Astronomy:Pioneer Venus Multiprobe
 Pioneer Venus Multiprobe | |
| Mission type | Venus atmospheric probes |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA / ARC |
| COSPAR ID | 1978-078A |
| SATCAT no. | 11001 |
| Website | National Space Science Data Center (NASA) |
| Mission duration | 4 months, 1 day, 13 hours, 22 minutes |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Bus | HS-507 |
| Manufacturer | Hughes |
| Launch mass | 904 kilograms (1,993 lb)[1] |
| Dry mass | 290 kilograms (640 lb) (bus) 315 kilograms (694 lb) (large probe) 3 x 90 kilograms (200 lb) (small probes) |
| Power | 241 W |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | August 8, 1978, 07:33 UTC[1] |
| Rocket | Atlas SLV-3D Centaur-D1AR |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 36 |
| End of mission | |
| Last contact | December 9, 1978, 20:22:55 UTC (bus) December 9, 1978, 20:55:34 UTC (day probe) |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Heliocentric |
| Semi-major axis | 0.9 Astronomy:astronomical unit|astronomical units (130,000,000 km; 84,000,000 mi) |
| Eccentricity | 0.19 |
| Perihelion altitude | 0.69 Astronomy:astronomical unit|astronomical units (103,000,000 km; 64,000,000 mi) |
| Aphelion altitude | 1.01 Astronomy:astronomical unit|astronomical units (151,000,000 km; 94,000,000 mi) |
| Inclination | 2.3 degrees |
| Period | 284.0 days |
| Venus atmospheric probe | |
| Spacecraft component | Large Probe |
| Atmospheric entry | December 9, 1978, 18:45:32 UTC |
| Impact date | 19:39:53 UTC |
| Impact site | [ ⚑ ] 4°24′N 304°00′E / 4.4°N 304.0°E |
| Venus atmospheric probe | |
| Spacecraft component | North Probe |
| Atmospheric entry | December 9, 1978, 18:49:40 UTC |
| Impact date | 19:42:40 UTC |
| Impact site | [ ⚑ ] 59°18′N 4°48′E / 59.3°N 4.8°E |
| Venus atmospheric probe | |
| Spacecraft component | Day Probe |
| Atmospheric entry | December 9, 1978, 18:52:18 UTC |
| Impact date | 19:47:59 UTC |
| Impact site | [ ⚑ ] 31°18′S 317°00′E / 31.3°S 317.0°E |
| Venus atmospheric probe | |
| Spacecraft component | Night Probe |
| Atmospheric entry | December 9, 1978, 18:56:13 UTC |
| Impact date | 19:52:05 UTC |
| Impact site | [ ⚑ ] 28°42′S 56°42′E / 28.7°S 56.7°E |
| Venus atmospheric probe | |
| Atmospheric entry | December 9, 1978, 20:21:52 UTC |
The Pioneer Venus Multiprobe, also known as Pioneer Venus 2 or Pioneer 13, was a spacecraft launched in 1978 to explore Venus as part of NASA's Pioneer program. This part of the mission included a spacecraft bus which was launched from Earth carrying one large and three smaller probes, which after separating penetrated the Venusian atmosphere at a different location, returning data as they descended into the planet's thick atmosphere. The entry occurred on December 9, 1978.
In context
There was also an orbiter launched in 1978, part of the overall Pioneer Venus project along with this entry probe mission. Whereas the probes entered the atmosphere in 1978, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter would stay in orbit throughout the 1980s and the early 1990s. The next major mission was the Magellan spacecraft, which was an orbiter capable of mapping Venus by seeing through its opaque clouds with radar.
Spacecraft

The Pioneer Venus Multiprobe bus was constructed by the Hughes Aircraft Company, built around the HS-507 bus. It was cylindrical in shape, with a diameter of 2.5 meters (8 ft 2 in) and a mass of 290 kilograms (640 lb). Unlike the probes, which did not begin making direct measurements until they had decelerated lower in the atmosphere, the bus returned data on Venus' upper atmosphere.
