Biology:Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
 Generic protein structure example |
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, (GSK-3 beta), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSK3B gene.[1][2] In mice, the enzyme is encoded by the Gsk3b gene.[3] Abnormal regulation and expression of GSK-3 beta is associated with an increased susceptibility towards bipolar disorder.[4]
Function
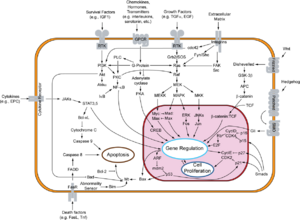
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a proline-directed serine-threonine kinase that was initially identified as a phosphorylating and an inactivating agent of glycogen synthase. Two isoforms, alpha (GSK3A) and beta, show a high degree of amino acid homology.[1] GSK3B is involved in energy metabolism, neuronal cell development, and body pattern formation.[5][6] It might be a new therapeutic target for ischemic stroke.
Disease relevance
Homozygous disruption of the Gsk3b locus in mice results in embryonic lethality during mid-gestation.[3] This lethality phenotype could be rescued by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor.[3]
Two SNPs at this gene, rs334558 (-50T/C) and rs3755557 (-1727A/T), are associated with efficacy of lithium treatment in bipolar disorder.[7]
Signaling pathways
Pharmacological inhibition of ERK1/2 restores GSK-3 beta activity and protein synthesis levels in a model of tuberous sclerosis.[8]
Interactions
GSK3B has been shown to interact with:
- AKAP11,[10]
- AXIN1,[11][12]
- AXIN2,[13][14]
- AR,[15]
- CTNNB1,[16][17]
- DNM1L,[18]
- MACF1[19]
- MUC1,[20][21]
- SMAD3[22]
- NOTCH1,[23]
- NOTCH2,[24]
- P53,[25]
- PRKAR2A,[10]
- SGK3,[26] and
- TSC2.[11][27]
See also
- Glycogen synthase kinase 3
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Mitogen inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta in intact cells via serine 9 phosphorylation". The Biochemical Journal 303 (Pt 3): 701–4. November 1994. doi:10.1042/bj3030701. PMID 7980435.
- ↑ "Molecular cloning and characterization of the human glycogen synthase kinase-3beta promoter". Genomics 60 (2): 121–8. September 1999. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5875. PMID 10486203.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation". Nature 406 (6791): 86–90. July 2000. doi:10.1038/35017574. PMID 10894547. Bibcode: 2000Natur.406...86H.

- ↑ "The involvement of GSK3beta in bipolar disorder: integrating evidence from multiple types of genetic studies". European Neuropsychopharmacology 20 (6): 357–68. June 2010. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2010.02.008. PMID 20226637.
- ↑ "Glycogen synthase kinase-3: functions in oncogenesis and development". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer 1114 (2–3): 147–62. December 1992. doi:10.1016/0304-419X(92)90012-N. PMID 1333807.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: GSK3B glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=2932.
- ↑ "Haplotype analysis of GSK-3β gene polymorphisms in bipolar disorder lithium responders and nonresponders". Clinical Neuropharmacology 37 (4): 108–10. 2013. doi:10.1097/WNF.0000000000000039. PMID 24992082.
- ↑ "Inhibition of ERK1/2 Restores GSK3β Activity and Protein Synthesis Levels in a Model of Tuberous Sclerosis". Scientific Reports 7 (1): 4174. June 2017. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-04528-5. PMID 28646232. Bibcode: 2017NatSR...7.4174P.
- ↑ EMBL-EBI. "EMBL European Bioinformatics Institute" (in en). http://www.ebi.ac.uk..
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "A-kinase anchoring protein AKAP220 binds to glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta ) and mediates protein kinase A-dependent inhibition of GSK-3beta". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (40): 36955–61. October 2002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206210200. PMID 12147701.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "The tuberin-hamartin complex negatively regulates beta-catenin signaling activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 278 (8): 5947–51. February 2003. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200473200. PMID 12511557.
- ↑ "Axin, an inhibitor of the Wnt signalling pathway, interacts with beta-catenin, GSK-3beta and APC and reduces the beta-catenin level". Genes to Cells 3 (6): 395–403. June 1998. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2443.1998.00198.x. PMID 9734785.
- ↑ "Hot spots in beta-catenin for interactions with LEF-1, conductin and APC". Nature Structural Biology 7 (9): 800–7. September 2000. doi:10.1038/79039. PMID 10966653.
