Astronomy:Gemini 3
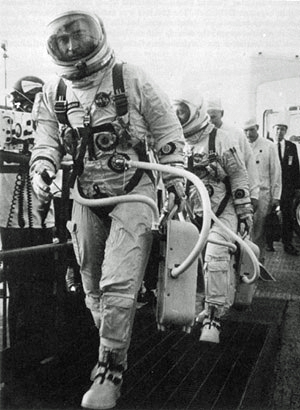 Astronauts John Young and Gus Grissom walk up the ramp leading to the elevator that will carry them to the spacecraft for the first crewed Gemini mission | |
| Mission type | Test flight |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1965-024A |
| SATCAT no. | S001301 |
| Mission duration | 4 hours, 52 minutes, 31 seconds |
| Distance travelled | 128,748 km (80,000 mi; 69,518 nmi) |
| Orbits completed | 3 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Gemini SC3 |
| Manufacturer | McDonnell |
| Launch mass | 3,237 kg (7,136 lb) |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 2 |
| Members |
|
| Callsign | Molly Brown |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | March 23, 1965, 14:24:00 UTC |
| Rocket | Titan II GLV, s/n 62-12558 |
| Launch site | Cape Kennedy LC-19 |
| End of mission | |
| Recovered by | missing name |
| Landing date | March 23, 1965, 19:16:31 UTC |
| Landing site | [ ⚑ ] 22°26′N 70°51′W / 22.433°N 70.85°W |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 161 km (100 mi; 87 nmi) |
| Apogee altitude | 225 km (140 mi; 121 nmi) |
| Inclination | 32.6° |
| Period | 88.35 minutes |
| Epoch | March 23, 1965[1] |
 Mission insignia  Grissom and Young | |
Gemini 3 (officially Gemini III) was the first crewed mission in NASA's Project Gemini and was the first time two American astronauts flew together into space. On March 23, 1965, astronauts Gus Grissom and John Young flew three low Earth orbits in their spacecraft, which they nicknamed Molly Brown. It was the first U.S. mission in which the crew fired thrusters to change the size and shape of their orbit, a key test of spacecraft maneuverability vital for planned flights to the Moon. It was also the final crewed flight controlled from Cape Kennedy Air Force Station in Florida, before mission control functions were moved to a new control center at the newly opened Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas.
Crew
| Position | Astronaut | |
|---|---|---|
| Command Pilot | Virgil I. "Gus" Grissom Second and last spaceflight | |
| Pilot | John W. Young First spaceflight | |
Backup crew
| Position | Astronaut | |
|---|---|---|
| Command Pilot | Walter M. Schirra | |
| Pilot | Thomas P. Stafford | |
| This was the prime crew on Gemini 6A. | ||
Original crew
| Position | Astronaut | |
|---|---|---|
| Command Pilot | Alan B. Shepard | |
| Pilot | Thomas P. Stafford | |
| The crew of Gemini 3 was changed after Shepard was grounded with an inner ear disorder in late 1963. | ||
Support crew
- Roger B. Chaffee (Houston CAPCOM)[2]
- L. Gordon Cooper Jr. (Cape CAPCOM)[2]
Mission parameters
- Mass: 3,236.9 kg (7,136 lb)
- Perigee: 161.2 kilometers (100.2 mi)
- Apogee: 224.2 kilometers (139.3 mi)
- Inclination: 32.6 degrees
- Period: 88.3 minutes
Objectives

The mission's primary goal was to test the new, maneuverable Gemini spacecraft. In space, the crew fired thrusters to change the shape of their orbit, shift their orbital plane slightly, and drop to a lower altitude. Other firsts were achieved on Gemini 3: two people flew aboard an American spacecraft (the Soviet Union launched a three-person crew on Voskhod 1 in 1964 and a two-person crew just a few days earlier on Voskhod 2, upstaging the two-person Gemini and three-person Apollo programs), and the first crewed reentry where the spacecraft was able to produce lift to change its touchdown point.