The bus was targeted to enter the Venusian atmosphere at a shallow entry angle and transmit data until destruction by the heat of atmospheric friction. The objective was to study the structure and composition of the atmosphere down to the surface, the nature and composition of the clouds, the radiation field and energy exchange in the lower atmosphere, and local information on atmospheric circulation patterns. With no heat shield or parachute, the bus made upper atmospheric measurements with two instruments:
- BIMS – an ion mass spectrometer to determine the origin and long-term development of the Venusian atmosphere, the dynamics of the upper atmosphere layers, its energy balance and the effect of solar radiation and interplanetary space on those layers. This instrument had a range of 1 to 46 u, used 6 W of power and weighed 5 kilograms (11 lb).
- BNMS – a neutral mass spectrometer. This made measurements of the interaction between the solar wind and Venus, the photochemistry of the upper layers of and heat distribution in the Venusian atmosphere. It had a range of 1 to 60 u, weighed 1 kilogram (2.2 lb), and used ~1 W of power.
The spacecraft operated down to an altitude of about 110 kilometres (68 mi) before disintegrating.
Probes
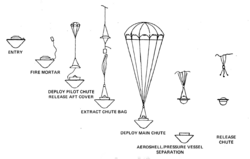
The spacecraft carried one large and three small atmospheric probes, designed to collect data as they descended into the atmosphere of Venus. The probes did not carry photographic instruments, and were not designed to survive landing – the smaller probes were not equipped with parachutes, and the larger probe's parachute was expected to detach as it neared the ground. All four probes continued transmitting data until impact; however, one survived and continued to transmit data from the surface.
Large probe

The large probe carried seven experiments, contained within a sealed spherical pressure vessel. The science experiments were:
- LNMS – neutral mass spectrometer to measure the atmospheric composition
- LGC – gas chromatograph to measure the atmospheric composition
- LSFR – solar flux radiometer to measure solar flux penetration in the atmosphere
- LIR – infrared radiometer to measure distribution of infrared radiation
- LCPS – cloud particle size spectrometer to measure particle size and shape
- LN – nephelometer to search for cloud particles
- temperature, pressure, and acceleration sensors
This pressure vessel was encased in a nose cone and aft protective cover. After deceleration from initial atmospheric entry at about 11.5 kilometers per second (7.1 mi/s) near the equator on the night side of Venus, a parachute was deployed at 67 kilometres (42 mi) altitude. The large probe was about 150 centimeters (59 in) in diameter and the pressure vessel itself was 73.2 centimeters (28.8 in) in diameter.
Small probes
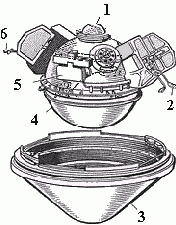
Three identical small probes, around 0.8 meters (2 ft 7 in) in diameter, were deployed. These probes consisted of spherical pressure vessels surrounded by an aeroshell, but unlike the large probe, they had no parachutes and the aeroshells did not separate from the probes.
The science experiments were:[2]
- a neutral mass spectrometer to measure the atmospheric composition
- a gas chromatograph to measure the atmospheric composition
- SNFR – solar flux radiometer to measure solar flux penetration in the atmosphere
- an infrared radiometer to measure distribution of infrared radiation
- MTUR – cloud particle size spectrometer to measure particle size and shape
- SN – nephelometer to search for cloud particles
- SAS – temperature, pressure, and acceleration sensors
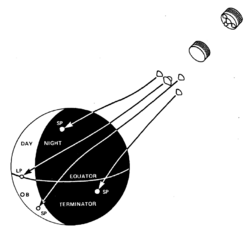
The radio signals from all four probes were also used to characterize the winds, turbulence, and propagation in the atmosphere. The small probes were each targeted at different parts of the planet and were named accordingly.[3]
- The North probe entered the atmosphere at about 60 degrees north latitude on the day side.
- The Night probe entered on the night side.
- The Day probe entered well into the day side, and was the only one of the four probes which continued to send radio signals back after impact, for over an hour.
