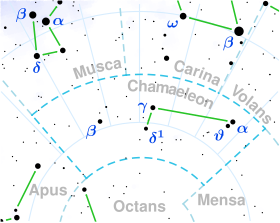
Astronomy:Zeta Chamaeleontis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Chamaeleon |
| Right ascension | 09h 33m 53.37537s[1] |
| Declination | −80° 56′ 28.5287″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.07[2] (5.06 - 5.17)[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B5V[2] |
| Variable type | eclipsing[4]+ELL[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −42.0±4.2 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −34.582[1] mas/yr Dec.: +13.564[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 6.0043 ± 0.1134[1] mas |
| Distance | 540 ± 10 ly (167 ± 3 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.15[2] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 3.12[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 4.75[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 522[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.55[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 15,655[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.31[6] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 103[10] km/s |
| Age | 184[11] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |

Zeta Chamaeleontis, Latinized from ζ Chamaeleontis, is a star located in the constellation Chamaeleon. It is a 5th magnitude star, faintly visible to the naked eye under good observing conditions. Located around 540 light-years distant, it shines with a luminosity approximately 522 times that of the Sun and has a surface temperature of 15,655 K.
South African Astronomer A.W.J. Cousins noted ζ Cha to vary between magnitudes 5.06 and 5.17 in 1960.[13] It was classified as a Beta Cephei variable in the Hipparcos and Tycho Catalogues (ESA 1997), with a period of 1.07 days,[14] before being reclassified as a slowly pulsating B star in the 2011 version.[15] It is now known to be an eclipsing binary star, with a period of 2.7 days,[4] with continuous variation through the whole cycle due to the ellipsoidal shape of the component stars.[5]
It is a B5V main sequence star with an effective temperature of 15,655 K, an absolute magnitude of −1.15 and a mass of 3.1 solar masses, although the properties are evaluated treating the system as a single star.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ Samus, N. N. et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports. 5.1 61 (1): 80–88. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 IJspeert, L. W.; Tkachenko, A.; Johnston, C.; Garcia, S.; De Ridder, J.; Van Reeth, T.; Aerts, C. (August 2021). "An all-sky sample of intermediate- to high-mass OBA-type eclipsing binaries observed by TESS". Astronomy & Astrophysics 652: A120. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202141489. Bibcode: 2021A&A...652A.120I.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Zeta Cha". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=9399.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Anders, F.; Khalatyan, A.; Chiappini, C.; Queiroz, A. B.; Santiago, B. X.; Jordi, C.; Girardi, L.; Brown, A. G. A. et al. (2019). "Photo-astrometric distances, extinctions, and astrophysical parameters for Gaia DR2 stars brighter than G = 18". Astronomy and Astrophysics 628: A94. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935765. Bibcode: 2019A&A...628A..94A.
- ↑ Kervella, Pierre; Arenou, Frédéric; Thévenin, Frédéric (2022). "Stellar and substellar companions from Gaia EDR3". Astronomy & Astrophysics 657: A7. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202142146. Bibcode: 2022A&A...657A...7K.
- ↑ McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (2012). "Fundamental Parameters and Infrared Excesses of Hipparcos Stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 427 (1): 343–57. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x. Bibcode: 2012MNRAS.427..343M.
- ↑ Cardiel, Nicolás; Zamorano, Jaime; Bará, Salvador; Sánchez De Miguel, Alejandro; Cabello, Cristina; Gallego, Jesús; García, Lucía; González, Rafael et al. (2021). "Synthetic RGB photometry of bright stars: Definition of the standard photometric system and UCM library of spectrophotometric spectra". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 504 (3): 3730. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab997. Bibcode: 2021MNRAS.504.3730C.
- ↑ Glebocki, R.; Gnacinski, P. (2005). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalog of Stellar Rotational Velocities (Glebocki+ 2005)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: III/244. Originally Published in: 2005csss...13..571G; 2005yCat.3244....0G 3244. Bibcode: 2005yCat.3244....0G.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (December 2012). "Dependence of kinematics on the age of stars in the solar neighborhood". Astronomy Letters 38 (12): 771–782. doi:10.1134/S1063773712120031. ISSN 0320-0108. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..771G.
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ Cousins, A.W.J. (1960). "New Bright Variable Stars". Monthly Notes of the Astronomical Society of Southern Africa 19: 56. Bibcode: 1960MNSSA..19...56C.
- ↑ ESA (1997). The HIPPARCOS and TYCHO catalogues. Astrometric and photometric star catalogues derived from the ESA HIPPARCOS Space Astrometry Mission. 1200. ISBN 9290923997. Bibcode: 1997ESASP1200.....E.
- ↑ Dubath, P.; Rimoldini, L.; Süveges, M.; Blomme, J.; López, M.; Sarro, L. M.; De Ridder, J.; Cuypers, J. et al. (2011). "Random forest automated supervised classification of Hipparcos periodic variable stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 414 (3): 2602–17. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.18575.x. Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.414.2602D.
 |