Astronomy:NGC 3928
From HandWiki
| NGC 3928 | |
|---|---|
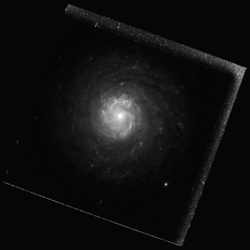 Hubble Space Telescope image of NGC 3928 | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Ursa Major |
| Right ascension | 11h 51m 47s[1] |
| Declination | +48° 40′ 59″[1] |
| Redshift | 0.000764[2] |
| Helio radial velocity | 988 ± 4 km/s[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | 13.1[1] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | SA(s)b[2] |
| Size | ~18,000 ly (5.6 kpc) |
| Other designations | |
| NGC 3928, UGC 6834, MCG+08-22-019, PGC 37136[1] | |
NGC 3928, also known as the Miniature Spiral,[3][4] is a lenticular galaxy, sometimes classified as a dwarf spiral galaxy, in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by William Herschel on March 9, 1788.[5]
Gallery
-
NGC 3928 (SDSS DR14)
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "NGC 3928". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=NGC+3928.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". http://ned.ipac.caltech.edu/cgi-bin/nph-objsearch?objname=NGC+3928.
- ↑ "Elliptical Galaxy in Ursa Major". https://theskylive.com/sky/deepsky/ngc3928-miniature-spiral-object.
- ↑ Stoyan, Ronald; Schurig, Stephan (2014). interstellarum Deep Sky Atlas. Erlangen: Cambridge University Press; Oculum-Verlag GmbH. ISBN 978-1-107-50338-0. OCLC 920437579. http://www.deep-sky-atlas.com/.
- ↑ Seligman, Courtney. "New General Catalog Objects: NGC 3900 - 3949". https://cseligman.com/text/atlas/ngc39.htm#3928.
External links
- NGC 3928 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to NGC 3928. |
 |

