Astronomy:NR Canis Majoris
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Canis Major |
| Right ascension | 07h 27m 07.99012s[2] |
| Declination | −17° 51′ 53.5058″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.60[3] (5.66 + 9.23)[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F2V[5] |
| B−V color index | +0.314±0.002[3] |
| Variable type | δ Sct[6] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −29.2±2.9[3] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −2.420[2] mas/yr Dec.: +1.388[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 10.9688 ± 0.0917[2] mas |
| Distance | 297 ± 2 ly (91.2 ± 0.8 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 0.78[3] |
| Details | |
| A | |
| Mass | 1.62[7] or 2.18±0.04[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 3.90+0.18 −0.24[2] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 37.4±0.4[2] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.65[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,227+238 −160[2] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 185[9] km/s |
| Age | 1.494[7] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
NR Canis Majoris is a binary star[11] system in the southern constellation of Canis Major, located to the east of Sirius and Gamma Canis Majoris near the constellation border with Puppis. It has a yellow-white hue and is dimly visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 5.60.[3] It is located at a distance of approximately 297 light years from the Sun based on parallax.[2] The system is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −29 km/s,[3] and in about three million years it is predicted to approach within 14.1+4.7
−4.0 ly.[12] At that time, the star will become the brightest in the night sky, potentially reaching magnitude −0.88.[13]
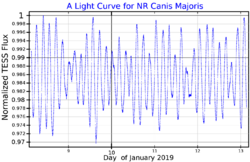
The magnitude 5.66[4] primary component is an F-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of F2V.[5] It is a Delta Scuti variable[6] that varies by a few hundredths of a magnitude over roughly 16 hours.[14] The star is an estimated 1.5 billion years old.[7] It has a high rate of spin with a projected rotational velocity of 185 km/s, which is giving the star an equatorial bulge that is estimated to be 8% larger than the polar radius.[9]
The secondary companion is magnitude 9.23 and lies at an angular separation of 1.3″ along a position angle of 39°, as of 2005.[4]
References
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Mason, B. D. et al. (2014). "The Washington Visual Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal 122 (6): 3466. doi:10.1086/323920. Bibcode: 2001AJ....122.3466M. http://vizier.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR?-source=B/wds. Retrieved 2015-07-22.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Houk, Nancy; Smith-Moore, M. (1978). Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars. 4. Ann Arbor: Department of Astronomy, University of Michigan. Bibcode: 1988mcts.book.....H.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Samus, N. N. et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports. 5.1 61 (1): 80–88. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2015). "The Ages of Early-Type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets". The Astrophysical Journal 804 (2): 146. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/2/146. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...804..146D.
- ↑ Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities". Astronomy & Astrophysics 537: A120. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691. Bibcode: 2012A&A...537A.120Z.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 van Belle, Gerard T. (March 2012). "Interferometric observations of rapidly rotating stars". The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review 20 (1): 51. doi:10.1007/s00159-012-0051-2. Bibcode: 2012A&ARv..20...51V.
- ↑ "NR CMa". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=NR+CMa.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x. Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.389..869E.
- ↑ Bailer-Jones, C. A. L. (March 2015). "Close encounters of the stellar kind". Astronomy & Astrophysics 575: 13. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201425221. A35. Bibcode: 2015A&A...575A..35B.
- ↑ Tomkin, Jocelyn (April 1998). "Once and Future Celestial Kings". Sky and Telescope 95 (4): 59–63. Bibcode: 1998S&T....95d..59T.
- ↑ Watson, Christopher (4 January 2010). "LS Canis Majoris". AAVSO Website. American Association of Variable Star Observers. http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=5446. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
 |