Launch
The Pioneer Venus Multiprobe was launched by an Atlas SLV-3D Centaur-D1AR rocket, which flew from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 36 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station . The launch occurred at 07:33 on August 8, 1978, and deployed the Multiprobe into heliocentric orbit for its coast to Venus.
Arrival at Venus
Prior to the Multiprobe reaching Venus, the four probes were deployed from the main bus. The large probe was released on November 16, 1978, and the three small probes on November 20.
All four probes and the bus reached Venus on December 9, 1978. The large probe was the first to enter the atmosphere, at 18:45:32 UTC, followed over the next 11 minutes by the other three probes. The bus entered the atmosphere at 20:21:52 UTC and returned its last signal at 20:22:55 from an altitude of 110 kilometres (68 mi).
The four probes transmitted data until they impacted the surface of Venus. The Day Probe survived the impact, returning data from the surface for 67 minutes and 37 seconds after reaching the surface.[4]
| Entry time (200 km) | Impact time | Loss of signal | Impact coordinates | Solar Zenith Angle | Local Venus time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Probe | 18:45:32 | 19:39:53 | 19:39:53 | [ ⚑ ] 4°24′N 304°00′E / 4.4°N 304.0°E | 65.7 | 7:38 |
| North Probe | 18:49:40 | 19:42:40 | 19:42:40 | [ ⚑ ] 59°18′N 4°48′E / 59.3°N 4.8°E |
108.0 | 3:35 |
| Day Probe | 18:52:18 | 19:47:59 | 20:55:34 | [ ⚑ ] 31°18′S 317°00′E / 31.3°S 317.0°E |
79.9 | 6:46 |
| Night Probe | 18:56:13 | 19:52:05 | 19:52:07 | [ ⚑ ] 28°42′S 56°42′E / 28.7°S 56.7°E | 150.7 | 0:07 |
| Bus | 20:21:52 | (signal lost at 110 km altitude) | 20:22:55 | [ ⚑ ] 37°54′S 290°54′E / 37.9°S 290.9°E (estimated) | 60.7 | 8:30 |
Scientific results
Below the altitude of 50 kilometres (31 mi) the temperatures measured by the four probes are identical to within a few degrees. They are between 448 and 459 °C (838 and 858 °F) on the surface. The ground pressure is between 86.2 and 94.5 bars (8,620 and 9,450 kPa). Nephelometers identified three cloud layers with different characteristics. The most remarkable discovery was that the ratio of 36argon / 40argon isotopes was much higher than in the Earth's atmosphere, which seems to indicate that the genesis of the Venusian atmosphere is very different from that of Earth. The reconstituted trajectory of atmospheric probes was determined that the wind averaged a speed of 200 metres per second (660 ft/s) in the middle cloud layer at 50 metres per second (160 ft/s) at the base of these clouds and just 1 metre per second (3.3 ft/s) at the ground. Overall data from airborne sensors confirmed, while specifying the data obtained by the Soviet space probe Venera program that preceded this mission.[5]
Trajectory
Diagram of the PVM's path to planet Venus from Earth in 1978, and this also notes the launch of the Pioneer Venus Orbiter which took place that year also.
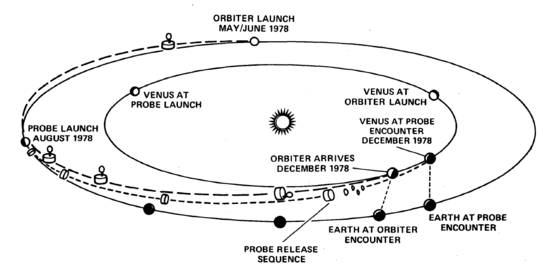
Graphic overview

See also
- Pioneer Venus Orbiter
- List of missions to Venus
- Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes
- Galileo Probe (Jupiter atmospheric probe delivered by Galileo spacecraft)
- List of spacecraft powered by non-rechargeable batteries
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Pioneer Venus Multiprobe/Pioneer Venus 2/Pioneer 13". NASA's Solar System Exploration website. https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/pioneer-venus-2/in-depth/.