- ↑ "The ankyrin repeat protein Diversin recruits Casein kinase Iepsilon to the beta-catenin degradation complex and acts in both canonical Wnt and Wnt/JNK signaling". Genes & Development 16 (16): 2073–84. August 2002. doi:10.1101/gad.230402. PMID 12183362.
- ↑ "Suppression of androgen receptor-mediated transactivation and cell growth by the glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in prostate cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (31): 32444–52. July 2004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313963200. PMID 15178691.
- ↑ "The interaction between beta-catenin, GSK3beta and APC after motogen induced cell-cell dissociation, and their involvement in signal transduction pathways in prostate cancer". International Journal of Oncology 18 (4): 843–7. April 2001. doi:10.3892/ijo.18.4.843. PMID 11251183.
- ↑ "DIX domains of Dvl and axin are necessary for protein interactions and their ability to regulate beta-catenin stability". Molecular and Cellular Biology 19 (6): 4414–22. June 1999. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.6.4414. PMID 10330181.
- ↑ "Human dynamin-like protein interacts with the glycogen synthase kinase 3beta". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 249 (3): 697–703. August 1998. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9253. PMID 9731200.
- ↑ "Skin stem cells orchestrate directional migration by regulating microtubule-ACF7 connections through GSK3β". Cell 144 (3): 341–52. February 2011. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.033. PMID 21295697.
- ↑ "Interaction of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta with the DF3/MUC1 carcinoma-associated antigen and beta-catenin". Molecular and Cellular Biology 18 (12): 7216–24. December 1998. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.12.7216. PMID 9819408.
- ↑ "The c-Src tyrosine kinase regulates signaling of the human DF3/MUC1 carcinoma-associated antigen with GSK3 beta and beta-catenin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276 (9): 6061–4. March 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000754200. PMID 11152665.
- ↑ "Axin and GSK3- control Smad3 protein stability and modulate TGF- signaling". Genes & Development 22 (1): 106–20. January 2008. doi:10.1101/gad.1590908. PMID 18172167.
- ↑ "Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta modulates notch signaling and stability". Current Biology 12 (12): 1006–11. June 2002. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00888-6. PMID 12123574.
- ↑ "Phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta down-regulates Notch activity, a link for Notch and Wnt pathways". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 278 (34): 32227–35. August 2003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304001200. PMID 12794074.
- ↑ "Direct, activating interaction between glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and p53 after DNA damage". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99 (12): 7951–5. June 2002. doi:10.1073/pnas.122062299. PMID 12048243. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...99.7951W.
- ↑ "Human serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase-like kinase (SGKL) phosphorylates glycogen syntheses kinase 3 beta (GSK-3beta) at serine-9 through direct interaction". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 293 (4): 1191–6. May 2002. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00349-2. PMID 12054501.
- ↑ "TSC2 integrates Wnt and energy signals via a coordinated phosphorylation by AMPK and GSK3 to regulate cell growth". Cell 126 (5): 955–68. September 2006. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.055. PMID 16959574.
Further reading
- "Glycogen synthase kinase3 beta phosphorylates serine 33 of p53 and activates p53's transcriptional activity". BMC Cell Biology 2: 12. 2001. doi:10.1186/1471-2121-2-12. PMID 11483158.
- "Glycogen synthase kinase-3: functions in oncogenesis and development". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer 1114 (2–3): 147–62. December 1992. doi:10.1016/0304-419X(92)90012-N. PMID 1333807.
- "Hyperphosphorylation of tau in PHF". Neurobiology of Aging 16 (3): 365–71; discussion 371–80. 1995. doi:10.1016/0197-4580(95)00027-C. PMID 7566346.
- "Mood stabilizers, glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and cell survival". Molecular Psychiatry 7 (Suppl 1): S35-45. 2002. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001017. PMID 11986994.
- "GSK3beta signalling: casting a wide net in Alzheimer's disease". Neuro-Signals 11 (5): 251–61. 2003. doi:10.1159/000067423. PMID 12566926.
- "GSK-3β inhibitor TWS119 attenuates rtPA-induced hemorrhagic transformation and activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway after acute ischemic stroke in rats". Molecular Neurobiology 53 (10): 7028–7036. December 2016. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9607-2. PMID 26671619.
- "[Schizophrenia, neurodevelopment and glycogen synthase kinase-3]". Harefuah 142 (8–9): 636–42, 644. September 2003. PMID 14518171.
- "PTEN and GSK3beta: key regulators of progression to androgen-independent prostate cancer". Oncogene 25 (3): 329–37. January 2006. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209020. PMID 16421604.
External links
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3B)
 |















