Biology:6-methylsalicylic-acid synthase
From HandWiki
Short description: Class of enzymes
| 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 2.3.1.165 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9045-37-8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
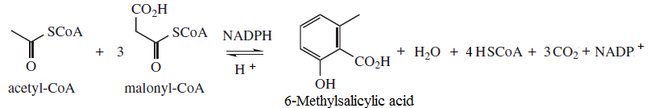
In enzymology, a 6-methylsalicylic-acid synthase (EC 2.3.1.165) is a polyketide synthase that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- acetyl-CoA + 3 malonyl-CoA + NADPH + H+ [math]\displaystyle{ \rightleftharpoons }[/math] 6-methylsalicylate + 4 CoA + 3 CO2 + NADP+ + H2O
The 4 substrates of this enzyme are acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA, NADPH, and H+, whereas its 5 products are 6-methylsalicylate, CoA, CO2, NADP+, and H2O.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. The systematic name of this enzyme class is acyl-CoA:malonyl-CoA C-acyltransferase (decarboxylating, oxoacyl-reducing, thioester-hydrolysing and cyclizing). Other names in common use include MSAS, and 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase.
References
- "Purification and properties of 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase from Penicillium patulum". Biochem. J. 288 (Pt 3): 839–46. December 1992. PMID 1471999.
- "Structural similarities between 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase from Penicillium patulum and vertebrate type I fatty acid synthase: evidence from thiol modification studies". Biochemistry 35 (38): 12267–74. 1996. doi:10.1021/bi960422e. PMID 8823160.
- "Tolerance and specificity of recombinant 6-methylsalicyclic acid synthase". Metab. Eng. 1 (2): 180–7. 1999. doi:10.1006/mben.1999.0113. PMID 10935930.
 |