- ↑ "Pioneer Venus Project Information". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/pioneer_venus.html.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Pioneer Venus Probes. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, 2005.
- ↑ NASA. Pioneer Venus 2, NASA Science: Solar System Exploration, February 3, 2021. Retrieved 24 April 2022.
- ↑ Paolo Ulivi et David M. Harland, Robotic Exploration of the Solar System Part 1, The Golden Age 1957–1982, Springer Praxis, 2007 (ISBN 978-0-387-49326-8)
External links
- NASA: Pioneer Venus Project Information
- Pioneer Venus Program Page by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- NSSDC Master Catalog: Spacecraft Pioneer Venus Probe Bus. (Other components of the mission have their own pages at this site too.)
Articles in Science Magazine issue 4401 (1979)
- Donahue, T. M. (6 July 1979). "Pioneer Venus Results: An Overview". Science 205 (4401): 41–44. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.41. PMID 17778895. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...41D. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/41.
- Colin, Lawrence (6 July 1979). "Encounter with Venus: An Update". Science 205 (4401): 44–46. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.44. PMID 17778896. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...44C. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/44.
- Seiff, Alvin; Kirk, Donn B.; Young, Richard E.; Sommer, Simon C.; Blanchard, Robert C.; Findlay, John T.; Kelly, G. M. (6 July 1979). "Thermal Contrast in the Atmosphere of Venus: Initial Appraisal from Pioneer Venus Probe Data". Science 205 (4401): 46–49. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.46. PMID 17778897. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...46S. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/46.
- Hoffman, J. H.; Hodges, R. R.; McElroy, M. B.; Donahue, T. M.; Kolpin, M. (6 July 1979). "Composition and Structure of the Venus Atmosphere: Results from Pioneer Venus". Science 205 (4401): 49–52. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.49. PMID 17778898. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...49H. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/49.
- Oyama, V. I.; Carle, G. C.; Woeller, F.; Pollack, J. B. (6 July 1979). "Laboratory Corroboration of the Pioneer Venus Gas Chromatograph Analyses". Science 205 (4401): 52–54. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.52. PMID 17778899. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...52O. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/52.
- Niemann, H. B.; Hartle, R. E.; Hedin, A. E.; Kasprzak, W. T.; Spencer, N. W.; Hunten, D. M.; Carignan, G. R. (6 July 1979). "Venus Upper Atmosphere Neutral Gas Composition: First Observations of the Diurnal Variations". Science 205 (4401): 54–56. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.54. PMID 17778900. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...54N. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/54.
- Pollack, James B.; Black, David C. (6 July 1979). "Implications of the Gas Compositional Measurements of Pioneer Venus for the Origin of Planetary Atmospheres". Science 205 (4401): 56–59. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.56. PMID 17778901. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...56P. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/56.
- Stewart, A. Ian; Barth, Charles A. (6 July 1979). "Ultraviolet Night Airglow of Venus". Science 205 (4401): 59–62. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.59. PMID 17778902. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...59S. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/59.
- Keating, G. M.; Taylor, F. W.; Nicholson, J. Y.; Hinson, E. W. (6 July 1979). "Short-Term Cyclic Variations and Diurnal Variations of the Venus Upper Atmosphere". Science 205 (4401): 62–64. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.62. PMID 17778903. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...62K. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/62.
- Taylor, F. W.; Diner, D. J.; Elson, L. S.; McCleese, D. J.; Martonchik, J. V.; Delderfield, J.; Bradley, S. P.; Schofield, J. T. et al. (6 July 1979). "Temperature, Cloud Structure, and Dynamics of Venus Middle Atmosphere by Infrared Remote Sensing from Pioneer Orbiter". Science 205 (4401): 65–67. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.65. PMID 17778904. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...65T. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/65.