The mission also tested a system that had originally been designed for the cancelled Mercury-Atlas 10 mission, in which water was injected into the plasma sheath surrounding the capsule during re-entry. This had the effect of improving communications with the ground.[3]
First orbital maneuver by crewed spacecraft
On March 23, 1965, at 15:57:00 UTC, at the end of the first orbit, over Corpus Christi, Texas, a 1-minute 14 second burn of the Orbit Attitude and Maneuvering System (OAMS) engines gave a reverse delta-V of 15.5 meters per second (51 ft/s), which changed the orbit from 161.2 by 224.2 kilometers (87.0 by 121.1 nautical miles) (with a period of 88.3 minutes), to an orbit of 158 by 169 kilometers (85 by 91 nmi) (period of 87.8 minutes). This was the first orbital maneuver made by any crewed spacecraft.
Flight


Grissom, hoping to avoid duplication of the experience with his Mercury flight Liberty Bell 7 in which the capsule sank after splashdown, came up with the nickname Molly Brown, in a playful reference to the Broadway musical The Unsinkable Molly Brown.[4] Grissom and Young decided on Gemini 3 as the spacecraft's official name, and Molly Brown became its unofficial nickname.[5]
The only major incident during the orbital phase involved a contraband corned beef sandwich that Young had smuggled on board, hiding it in a pocket of his spacesuit (though Director of Flight Crew Operations Deke Slayton wrote in his autobiography that he gave Young permission to do so). Grissom found this to be highly amusing, saying later, "After the flight our superiors at NASA let us know in no uncertain terms that non-man-rated corned beef sandwiches were out for future space missions. But John's deadpan offer of this strictly non-regulation goodie remains one of the highlights of our flight for me."[6]
The crewmen each took a few bites before the sandwich was restowed. The crumbs it released could have wreaked havoc with the craft's electronics, so the crewmen were reprimanded when they returned to Earth. Other crews were warned not to pull the same type of stunt.[7]
Two small failures occurred in-flight. The first was an experiment testing the synergistic effect of zero gravity on sea urchin eggs. A lever essential to the experiment broke off when pulled. The second involved the photographic coverage objective. It was only partially successful due to an improper lens setting on the 16 mm camera.
Early in the flight, the crew noticed the craft gradually yawing left:
00 18 41 (Command Pilot) I seem to have a leak. There must be a leak in one of the thrusters, because I get a continuous yaw left.
00 18 53 (CapCom) Roger. Understand that you get a continuous yaw left.
00 18 57 (Command Pilot) Very slight. Very slow drift.[8]
First attributed to a stuck thruster, the problem was traced to a venting water boiler.[9]
The crewmen made their first orbit change an hour and a half into the flight. The burn lasted 75 seconds and moved them from a 122-by-175-kilometer (66-by-94-nautical-mile) orbit to a nearly circular one with a drop in speed of 15 m/s (49 ft/s). The second burn, changing the orbital inclination by 0.02 degrees, was made 45 minutes later. The last burn, during the third orbit, lowered the perigee to 72 km (39 nmi). This was made so, in case the retrorockets had failed, the spacecraft would still have reentered the atmosphere. The experience of reentry initially matched expectations, with even the color and pattern of the plasma sheath that enveloped the capsule matching those produced for ground simulations. However, it soon became clear that Molly Brown was off course and would land 69 km (37 nmi) off target. Though wind tunnel studies had suggested the spacecraft could maneuver to make up for the discrepancy, Gemini's real lift was far less than predicted, and Grissom was unable to significantly adjust course. Molly Brown ultimately landed 84 km (45 nmi) short of its intended splashdown point.[10]
This was not the only unexpected event of the short descent: After its parachutes were deployed, the spacecraft shifted from a vertical to horizontal attitude. The change was so sudden that Grissom cracked his faceplate (made of acrylic) on the control panel in front of him. Later Gemini spacesuits and all Apollo and Space Shuttle (both launch-entry and EVA suits) used polycarbonate plastic.

