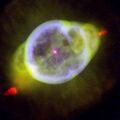
Astronomy:NGC 3242
| Emission nebula | |
|---|---|
| Planetary nebula | |
 | |
| Observation data: J2000 epoch | |
| Right ascension | 10h 24m 46.1s[1] |
| Declination | −18° 38′ 32.6″[1] |
| Distance | 4800±500[2] ly |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.60 |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 25″ |
| Constellation | Hydra |
| Designations | Ghost of Jupiter, Jupiter's Ghost, Eye Nebula, Caldwell 59 |
NGC 3242 (also known as the Ghost of Jupiter, Eye Nebula or Caldwell 59) is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Hydra.
William Herschel discovered the nebula on February 7, 1785, and catalogued it as H IV.27. John Herschel observed it from the Cape of Good Hope, South Africa , in the 1830s, and numbered it as h 3248, and included it in the 1864 General Catalogue as GC 2102; this became NGC 3242 in J. L. E. Dreyer's New General Catalogue of 1888.
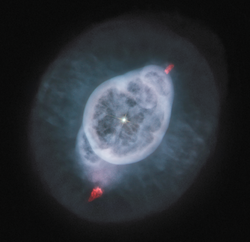
This planetary nebula is most frequently called the Ghost of Jupiter, or Jupiter's Ghost due to its similar shape to the planet, but it is also sometimes referred to as the Eye Nebula.[3] The nebula measures around two light years long from end to end, and contains a central white dwarf with an apparent magnitude of 11. The inner layers of the nebula were formed some 1,500 years ago.[4] The two ends of the nebula are marked by FLIERs, lobes of fast moving gas often tinted red in false-color pictures.[5] NGC 3242 can easily be observed with amateur telescopes and appears bluish-green to most observers. Larger telescopes can distinguish the outer halo as well.[6]
At the center of NGC 3242 is an O-type star with a spectral type of O(H).[7]
Gallery
-
Imaged with a 10" Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope
-
A different Hubble image of the core region
-
Ultraviolet image from NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer
-
Infrared, Spitzer Space Telescope
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "NGC 3242". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=NGC+3242.
- ↑ Gaia Collaboration et al. (2018b): Summary of the contents and survey properties
- ↑ Frommert, Hartmut. "NGC 3242". SEDS. http://spider.seds.org/spider/Misc/n3242.html.
- ↑ Mobberley, Martin (2009). The Caldwell Objects and How to Observe Them. New York: Springer Science+Business Media, LLC. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-4419-0326-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=amPrWoOWgHcC&pg=PA128.
- ↑ "NGC 3242, Ghost of Jupiter". ESA. http://www.spacetelescope.org/projects/fits_liberator/fitsimages/danny_lacrue_1/.
- ↑ "The Ghost of Jupiter". http://www.skyhound.com/sh/archive/mar/NGC_3242.html.
- ↑ González-Santamaría, I.; Manteiga, M.; Manchado, A.; Ulla, A.; Dafonte, C.; López Varela, P. (2021). "Planetary nebulae in Gaia EDR3: Central star identification, properties, and binarity". Astronomy & Astrophysics 656: A51. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202141916. Bibcode: 2021A&A...656A..51G.
External links
- The Hubble European Space Agency Information Centre – Hubble picture and information on NGC 3242
- NGC 3242 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
- NGC3242 on astro-pics.com
- FLIERs in NGC 3242
 |