- Blamont, Jacques; Ragent, Boris (6 July 1979). "Further Results of the Pioneer Venus Nephelometer Experiment". Science 205 (4401): 67–70. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.67. PMID 17778905. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...67B. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/67.
- Knollenberg, Robert G.; Hunten, D. M. (6 July 1979). "Clouds of Venus: A Preliminary Assessment of Microstructure". Science 205 (4401): 70–74. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.70. PMID 17778906. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...70K. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/70.
- Travis, L. D.; Coffeen, D. L.; Del Genio, A. D.; Hansen, J. E.; Kawabata, K.; Lacis, A. A.; Lane, W. A.; Limaye, S. S. et al. (6 July 1979). "Cloud Images from the Pioneer Venus Orbiter". Science 205 (4401): 74–76. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.74. PMID 17778907. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...74T.
- Pollack, James B.; Ragent, Boris; Boese, Robert; Tomasko, Martin G.; Blamont, Jacques; Knollenberg, Robert G.; Esposito, Larry W.; Stewart, A. Ian et al. (6 July 1979). "Nature of the Ultraviolet Absorber in the Venus Clouds: Inferences Based on Pioneer Venus Data". Science 205 (4401): 76–79. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.76. PMID 17778908. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...76P. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/76.
- Tomasko, Martin G.; Doose, Lyn R.; Smith, Peter H. (6 July 1979). "Absorption of Sunlight in the Atmosphere of Venus". Science 205 (4401): 80–82. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.80. PMID 17778909. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...80T. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/80.
- Suomi, V. E.; Sromovsky, L. A.; Revercomb, H. E. (6 July 1979). "Preliminary Results of the Pioneer Venus Small Probe Net Flux Radiometer Experiment". Science 205 (4401): 82–85. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.82. PMID 17778910. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...82S. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/82.
- Counselman, C. C.; Gourevitch, S. A.; King, R. W.; Loriot, G. B.; Prinn, R. G. (6 July 1979). "Venus Winds Are Zonal and Retrograde Below the Clouds". Science 205 (4401): 85–87. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.85. PMID 17778911. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...85C. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/85.
- Woo, Richard; Armstrong, J. W.; Kendall, William B. (6 July 1979). "Measurements of Turbulence in the Venus Atmosphere Deduced from Pioneer Venus Multiprobe Radio Scintillations". Science 205 (4401): 87–89. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.87. PMID 17778912. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...87W. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/87.
- Pettengill, Gordon H.; Ford, Peter G.; Brown, Walter E.; Kaula, William M.; Masursky, Harold; Eliason, Eric; McGill, George E. (6 July 1979). "Venus: Preliminary Topographic and Surface Imaging Results from the Pioneer Orbiter". Science 205 (4401): 90–93. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.90. PMID 17778913. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...90P. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/90.
- Phillips, Roger J.; Sjogren, William L.; Abbott, Elsa A.; Smith, John C.; Wimberly, Ray N.; Wagner, Cari A. (6 July 1979). "Gravity Field of Venus: A Preliminary Analysis". Science 205 (4401): 93–96. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.93. PMID 17778914. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...93P. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/93.
- Taylor, Harry A.; Brinton, Henry C.; Bauer, Siegfried J.; Hartle, Richard E.; Cloutier, Paul A.; Daniell, Robert E.; Donahue, Thomas M. (6 July 1979). "Ionosphere of Venus: First Observations of Day-Night Variations of the Ion Composition". Science 205 (4401): 96–99. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.96. PMID 17778915. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...96T. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/96.
- Kliore, A. J.; Patel, I. R.; Nagy, A. F.; Cravens, T. E.; Gombosi, T. I. (6 July 1979). "Initial Observations of the Nightside Ionosphere of Venus from Pioneer Venus Orbiter Radio Occultations". Science 205 (4401): 99–102. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.99. PMID 17778916. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...99K. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/99.
- Brace, L. H.; Theis, R. F.; Niemann, H. B.; Mayr, H. G.; Hoegy, W. R.; Nagy, A. F. (6 July 1979). "Empirical Models of the Electron Temperature and Density in the Nightside Venus Ionosphere". Science 205 (4401): 102–105. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.102. PMID 17778917. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..102B. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/102.