Upon landing, the astronauts decided to stay in the capsule, not wanting to open the hatch before the arrival of the recovery ship. The crew spent an uncomfortable half-hour in a spacecraft not designed to be a boat. Due to unexpected smoke from the thrusters, the astronauts decided to deviate from the post landing checklist and to keep their helmets on with the face plates closed for some time after splashdown.[8] missing name recovered the craft and crew.[11] The Gemini III mission was supported by 10,185 personnel, 126 aircraft and 27 ships from the United States Department of Defense.
Insignia

The mission insignia was not worn by the flight crew as a patch, like those from Gemini 5 onwards. The Gemini 3 The Molly Brown emblem was designed and minted on gold-plated, sterling silver, 1-inch (25 mm) medallions. The crew carried a number of these medallions into space to give to their families and friends. The same design was printed on the cover of Grissom's book Gemini!: A Personal Account of Man's Venture Into Space. Young was seen wearing the emblem as a patch, produced post-flight, on his flightsuit as late as 2002.
Spacecraft location
The spacecraft is on display within the Grissom Memorial of Spring Mill State Park, two miles east of Grissom's hometown of Mitchell, Indiana.
See also
References
- ↑ McDowell, Jonathan. "SATCAT". Jonathan's Space Pages. http://planet4589.org/space/log/satcat.txt.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Gemini 3 (3)". August 25, 2000. http://science.ksc.nasa.gov/history/gemini/gemini-3/gemini-3.html.
- ↑ NASA: Gemini 3
- ↑ Jones, Clarence (24 March 1965). "The 'Molly' Bit ...". The Miami Herald (Knight Ridder): p. 1. ISSN 0898-865X. https://www.newspapers.com/article/the-miami-herald-that-molly-bit/168744629/.
- ↑ Wilder, Paul (24 March 1965). "Humphrey Hails Space Feat, Takes Needling From Press". The Tampa Tribune: p. 5A. https://www.newspapers.com/article/the-tampa-tribune-humphrey-hails-space-f/168745408/.
- ↑ Grissom, Gus; Young, John (April 2, 1965). "Astronauts'Own Story". The Miami News (Cox Enterprises): pp. 1A,4A. https://www.newspapers.com/article/the-miami-news-our-gemini-astronauts-tel/168746836/.
- ↑ "NASA History: Detailed Biographies of Apollo I Crew - Gus Grissom". NASA. https://history.nasa.gov/Apollo204/zorn/grissom.htm.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Gemini III radio transcript on Spacelog". National Astronaut and Space Administration. April 1965. http://gemini3.spacelog.org/00:00:18:41/00:00:18:57/#log-line-1121.
- ↑ French, Francis and Burgess, Colin. "In the Shadow of the Moon". University of Nebraska Press, 2007, p. 11.
- ↑ Hacker, Barton; Grimwood, James (1966). On the Shoulders of Titans. Washington D.C.: NASA. p. 236.
- ↑ Lyons, Richard (March 24, 1965). "2 Gemini Firsters Touch All Bases". Daily News (New York: News Syndicate Co. Inc.): p. 3. https://www.newspapers.com/article/daily-news-2-gemini-firsters-touch-all-b/168619813/.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
- Hacker, Barton C.; Grimwood, James M. (1977). On The Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini. The NASA Historical Series. Washington, D.C.: National Aeronautics and Space Administration. NASA SP-4203. http://www.hq.nasa.gov/office/pao/History/SP-4203/cover.htm.
- Garrett, Russ; Ogle, Matthew (2011). "Gemini III radio transcripts". Spacelog. http://gemini3.spacelog.org/.
- NASA PAO (March 17, 1965). "NASA Gemini 3 Press Kit" (PDF) (Press release). Washington, D.C.: National Aeronautics and Space Admininstration. Release No.: 65-81. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 21, 2009. Retrieved March 27, 2025.
External links
- "GEMINI 3 Launch to Staging" on YouTube
- Spaceflight Mission Patches
- Astronaut John W. Young tribute website
- Gemini 3 at A Field Guide To American Spacecraft
- slideshow by Life magazine
 |


