Biology:Group IV pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases
| Pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylase, pyridoxal binding domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
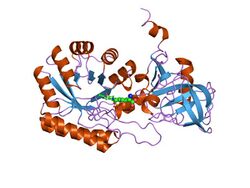 crystal structure of a d,l-lysine complex of diaminopimelate decarboxylase | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Orn_Arg_deC_N | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02784 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0036 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022644 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00685 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1qu4 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylase, C-terminal sheet domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
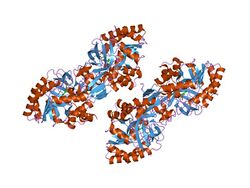 a dimer interface mutant of ornithine decarboxylase reveals structure of gem diamine intermediate | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Orn_DAP_Arg_deC | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00278 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022643 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00685 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1qu4 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, group IV pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases are a family of enzymes comprising ornithine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.17, lysine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.18, arginine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.19 and diaminopimelate decarboxylaseEC 4.1.1.20.[1] It is also known as the Orn/Lys/Arg decarboxylase class-II family.
Pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent amino acid decarboxylases can be divided into four groups based on amino acid sequence. Group IV comprises eukaryotic ornithine and lysine decarboxylase and the prokaryotic biosynthetic type of arginine decarboxylase and diaminopimelate decarboxylase.[1]
Members of this family while most probably evolutionary related, do not share extensive regions of sequence similarities. The proteins contain a conserved lysine residue which is known, in mouse ODC to be the site of attachment of the pyridoxal-phosphate group.[2] The proteins also contain a stretch of three consecutive glycine residues and has been proposed to be part of a substrate-binding region.[3]
See also
- Group I pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases
- Group II pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases
- Group III pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Multiple evolutionary origin of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent amino acid decarboxylases". Eur. J. Biochem. 221 (3): 997–1002. May 1994. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18816.x. PMID 8181483.
- ↑ "Mechanism of the irreversible inactivation of mouse ornithine decarboxylase by alpha-difluoromethylornithine. Characterization of sequences at the inhibitor and coenzyme binding sites". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (1): 150–8. January 1992. PMID 1730582.
- ↑ "Nucleotide sequence and analysis of the speA gene encoding biosynthetic arginine decarboxylase in Escherichia coli". J. Bacteriol. 172 (8): 4631–40. August 1990. doi:10.1128/jb.172.8.4631-4640.1990. PMID 2198270.
 |