- Knudsen, W. C.; Spenner, K.; Whitten, R. C.; Spreiter, J. R.; Miller, K. L.; Novak, V. (6 July 1979). "Thermal Structure and Energy Influx to the Day- and Nightside Venus Ionosphere". Science 205 (4401): 105–107. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.105. PMID 17778918. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..105K. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/105.
- Nagy, A. F.; Cravens, T. E.; Chen, R. H.; Taylor, H. A.; Brace, L. H.; Brinton, H. C. (6 July 1979). "Comparison of Calculated and Measured Ion Densities on the Dayside of Venus". Science 205 (4401): 107–109. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.107. PMID 17778919. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..107N. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/107.
- Bauer, Siegfried J.; Donahue, Thomas M.; Hartle, Richard E.; Taylor, Harry A. (6 July 1979). "Venus Ionosphere: Photochemical and Thermal Diffusion Control of Ion Composition". Science 205 (4401): 109–112. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.109. PMID 17778920. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..109B. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/109.
- Taylor, W. W. L.; Scarf, F. L.; Russell, C. T.; Brace, L. H. (6 July 1979). "Absorption of Whistler Mode Waves in the Ionosphere of Venus". Science 205 (4401): 112–114. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.112. PMID 17778921. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..112T. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/112.
- Russell, C. T.; Elphic, R. C.; Slavin, J. A. (6 July 1979). "Initial Pioneer Venus Magnetic Field Results: Nightside Observations". Science 205 (4401): 114–116. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.114. PMID 17778922. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..114R. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/114.
- Intriligator, D. S.; Collard, H. R.; Mihalov, J. D.; Whitten, R. C.; Wolfe, J. H. (6 July 1979). "Electron Observations and Ion Flows from the Pioneer Venus Orbiter Plasma Analyzer Experiment". Science 205 (4401): 116–119. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.116. PMID 17778923. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..116I. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/116.
- Evans, W. D.; Glore, J. P.; Klebesadel, R. W.; Laros, J. G.; Tech, E. R.; Spalding, R. E. (6 July 1979). "Gamma-Ray Burst Observations by Pioneer Venus Orbiter". Science 205 (4401): 119–121. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.119. PMID 17778924. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..119E. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/119.
- Donahue, T. M. (6 July 1979). "Pioneer Venus Results: An Overview". Science 205 (4401): 41–44. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.41. PMID 17778895. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...41D. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/41.
- Colin, Lawrence (6 July 1979). "Encounter with Venus: An Update". Science 205 (4401): 44–46. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.44. PMID 17778896. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...44C. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/44.
- Seiff, Alvin; Kirk, Donn B.; Young, Richard E.; Sommer, Simon C.; Blanchard, Robert C.; Findlay, John T.; Kelly, G. M. (6 July 1979). "Thermal Contrast in the Atmosphere of Venus: Initial Appraisal from Pioneer Venus Probe Data". Science 205 (4401): 46–49. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.46. PMID 17778897. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...46S. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/46.
- Hoffman, J. H.; Hodges, R. R.; McElroy, M. B.; Donahue, T. M.; Kolpin, M. (6 July 1979). "Composition and Structure of the Venus Atmosphere: Results from Pioneer Venus". Science 205 (4401): 49–52. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.49. PMID 17778898. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...49H. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/49.
- Oyama, V. I.; Carle, G. C.; Woeller, F.; Pollack, J. B. (6 July 1979). "Laboratory Corroboration of the Pioneer Venus Gas Chromatograph Analyses". Science 205 (4401): 52–54. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.52. PMID 17778899. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...52O. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/52.
- Niemann, H. B.; Hartle, R. E.; Hedin, A. E.; Kasprzak, W. T.; Spencer, N. W.; Hunten, D. M.; Carignan, G. R. (6 July 1979). "Venus Upper Atmosphere Neutral Gas Composition: First Observations of the Diurnal Variations". Science 205 (4401): 54–56. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.54. PMID 17778900. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...54N. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/54.
