner main-belt at a distance of 2.1–2.7 AU once every 3 years and 9 months (1,361 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.13 and an inclination of 13° with respect to the ecliptic.[1] The body's observation arc begins with its official discovery observation at Palomar, as no precoveries were taken, and no prior identifications were made.[3]
Physical characteristics
Diameter and albedo
According to the survey carried out by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer with its subsequent NEOWISE mission, Tiziano measures 5.239 kilometers in diameter and its surface has an albedo of 0.099.[4] It has an absolute magnitude of 14.4[1]
Rotation period
As of 2017, the asteroid's rotation period, shape and spectral type remain unknown.[1][6]
Naming
This minor planet was named after Tiziano Vecellio (c. 1488–1576) known in English as Titian, who was an Italian Renaissance painter and the most important member of the Venetian school. His application and use of color, would exercise a profound influence not only on painters of the Italian Renaissance, but on future generations of Western art. Titian is famous for the Equestrian Portrait of Charles V and for the Portrait of Pope Paul III.[2] The official naming citation was published by the Minor Planet Center on 2 April 1999 (M.P.C. 34356).[7]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 9905 Tiziano (4611 P-L)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2009905.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Schmadel, Lutz D. (2007). "(9905) Tiziano". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names – (9905) Tiziano. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 713. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29925-7_7744. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "9905 Tiziano (4611 P-L)". Minor Planet Center. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?object_id=9905.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Masiero, Joseph R.; Mainzer, A. K.; Grav, T.; Bauer, J. M.; Cutri, R. M.; Dailey, J. et al. (November 2011). "Main Belt Asteroids with WISE/NEOWISE. I. Preliminary Albedos and Diameters". The Astrophysical Journal 741 (2): 20. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/741/2/68. Bibcode: 2011ApJ...741...68M. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/bib_query?bibcode=2011ApJ...741...68M. Retrieved 17 March 2017.
- ↑ "Minor Planet Discoverers". Minor Planet Center. 13 March 2017. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/iau/lists/MPDiscsNum.html.
- ↑ "LCDB Data for (9905) Tiziano". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). http://www.minorplanet.info/PHP/generateOneAsteroidInfo.php?AstInfo=9905%7CTiziano.
- ↑ "MPC/MPO/MPS Archive". Minor Planet Center. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/iau/ECS/MPCArchive/MPCArchive_TBL.html.
External links
- Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB), query form (info )
- Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, Google books
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Observatoire de Genève, Raoul Behrend
- Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets (5001)-(10000) – Minor Planet Center
- 9905 Tiziano at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 9905 Tiziano at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |

