Astronomy:Epsilon Corvi
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Corvus |
| Right ascension | 12h 10m 07.48058s[1] |
| Declination | –22° 37′ 11.1620″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +3.024[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K2 III[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.458[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.318[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +4.9[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: –71.74 mas/yr Dec.: +10.25 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 10.26 ± 0.16[1] mas |
| Distance | 318 ± 5 ly (97 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.82+0.15 −0.14[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 3.2[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 52[7] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.16[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 4320[8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.13[8] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 1.0[6] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
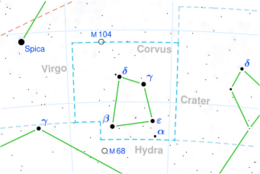
Epsilon Corvi (ε Crv, ε Corvi) is a star in the southern constellation of Corvus. It has the traditional name Minkar /ˈmɪŋkɑːr/, from Arabic منقار minqar meaning "beak [of the crow]"[10] The apparent visual magnitude is +3.0[2] and it is located at a distance of 318 light-years (97 parsecs) from Earth.[1]
In Chinese, 軫宿 (Zhěn Sù), meaning Chariot (asterism), refers to an asterism consisting of ε Corvi, γ Corvi, δ Corvi and β Corvi.[11] Consequently, ε Corvi itself is known as 軫宿二 (Zhěn Sù èr, English: the Second Star of Chariot.).[12]
Epsilon Corvi is a red giant with a stellar classification of K2 III, having consumed the hydrogen at its core and evolved away from the main sequence. It has about three times the Sun's mass.[6] The interferometry-measured angular diameter of this star is about 4.99 mas,[13] which, at its estimated distance, equates to a physical radius of about 52 times the radius of the Sun.[7] The effective temperature of the outer envelope is 4320 K,[8] giving it an orange hue that is characteristic of a K-type star.[14] Around 4 times as massive as the Sun, it spent much of its life as a main sequence star of spectral type B5V.[15]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Celis S., L. (October 1975), "Photoelectric photometry of late-type variable stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 22: 9–17, Bibcode: 1975A&AS...22....9C
- ↑ Houk, Nancy (1979), Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars, 4, Ann Arbor, Michigan: Dept. of Astronomy, University of Michigan, Bibcode: 1988mcts.book.....H
- ↑ Wielen, R. et al. (1999), "Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions", Veroeffentlichungen des Astronomischen Rechen-Instituts Heidelberg (Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg) 35 (35): 1, Bibcode: 1999VeARI..35....1W
- ↑ Carney, Bruce W. et al. (March 2008), "Rotation and Macroturbulence in Metal-Poor Field Red Giant and Red Horizontal Branch Stars", The Astronomical Journal 135 (3): 892–906, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/3/892, Bibcode: 2008AJ....135..892C
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Melo, C. H. F. et al. (August 2005), "On the nature of lithium-rich giant stars. Constraints from beryllium abundances", Astronomy and Astrophysics 439 (1): 227–235, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041805, Bibcode: 2005A&A...439..227M
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Lang, Kenneth R. (2006), Astrophysical formulae, Astronomy and astrophysics library, 1 (3rd ed.), Birkhäuser, ISBN 3-540-29692-1, https://books.google.com/books?id=OvTjLcQ4MCQC&pg=PA41. The radius (R*) is given by:
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 McWilliam, Andrew (December 1990), "High-resolution spectroscopic survey of 671 GK giants. I - Stellar atmosphere parameters and abundances", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 74: 1075–1128, doi:10.1086/191527, Bibcode: 1990ApJS...74.1075M
- ↑ "MINKAR -- Variable Star", SIMBAD (Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg), http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=Minkar, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ↑ Al-Sufi, Book Of Fixed Stars, Constellation: The Crow
- ↑ (in Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ↑ (in Chinese) 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表 , Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
- ↑ Richichi, A.; Percheron, I.; Khristoforova, M. (February 2005), "CHARM2: An updated Catalog of High Angular Resolution Measurements", Astronomy and Astrophysics 431 (2): 773–777, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20042039, Bibcode: 2005A&A...431..773R
- ↑ "The Colour of Stars", Australia Telescope, Outreach and Education (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation), December 21, 2004, http://outreach.atnf.csiro.au/education/senior/astrophysics/photometry_colour.html, retrieved 2012-01-16
- ↑ Kaler, James B. (Jim), "Minkar", Stars (University of Illinois), http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/minkar.html, retrieved 12 July 2015
 |