- Pollack, James B.; Black, David C. (6 July 1979). "Implications of the Gas Compositional Measurements of Pioneer Venus for the Origin of Planetary Atmospheres". Science 205 (4401): 56–59. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.56. PMID 17778901. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...56P. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/56.
- Stewart, A. Ian; Barth, Charles A. (6 July 1979). "Ultraviolet Night Airglow of Venus". Science 205 (4401): 59–62. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.59. PMID 17778902. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...59S. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/59.
- Keating, G. M.; Taylor, F. W.; Nicholson, J. Y.; Hinson, E. W. (6 July 1979). "Short-Term Cyclic Variations and Diurnal Variations of the Venus Upper Atmosphere". Science 205 (4401): 62–64. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.62. PMID 17778903. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...62K. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/62.
- Taylor, F. W.; Diner, D. J.; Elson, L. S.; McCleese, D. J.; Martonchik, J. V.; Delderfield, J.; Bradley, S. P.; Schofield, J. T. et al. (6 July 1979). "Temperature, Cloud Structure, and Dynamics of Venus Middle Atmosphere by Infrared Remote Sensing from Pioneer Orbiter". Science 205 (4401): 65–67. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.65. PMID 17778904. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...65T. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/65.
- Blamont, Jacques; Ragent, Boris (6 July 1979). "Further Results of the Pioneer Venus Nephelometer Experiment". Science 205 (4401): 67–70. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.67. PMID 17778905. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...67B. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/67.
- Knollenberg, Robert G.; Hunten, D. M. (6 July 1979). "Clouds of Venus: A Preliminary Assessment of Microstructure". Science 205 (4401): 70–74. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.70. PMID 17778906. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...70K. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/70.
- Travis, L. D.; Coffeen, D. L.; Del Genio, A. D.; Hansen, J. E.; Kawabata, K.; Lacis, A. A.; Lane, W. A.; Limaye, S. S. et al. (6 July 1979). "Cloud Images from the Pioneer Venus Orbiter". Science 205 (4401): 74–76. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.74. PMID 17778907. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...74T.
- Pollack, James B.; Ragent, Boris; Boese, Robert; Tomasko, Martin G.; Blamont, Jacques; Knollenberg, Robert G.; Esposito, Larry W.; Stewart, A. Ian et al. (6 July 1979). "Nature of the Ultraviolet Absorber in the Venus Clouds: Inferences Based on Pioneer Venus Data". Science 205 (4401): 76–79. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.76. PMID 17778908. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...76P. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/76.
- Tomasko, Martin G.; Doose, Lyn R.; Smith, Peter H. (6 July 1979). "Absorption of Sunlight in the Atmosphere of Venus". Science 205 (4401): 80–82. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.80. PMID 17778909. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...80T. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/80.
- Suomi, V. E.; Sromovsky, L. A.; Revercomb, H. E. (6 July 1979). "Preliminary Results of the Pioneer Venus Small Probe Net Flux Radiometer Experiment". Science 205 (4401): 82–85. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.82. PMID 17778910. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...82S. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/82.
- Counselman, C. C.; Gourevitch, S. A.; King, R. W.; Loriot, G. B.; Prinn, R. G. (6 July 1979). "Venus Winds Are Zonal and Retrograde Below the Clouds". Science 205 (4401): 85–87. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.85. PMID 17778911. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...85C. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/85.
- Woo, Richard; Armstrong, J. W.; Kendall, William B. (6 July 1979). "Measurements of Turbulence in the Venus Atmosphere Deduced from Pioneer Venus Multiprobe Radio Scintillations". Science 205 (4401): 87–89. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.87. PMID 17778912. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...87W. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/87.
- Pettengill, Gordon H.; Ford, Peter G.; Brown, Walter E.; Kaula, William M.; Masursky, Harold; Eliason, Eric; McGill, George E. (6 July 1979). "Venus: Preliminary Topographic and Surface Imaging Results from the Pioneer Orbiter". Science 205 (4401): 90–93. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.90. PMID 17778913. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...90P. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/90.
- Phillips, Roger J.; Sjogren, William L.; Abbott, Elsa A.; Smith, John C.; Wimberly, Ray N.; Wagner, Cari A. (6 July 1979). "Gravity Field of Venus: A Preliminary Analysis". Science 205 (4401): 93–96. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.93. PMID 17778914. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...93P. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/93.
- Taylor, Harry A.; Brinton, Henry C.; Bauer, Siegfried J.; Hartle, Richard E.; Cloutier, Paul A.; Daniell, Robert E.; Donahue, Thomas M. (6 July 1979). "Ionosphere of Venus: First Observations of Day-Night Variations of the Ion Composition". Science 205 (4401): 96–99. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.96. PMID 17778915. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...96T. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/96.
- Kliore, A. J.; Patel, I. R.; Nagy, A. F.; Cravens, T. E.; Gombosi, T. I. (6 July 1979). "Initial Observations of the Nightside Ionosphere of Venus from Pioneer Venus Orbiter Radio Occultations". Science 205 (4401): 99–102. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.99. PMID 17778916. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205...99K. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/99.
- Brace, L. H.; Theis, R. F.; Niemann, H. B.; Mayr, H. G.; Hoegy, W. R.; Nagy, A. F. (6 July 1979). "Empirical Models of the Electron Temperature and Density in the Nightside Venus Ionosphere". Science 205 (4401): 102–105. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.102. PMID 17778917. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..102B. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/102.
- Knudsen, W. C.; Spenner, K.; Whitten, R. C.; Spreiter, J. R.; Miller, K. L.; Novak, V. (6 July 1979). "Thermal Structure and Energy Influx to the Day- and Nightside Venus Ionosphere". Science 205 (4401): 105–107. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.105. PMID 17778918. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..105K. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/105.
- Nagy, A. F.; Cravens, T. E.; Chen, R. H.; Taylor, H. A.; Brace, L. H.; Brinton, H. C. (6 July 1979). "Comparison of Calculated and Measured Ion Densities on the Dayside of Venus". Science 205 (4401): 107–109. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.107. PMID 17778919. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..107N. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/107.
- Bauer, Siegfried J.; Donahue, Thomas M.; Hartle, Richard E.; Taylor, Harry A. (6 July 1979). "Venus Ionosphere: Photochemical and Thermal Diffusion Control of Ion Composition". Science 205 (4401): 109–112. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.109. PMID 17778920. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..109B. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/109.
- Taylor, W. W. L.; Scarf, F. L.; Russell, C. T.; Brace, L. H. (6 July 1979). "Absorption of Whistler Mode Waves in the Ionosphere of Venus". Science 205 (4401): 112–114. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.112. PMID 17778921. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..112T. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/112.
- Russell, C. T.; Elphic, R. C.; Slavin, J. A. (6 July 1979). "Initial Pioneer Venus Magnetic Field Results: Nightside Observations". Science 205 (4401): 114–116. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.114. PMID 17778922. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..114R. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/114.
- Intriligator, D. S.; Collard, H. R.; Mihalov, J. D.; Whitten, R. C.; Wolfe, J. H. (6 July 1979). "Electron Observations and Ion Flows from the Pioneer Venus Orbiter Plasma Analyzer Experiment". Science 205 (4401): 116–119. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.116. PMID 17778923. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..116I. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/116.
- Evans, W. D.; Glore, J. P.; Klebesadel, R. W.; Laros, J. G.; Tech, E. R.; Spalding, R. E. (6 July 1979). "Gamma-Ray Burst Observations by Pioneer Venus Orbiter". Science 205 (4401): 119–121. doi:10.1126/science.205.4401.119. PMID 17778924. Bibcode: 1979Sci...205..119E. https://archive.org/details/sim_science_1979-07-06_205_4401/page/119.
 |





